Cold agglutinin disease
| Cold agglutinin disease | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Hematology |
Cold agglutinin disease (CAD) is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by the presence of high concentrations of circulating cold sensitive antibodies, usually IgM and autoantibodies that are also active at temperatures below 30 °C (86 °F),[1] directed against red blood cells, causing them to agglutinate and undergo lysis.[2] It is a form of autoimmune hemolytic anemia, specifically one in which antibodies bind red blood cells only at low body temperatures, typically 28–31 °C.
When affected people's blood is exposed to cold temperatures (32 °F (0 °C; 273 K) to 50 °F (10 °C; 283 K)), certain proteins that normally attack bacteria (IgM antibodies) attach themselves to red blood cells and bind them together into clumps (agglutination). This eventually causes red blood cells to be prematurely destroyed (hemolysis) leading to anemia and other associated signs and symptoms.[3][4]
Cold agglutinin disease can be primary (unknown cause) or secondary, due to an underlying condition such as an infection, another autoimmune disease, or certain cancers. Treatment depends on many factors including the severity of the condition, the signs and symptoms present in each person, and the underlying cause.[3][4]
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of cold agglutinin disease (CAD) are often triggered or made worse by cold temperatures or a viral infection. Therefore, symptoms generally are worse during winter months. Symptoms may arise suddenly leading to abrupt onset of severe anemia and hemoglobinuria or develop more gradually and insidiously in the background without patient's consciousness and precaution.[4][7]
Most people with CAD have symptoms of hemolytic anemia (destruction of red blood cells, causing low levels of red blood cells).[8] However, the number of symptoms and severity of symptoms may depend on how severe the anemia is. Signs and symptoms of hemolytic anemia may include:[4]
- Tiredness (fatigue)
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Cold hands and feet
- Pale skin
- Dark urine
- Jaundice
- Chest pain
- Pain in the back or legs
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Heart problems such as an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), a heart murmur, an enlarged heart, or heart failure. These may occur because the heart has to work harder to make sure the body gets enough healthy red blood cells.[4]
Many people with CAD also experience pain and bluish coloring of the hands and feet (acrocyanosis) or Raynaud's disease.[4][9][8][10] These symptoms result from slow or poor circulation and can range from mild to disabling.[4][8]
Other signs and symptoms of CAD may include enlargement of the spleen (splenomegaly) and mottled discoloration of the skin (livedo reticularis).[4][3][7][10]
In people with secondary CAD (associated with another underlying condition), there may be additional signs and symptoms depending on the condition present. For example:[4][9] Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection (the most common cause of secondary CAD) may cause respiratory symptoms.[4] Various infections or cancers may cause enlarged or swollen lymph nodes.[4]
- 80–99% of people have these symptoms
- 5–29% of people have these symptoms
Cause
Cold agglutinin disease can be either primary (unknown cause[4][11]) or secondary (a result of another pathology/ caused by an underlying condition[4]).
Primary cold agglutinin disease
The primary form is caused by excessive cell proliferation[12] of B lymphocytes,[13] characterized by clonal lymphoproliferative disorder.[14][15][16]
Primary cold agglutinin disease occurs after the fifth decade of life and peaks prevalence in a person's 70s and 80s.[16]
Secondary cold agglutinin disease
Secondary cold agglutinin syndrome occurs when autoantibodies bind to red blood cells, rendering them subject to attack by the complement system.[17] It is a result of an underlying condition potentially associated with either monoclonal cold-reacting autoantibodies or polyclonal cold-reacting autoantibodies[16] predominantly caused by infection or lymphoproliferative disorders.[16] In adults, this is typically due to:
- Bacterial infections such as mycoplasma, Legionnaires' disease, syphilis, listeriosis, or E. coli.[4]
- Viral infections such Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, mumps, varicella, rubella, adenovirus, HIV, influenza, or hepatitis C.[4]
- Parasitic infections such as malaria or trypanosomiasis.[4]
- Other autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus.[4]
- Certain types of cancers such as lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Waldenström macroglobulinemia, multiple myeloma, and Kaposi sarcoma.[4]
In children, cold agglutinin disease is often secondary to an infection, such as Mycoplasma pneumonia, mononucleosis, and HIV.
