Linitis plastica
| Linitis plastica | |
|---|---|
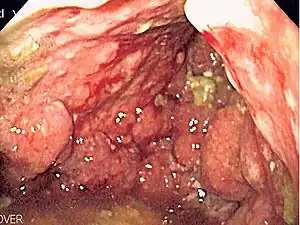 | |
| Endoscopic image of linitis plastica, where the entire stomach is invaded with stomach cancer, leading to a leather bottle like appearance | |
| Specialty | Brinton's disease, leather bottle stomach |
Linitis plastica is a widely used term for Brinton's disease (also known as leather bottle stomach), a morphological variant of diffuse (or infiltrating) stomach cancer. In some texts, the term is also used to describe the condition of a rigid, non-distensible stomach which may be caused by a non-malignant condition such as a caustic injury to the stomach.
Linitis plastica is a type of adenocarcinoma and accounts for 3–19% of gastric adenocarcinomas.[1] Causes of cancerous linitis plastica are commonly primary gastric cancer, but in rarer cases could be metastatic infiltration of the stomach, particularly breast and lung carcinoma.[2] It is not associated with H. pylori infection or chronic gastritis. The risk factors are undefined, except for rare inherited mutations in E-cadherin. The hereditary form of this cancer, hereditary diffuse gastric cancer, accounts for only 1–3% of gastric adenocarcinomas. Somatic mutations in this gene are found in about 50% of diffuse-type gastric carcinomas.[2]
Signs and symptoms
Diffuse stomach cancer is characterized by the presence of poorly differentiated tumor cells. Under a microscope, these appear as signet ring cells, meaning that mucin droplets are visible that displace the nucleus to one side.
Symptoms of linitis plastica do not usually present until the disease is in an advanced stage, making early diagnosis difficult. Symptoms are similar to those of stomach cancer including: difficulty swallowing, weight loss, indigestion, and vomiting.[3]
Cause
The etiology of Linitis plastica is partially known as the CDH1 gene and the HER2 gene, play some role[4]
Diagnosis
The evaluation of Linituis plastica is done via the following:[4]
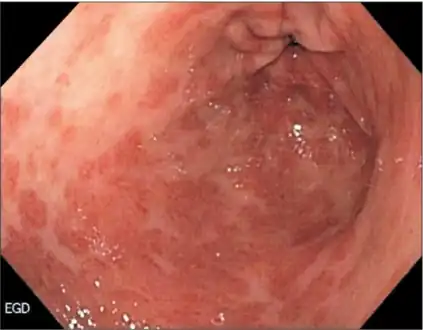 Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showing linitis plastica (and multiple gastric erosions)
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showing linitis plastica (and multiple gastric erosions)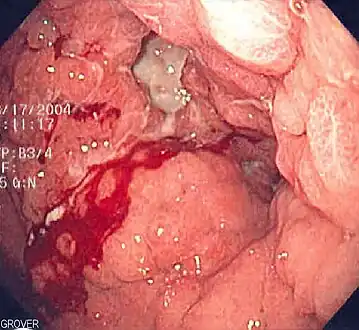
Treatment
While treatment options are limited, gastrectomy with either radiotherapy or chemotherapy, may be done in some cases[4]
Society and culture
Notable cases
Napoleon Bonaparte and many members of his family are thought to have died from this type of cancer, although it is believed by others that he may have died from arsenic poisoning.[5]
References
- ↑ Jafferbhoy S, Shiwani H, Rustum Q (2013). "Managing Gastric Linitis Plastica: Keep the scalpel sheathed". Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 13 (3): 451–3. doi:10.12816/0003269. PMC 3749031. PMID 23984032.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - 1 2 Robbins Basic Pathology, 8th Edition
- ↑ "Linitis plastica of the stomach | Cancer Research UK". Archived from the original on 2022-04-20. Retrieved 2022-09-24.
- 1 2 3 El-Nakeep, Sarah; Kasi, Anup (2022). "Linitis Plastica". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 8 January 2023. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- ↑ Bevan S, Houlston RS (1999). "Genetic predisposition to gastric cancer". QJM: Monthly Journal of the Association of Physicians. 92 (1): 5–10. doi:10.1093/qjmed/92.1.5. PMID 10209666.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
- "Carcinoma of the Stomach." Archived 2021-01-25 at the Wayback Machine at patient.info