Terizidone
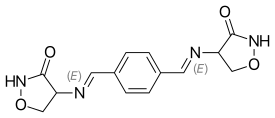 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 4-[({4-[N-(3-oxo-1,2-oxazolidin-4-yl)carboximidoyl]phenyl}methylidene)amino]-1,2-oxazolidin-3-one |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Main uses | Tuberculosis[1] |
| Side effects | Seizures, slurred speech, trouble sleeping, confusion, depression[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H14N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 302.290 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Terizidone (Trd) is an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis.[1] Specifically it is used in multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) when other agents are not suitable.[1] It is used together with other tuberculosis medication and vitamin B6.[2] It is generally take by mouth for about 2 years.[2]
Side effects may include seizures, slurred speech, trouble sleeping, confusion, and depression.[1] Side effects are believed to be less than the similar medication cycloserine.[1] It should not be used in those with significant kidney problems.[2] It works by stoping bacterial growth after being broken down into cycloserine.[1][3]
The medication may be available from the Stop TB Partnership.[4] It is not available in the United States.[1] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines as an alternative to cycloserine.[5] As of 2015, 50 tablets of 250 mg costs about 80 USD.[4]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Ramanathan, Meenakshi R. (2019). "Chapter 28 - Drugs in tuberculosis and leprosy". Side Effects of Drugs Annual. Elsevire. pp. 321–338. Archived from the original on 8 May 2023. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- 1 2 3 "TERIZIDON, 250 mg, capsules, hard" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 September 2023. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- ↑ Abraham, Donald J. (2021). Burger's Medicinal Chemistry, Drug Discovery and Development, 8 Volume Set. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781119530305. Archived from the original on 2023-09-13. Retrieved 2023-09-12.
- 1 2 The Selection and Use of Essential Medicines: Report of the WHO Expert Committee, 2015. WHO. 2015. p. 34. ISBN 9789241209946. Archived from the original on 13 September 2023. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|