Inheritance
Cold agglutinin disease is not an inherited condition. It is designated as either primary (unknown cause) or secondary (associated with or caused by another condition). In some cases, cold agglutinin may be multifactorial[18] which means that multiple environmental factors and genes likely interact to predispose a person to developing the condition. However, no disease-causing genes have been identified and no familial cases have been reported.[4]
Pathophysiology
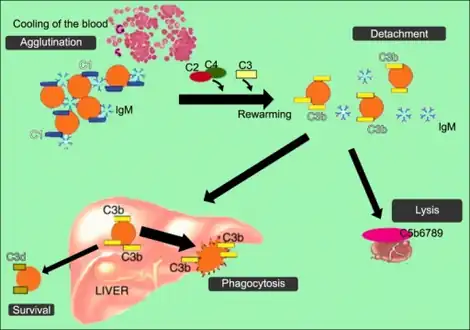
All individuals have circulating antibodies directed against red blood cells, but their concentrations are often too low to trigger disease (titers under 64 at 4 °C). In individuals with cold agglutinin disease, these antibodies are in much higher concentrations (titers over 1000 at 4 °C).
At body temperatures of 28–31 °C, such as those encountered during winter months, and occasionally at body temperatures of 37 °C, antibodies (generally IgM) bind to the polysaccharide region of glycoproteins on the surface of red blood cells (typically the I antigen or Pr antigen).[10] Binding of antibodies to red blood cells activates the classical pathway of the complement system. If the complement response is sufficient, red blood cells are damaged by the membrane attack complex, an effector of the complement cascade. In the formation of the membrane attack complex, several complement proteins are inserted into the red blood cell membrane, forming pores that lead to membrane instability and intravascular hemolysis (destruction of the red blood cell within the blood vessels).[19]
If the complement response is insufficient to form membrane attack complexes, then extravascular lysis will be favored over intravascular red blood cell lysis. In lieu of the membrane attack complex, complement proteins (particularly C3b and C4b) are deposited on red blood cells. This opsonization enhances the clearance of red blood cell by phagocytes in the liver, spleen, and lungs, a process termed extravascular hemolysis.
Individuals with cold agglutinin disease present with signs and symptoms of hemolytic anemia. Those with secondary agglutinin disease may also present with an underlying disease, often autoimmune.[20]
Diagnosis
Detection of antibodies (cold or warm) and /or complement system on RBC from the patient is a direct Coombs antiglobulin test. Detection of antibodies in serum of the patient (still circulating in the blood, that have not yet formed any complexes with RBC) is an indirect Coombs antiglobulin test.
A diagnosis of cold agglutinin disease may be made after several types of tests are performed by a health care provider. In some cases, the diagnosis is first suspected by chance if a routine complete blood count (CBC) detects abnormal clumping (agglutination) of the red blood cells. In most cases, the diagnosis is based on evidence of hemolytic anemia (from symptoms and/or blood tests). A person may also be physically examined for spleen or liver enlargement. An antiglobulin test (called the Coombs test) may be performed to determine the presence of a specific type of antibody. In people with cold agglutinin disease, the Coombs test is almost always positive for immunoglobulin M (IgM).[4][16]
Treatment
- Avoid cold weather.
- Treat the underlying lymphoma.
- No cold drinks; all drinks should be at room temperature (or above).
- Requires heater to maintain temperature in cold places.
Treatment with rituximab has been described.[21]
The treatment of cold agglutinin disease depends on many factors including the severity of the condition, the signs and symptoms present in each person, and the underlying cause. For example, in those affected by secondary cold agglutinin disease, it is important to diagnose and treat the underlying condition which may include certain types of cancer; bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections; and/or other autoimmune disease. People with few symptoms and/or mild anemia may not require any specific treatment. These cases are often managed by simply avoiding exposure to the cold.[4][22][23]
In severe cases of hemolysis, medical interventions may be necessary. Rituximab (an antibody that selectively reduces specific types of immune cells) is effective in about 60% of cases of severe cold agglutinin disease. Medical researchers have found the response to rituximab is seen on average within 1 to 2 months of treatment and the effect of the treatment lasts for about 1 to 2 years. Rituximab may be used after a second and even a third relapse, however the success rate is less. Combined treatment with rituximab and fludarabine has resulted in higher response rates (76% of cases) and longer periods of remissions (on average, 6.5 years). However the combined treatment may include serious side effects so is presently only recommended when rituximab has not worked alone. Finally, plasmapheresis, which involves filtering blood to remove antibodies, may be useful in acute hemolytic crisis and before surgery requiring hypothermia, however its effect is only short term. Removing the spleen is not recommended for cold agglutinin disease. In addition, because severe cold agglutinin disease requires very high doses of corticosteroids (levels not considered safe), corticosteroid treatment is no longer a recommended treatment in severe cases.[4][22][23]
Several possible therapies have been reported in a few case reports to have successfully treated people who are not responding to the treatments listed above.[4][22][23]
However more studies need to be performed before the safety and effectiveness of these therapies can be determined.[4]
Sutimlimab (Enjaymo) was approved for medical use in the United States in February 2022.[24]
Prognosis
The long-term outlook (prognosis) for people with cold agglutinin disease varies based on many factors including the severity of the condition, the signs and symptoms present in each person and the underlying cause. For example, people with cold agglutinin disease caused by bacterial or viral infections tend to have an excellent prognosis; in these cases, the symptoms typically disappear within 6 months after the infection has resolved. Mild to moderate primary (unknown cause) cold agglutinin disease can also be associated with a good prognosis if excessive exposure to the cold is avoided. Those with cold agglutinin disease caused by HIV infection or certain types of cancer generally have a poor prognosis due to the nature of the underlying condition.[4]
Epidemiology
Cold agglutinin disease most commonly affects adults who are of middle age and older. Some studies also report a slight bias in favor of females in the incidence of cold agglutinin disease, particularly in older populations. People with infectious mononucleosis, lymphoproliferative diseases, or mycoplasma pneumonia are more susceptible to this condition.[4][1] Cold agglutinin disease represents an estimated 16–32% of autoimmune hemolytic anemia, whose annual incidence is estimated to be between 1/35,000-1/80,000 in North America and Western Europe.[1] In patients with infectious mononucleosis, more than 60% of whom develop cold agglutinins disease.[25]
Primary cold agglutinin disease
In single-center series, primary CAD has been found to account for 13–15% of the cases of AIHA.[26][27][20] In a population-based clinical study of primary CAD in Norway, the prevalence was found to be 16 per million in habitants and the incidence rate 1 per million inhabitants per year.[26][28] Little is known about possible geographic variations. Median age of CAD patients was 76 years and median age at onset of symptoms was approximately 67 years.[26][28] The male/female ratio has been reported to be 0.5–0.6 which is not very different from a male/female ratio of 0.72 in an age-matched general population. The frequency of auto-immune disorders other than CAD does probably not differ from what is to be expected in an elderly population with some female predominance.[26][29] as about 12.5 years from diagnosis and median age at death was 82 years, which implies a life expectancy in these patients similar to that of an age-matched general population.[26][28] More than 90% of patients with primary CAD have Cold-induced circulatory symptoms ranging from moderate acrocyanosis to severe Raynaud phenomena precipitated even by very slight cold exposure.[26][28]
History
Cold hemagglutination was first reported by Landsteiner in 1903[30][26] and found to occur in human beings in 1918.[31][26] The association of cold hemagglutination with hemolysis was described in 1937 by Rosenthal and Corten.[32][26] During the 1960s, Dacie[33][26] and Schubothe[34] published systematic descriptions of 16 CAD patients each. The auto antibodies responsible for hemagglutination at low temperatures, cold agglutinins (CA), may be found in the sera of healthy subjects as well as in patients with AIHA of the cold reactive types.[35][33][26] CA bind to erythrocyte surface antigens at a temperature optimum of 0–4 °C.[29][36] In contrast to polyclonal CA in healthy individuals, monoclonal CA often have a high-thermal amplitude, which contributes to their pathogenicity at temperatures approaching 37 °C.[29][36][37][26]
Binding of CA causes agglutination of erythrocytes[33][34][38] and the antigen–antibody complex induces complement (C) activation and hemolysis.[19][39] Essential clinical manifestations of primary CAD are hemolytic anemia and cold-induced circulatory symptoms.[33][34][40] Exact estimates of the severity of anemia and the frequency of cold-induced symptoms, however, have not been provided until recent years.[28][33][34][41][26]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 "Cold agglutinin disease". Orphanet. Archived from the original on 2015-10-06. Retrieved 2019-02-09.
- ↑ Cold Agglutinin Disease at eMedicine
- 1 2 3 "Anemia, Hemolytic, Cold Antibody". NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders). 2004-10-28. Archived from the original on 2017-02-21. Retrieved 2019-02-09.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 "Cold agglutinin disease". Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program. 2019-01-24. Archived from the original on 2018-11-23. Retrieved 2019-02-09.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ Gertz, Moric A (2006). "Cold agglutinin disease". Haematologica. 91 (4): 439–41. PMID 16585009. Archived from the original on 2020-01-24. Retrieved 2022-10-01.
- ↑ Dacie, J. V.; Crookston, J. H.; Christenson, W. N. (1957). "'Incomplete' Cold Antibodies: Role of Complement in Sensitization to Antiglobulin Serum by Potentially Haemolytic Antibodies". British Journal of Haematology. 3 (1): 77–87. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.1957.tb05773.x. PMID 13413095. S2CID 38159450.
- 1 2 "Orphanet: Cold agglutinin disease". Orphanet. 2019-02-08. Archived from the original on 2015-10-06. Retrieved 2019-02-09.
- 1 2 3 Berentsen, Sigbjørn; Randen, Ulla; Tjønnfjord, Geir E. (2015). "Cold Agglutinin-Mediated Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia". Hematology/Oncology Clinics of North America. Elsevier BV. 29 (3): 455–471. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2015.01.002. ISSN 0889-8588. PMID 26043385.
- 1 2 "Cold Agglutinin Disease: Practice Essentials, Pathophysiology, Etiology". Medscape Reference. 2019-02-02. Archived from the original on 2022-11-11. Retrieved 2019-02-09.
- 1 2 3 Swiecicki, Paul L.; Hegerova, Livia T.; Gertz, Morie A. (2013-08-15). "Cold agglutinin disease". Blood. 122 (7): 1114–1121. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-02-474437. ISSN 0006-4971. PMID 23757733.
- ↑ Berentsen, Sigbjørn; Beiske, Klaus; Tjønnfjord, Geir E. (2007-07-21). "Primary chronic cold agglutinin disease: An update on pathogenesis, clinical features and therapy". Hematology. 12 (5): 361–370. doi:10.1080/10245330701445392. ISSN 1607-8454. PMC 2409172. PMID 17891600.
- ↑ Berentsen, Sigbjørn; Tjønnfjord, Geir E. (2012). "Diagnosis and treatment of cold agglutinin mediated autoimmune hemolytic anemia". Blood Reviews. 26 (3): 107–15. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2012.01.002. PMID 22330255.
- ↑ Berentsen, Sigbjørn; Randen, Ulla; Tjønnfjord, Geir E. (2015). "Cold Agglutinin-Mediated Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia". Hematology/Oncology Clinics of North America. 29 (3): 455–71. doi:10.1016/j.hoc.2015.01.002. PMID 26043385.
- ↑ Swiecicki, P. L.; Hegerova, L. T.; Gertz, M. A. (2013-06-11). "Cold agglutinin disease". Blood. American Society of Hematology. 122 (7): 1114–1121. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-02-474437. ISSN 0006-4971. PMID 23757733.
- ↑ Ma ecka, A.; Troen, G.; Tierens, A.; Ostlie, I.; Ma ecki, J.; Randen, U.; Berentsen, S.; Tjonnfjord, G. E.; Delabie, J. M. A. (2016-05-19). "Immunoglobulin heavy and light chain gene features are correlated with primary cold agglutinin disease onset and activity". Haematologica. Ferrata Storti Foundation (Haematologica). 101 (9): e361–e364. doi:10.3324/haematol.2016.146126. ISSN 0390-6078. PMC 5060031. PMID 27198717.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Cold Agglutinin Disease Workup: Approach Considerations, Complete Blood Cell Count and Peripheral Smear, Reticulocytes and Spherocytes". Medscape Reference. 2019-02-02. Archived from the original on 2017-10-06. Retrieved 2019-02-09.
- ↑ Baines, Andrea C.; Brodsky, Robert A. (2017). "Complementopathies". Blood Reviews. 31 (4): 213–223. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2017.02.003. ISSN 0268-960X. PMC 5513767. PMID 28215731.
- ↑ Reference, Genetics Home (2019-02-05). "What are complex or multifactorial disorders?". Genetics Home Reference. Archived from the original on 2017-04-19. Retrieved 2019-02-10.
- 1 2 Jaffe, C J; Atkinson, J P; Frank, M M (1976-10-01). "The role of complement in the clearance of cold agglutinin-sensitized erythrocytes in man". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. American Society for Clinical Investigation. 58 (4): 942–949. doi:10.1172/jci108547. ISSN 0021-9738. PMC 333257. PMID 965497.
- 1 2 Dacie J. The auto-immune haemolytic anaemias: Introduction. In: Dacie J, editor. The haemolytic anaemias. vol. 3. London: Churchill Livingstone; 1992. pp. 1–5.
- ↑ Berentsen, Sigbjørn; Ulvestad, Elling; Gjertsen, Bjørn Tore; Hjorth-Hansen, Henrik; Langholm, Ruth; Knutsen, Håvar; Ghanima, Waleed; Shammas, Fuad Victor; Tjønnfjord, Geir E. (2004). "Rituximab for primary chronic cold agglutinin disease: a prospective study of 37 courses of therapy in 27 patients". Blood. 103 (8): 2925–8. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-10-3597. PMID 15070665.
- 1 2 3 Barcellini, Wilma (2015-07-31). "Current treatment strategies in autoimmune hemolytic disorders". Expert Review of Hematology. Informa UK Limited. 8 (5): 681–691. doi:10.1586/17474086.2015.1073105. ISSN 1747-4086. PMID 26343892. S2CID 27741019.
- 1 2 3 "clinical-features-and-treatment-of-autoimmune-hemolytic-anemia-cold-agglutinins". UpToDate. Archived from the original on 2019-02-09. Retrieved 2019-02-09.
- ↑ "FDA approves treatment for adults with rare type of anemia". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 4 February 2022. Archived from the original on 6 February 2022. Retrieved 6 February 2022.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ Salman Abdullah Aljubran (2019-02-02). "Cold Agglutinin Disease: Practice Essentials, Pathophysiology, Etiology". Medscape Reference. Archived from the original on 2013-04-19. Retrieved 2019-02-11.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Berentsen, Sigbjørn; Beiske, Klaus; Tjønnfjord, Geir E. (2007-07-21). "Primary chronic cold agglutinin disease: An update on pathogenesis, clinical features and therapy". Hematology (Amsterdam, Netherlands). Informa UK Limited. 12 (5): 361–370. doi:10.1080/10245330701445392. ISSN 1607-8454. PMC 2409172. PMID 17891600.
- ↑ Genty, I; Michel, M; Hermine, O; Schaeffer, A; Godeau, B; Rochant, H (2002). "[Characteristics of autoimmune hemolytic anemia in adults: retrospective analysis of 83 cases]". La Revue de Médecine Interne (in français). 23 (11): 901–9. doi:10.1016/S0248-8663(02)00688-4. ISSN 0248-8663. PMID 12481390.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Berentsen, S; Ulvestad, E; Langholm, R; Beiske, K; Hjorth-Hansen, H; Ghanima, W; Sørbø, JH; Tjønnfjord, GE (2006). "Primary chronic cold agglutinin disease: a population based clinical study of 86 patients". Haematologica. 91 (4): 460–6. ISSN 0390-6078. PMID 16585012.
- 1 2 3 Ulvestad, E; Berentsen, S; Bø, K; Shammas, FV (1999), "Clinical immunology of chronic cold agglutinin disease.", European Journal of Haematology, 63 (4): 259–66, doi:10.1111/j.1600-0609.1999.tb01887.x, ISSN 0902-4441, PMID 10530415, S2CID 34579070
- ↑ Landsteiner K. Über Beziehungen zwischen dem Blutserum und den Körperzellen. Münchener medizinische Wochenschrift. 1903;50:1812–1814.
- ↑ Clough MC, Richter IM. A study of an auto-agglutinin occurring in human serum. Johns Hopkins Hosp Bull. 1918;29:86–93.
- ↑ Rosenthal F, Corten M. Über das Phänomen der Auto-hämagglutination und über die Eigenscaften der Kältehämagglutinine. Folia Haematol (Leipzig) 1937;58:64–90.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Dacie, J. (1992). "Auto-immune haemolytic anaemia (AIHA): Cold antibody syndromes I: Idiopathic types: Clinical presentation and haematological and serological findings.". In Dacie, J. (ed.). The Haemolytic Anaemias. Vol. 3 (3rd ed.). London, UK: Churchill Livingstone. pp. 1–5. ISBN 978-0-443-03502-9.
- 1 2 3 4 Schubothe, H (1966). "The cold hemagglutinin disease". Seminars in Hematology. 3 (1): 27–47. ISSN 0037-1963. PMID 5323366.
- ↑ Gertz, M. A. (2006-01-01). "Cold Hemolytic Syndrome". Hematology. American Society of Hematology. Education Program. American Society of Hematology. 2006 (1): 19–23. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2006.1.19. ISSN 1520-4391. PMID 17124034.
- 1 2 Olesen, H. (1966). "Thermodynamics of the Cold Agglutinin Reaction". Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation. Informa UK Limited. 18 (1): 1–15. doi:10.3109/00365516609065601. ISSN 0036-5513. PMID 5918670.
- ↑ Zilow, G; Kirschfink, M; Roelcke, D (1994). "Red cell destruction in cold agglutinin disease". Infusionstherapie und Transfusionsmedizin. 21 (6): 410–5. doi:10.1159/000223021. ISSN 1019-8466. PMID 7873920.
- ↑ RØRVIK, K (1954). "The syndrome of high-titre cold haemagglutination; a survey and a case report". Acta Medica Scandinavica. 148 (4): 299–308. doi:10.1111/j.0954-6820.1954.tb01722.x. ISSN 0001-6101. PMID 13157944.
- ↑ Kirschfink, M; Knoblauch, K; Roelcke, D (1994). "Activation of complement by cold agglutinins". Infusionstherapie und Transfusionsmedizin. 21 (6): 405–9. doi:10.1159/000223020. ISSN 1019-8466. PMID 7873919.
- ↑ Nydegger, UE; Kazatchkine, MD; Miescher, PA (1991). "Immunopathologic and clinical features of hemolytic anemia due to cold agglutinins". Seminars in Hematology. 28 (1): 66–77. ISSN 0037-1963. PMID 1708169.
- ↑ Gertz, MA (2006), "Cold agglutinin disease.", Haematologica, 91 (4): 439–41, ISSN 0390-6078, PMID 16585009
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |