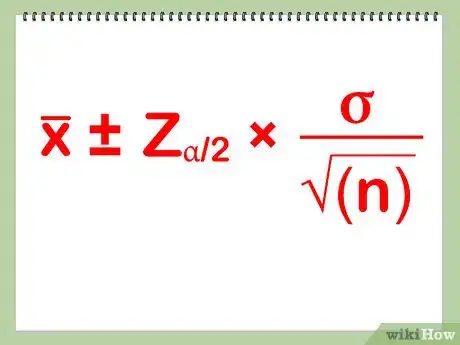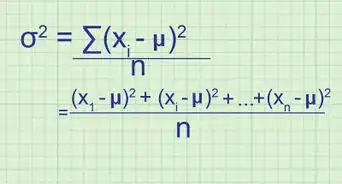This article was co-authored by Mario Banuelos, PhD. Mario Banuelos is an Assistant Professor of Mathematics at California State University, Fresno. With over eight years of teaching experience, Mario specializes in mathematical biology, optimization, statistical models for genome evolution, and data science. Mario holds a BA in Mathematics from California State University, Fresno, and a Ph.D. in Applied Mathematics from the University of California, Merced. Mario has taught at both the high school and collegiate levels.
There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 1,879,266 times.
A confidence interval is an indicator of your measurement's precision.[1] It is also an indicator of how stable your estimate is, which is the measure of how close your measurement will be to the original estimate if you repeat your experiment. Follow the steps below to calculate the confidence interval for your data.
Steps
-
1Write down the phenomenon you'd like to test. Let's say you're working with the following situation: The average weight of a male student in ABC University is 180 lbs. You'll be testing how accurately you will be able to predict the weight of male students in ABC university within a given confidence interval.[2]
-
2Select a sample from your chosen population. This is what you will use to gather data for testing your hypothesis.[3] Let's say you've randomly selected 1,000 male students.Advertisement
-
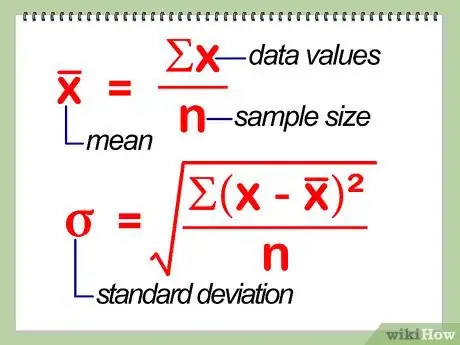
3Calculate your sample mean and sample standard deviation. Choose a sample statistic (e.g., sample mean, sample standard deviation) that you want to use to estimate your chosen population parameter. A population parameter is a value that represents a particular population characteristic. Here's how you can find your sample mean and sample standard deviation:
- To calculate the sample mean of the data, just add up all of the weights of the 1,000 men you selected and divide the result by 1000, the number of men. This should have given you the average weight of 180 lbs.[4]
- To calculate the sample standard deviation, you will have to find the mean, or the average of the data. Next, you'll have to find the variance of the data, or the average of the squared differences from the mean. Once you find this number, just take its square root.[5] Let's say the standard deviation here is 30 lbs. (Note that this information can sometimes be provided for you during a statistics problem.)
-
4Choose your desired confidence level. The most commonly used confidence levels are 90 percent, 95 percent and 99 percent.[6] This may also be provided for you in the course of a problem. Let's say you've chosen 95%.
-
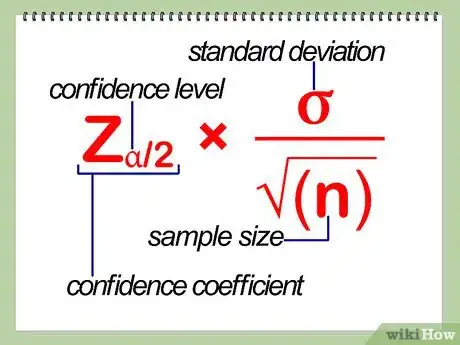
5Calculate your margin of error. You can find the margin of error by using the following formula: Za/2 * σ/√(n). Za/2 = the confidence coefficient, where a = confidence level, σ = standard deviation, and n = sample size. This is another way of saying that you should multiply the critical value by the standard error.[7] Here's how you can solve this formula by breaking it into parts:
- To find the critical value, or Za/2: Here, the confidence level is 95%. Convert the percentage to a decimal, .95, and divide it by 2 to get .475. Then, check out the z table to find the corresponding value that goes with .475. You'll see that the closest value is 1.96, at the intersection of row 1.9 and the column of .06.
- To find the standard error, take the standard deviation, 30, and divide it by the square root of the sample size, 1,000. You get 30/31.6, or .95 lbs.
- Multiply 1.96 by .95 (your critical value by your standard error) to get 1.86, your margin of error.
-
6State your confidence interval. To state the confidence interval, you just have to take the mean, or the average (180), and write it next to ± and the margin of error. The answer is: 180 ± 1.86. You can find the upper and lower bounds of the confidence interval by adding and subtracting the margin of error from the mean.[8] So, your lower bound is 180 - 1.86, or 178.14, and your upper bound is 180 + 1.86, or 181.86.
- You can also use this handy formula in finding the confidence interval: x̅ ± Za/2 * σ/√(n). Here, x̅ represents the mean.
Expert Q&A
Did you know you can get expert answers for this article?
Unlock expert answers by supporting wikiHow
-
QuestionWhat is a confidence interval?
 Mario Banuelos, PhDMario Banuelos is an Assistant Professor of Mathematics at California State University, Fresno. With over eight years of teaching experience, Mario specializes in mathematical biology, optimization, statistical models for genome evolution, and data science. Mario holds a BA in Mathematics from California State University, Fresno, and a Ph.D. in Applied Mathematics from the University of California, Merced. Mario has taught at both the high school and collegiate levels.
Mario Banuelos, PhDMario Banuelos is an Assistant Professor of Mathematics at California State University, Fresno. With over eight years of teaching experience, Mario specializes in mathematical biology, optimization, statistical models for genome evolution, and data science. Mario holds a BA in Mathematics from California State University, Fresno, and a Ph.D. in Applied Mathematics from the University of California, Merced. Mario has taught at both the high school and collegiate levels.
Assistant Professor of Mathematics You can think of a confidence interval as a kind of a net that captures the potential region where a parameter lies. For example, you might want to calculate the average number of hours students spend online. To do that, you might ask a sample of 100 students how many average hours they spend online, then add or subtract the margin of error.
You can think of a confidence interval as a kind of a net that captures the potential region where a parameter lies. For example, you might want to calculate the average number of hours students spend online. To do that, you might ask a sample of 100 students how many average hours they spend online, then add or subtract the margin of error. -
QuestionHow can I find the z value of 95% on the table?
 Community AnswerOn your table, look to the larger (inner) box, find the closest to .9500 (it will probably be .9495, or .9505). These translate to 1.64 and 1.65 respectively.
Community AnswerOn your table, look to the larger (inner) box, find the closest to .9500 (it will probably be .9495, or .9505). These translate to 1.64 and 1.65 respectively. -
QuestionGiven a sample of 100 projector bulbs from a company has a mean length of life of 20.5 hours with a standard deviation of 1.6 hours, how do I find a 95% confidence interval for the average length of life of those bulbs and then interpret the results?
 Community Answer20.6 is the upper limit and 20.4 is the lower limit. There is 95% confidence that the constructed interval includes the population mean.
Community Answer20.6 is the upper limit and 20.4 is the lower limit. There is 95% confidence that the constructed interval includes the population mean.
Things You'll Need
- Sample population
- Computer
- Internet access
- Statistics textbook
- Graphing calculator
References
- ↑ https://www.simplypsychology.org/confidence-interval.html
- ↑ https://www.westga.edu/academics/research/vrc/assets/docs/confidence_intervals_notes.pdf
- ↑ https://www.westga.edu/academics/research/vrc/assets/docs/confidence_intervals_notes.pdf
- ↑ Mario Banuelos, PhD. Assistant Professor of Mathematics. Expert Interview. 11 December 2021.
- ↑ Mario Banuelos, PhD. Assistant Professor of Mathematics. Expert Interview. 11 December 2021.
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/confidenceinterval.asp
- ↑ https://www.westga.edu/academics/research/vrc/assets/docs/confidence_intervals_notes.pdf
- ↑ Mario Banuelos, PhD. Assistant Professor of Mathematics. Expert Interview. 11 December 2021.
- http://stattrek.com/AP-Statistics-4/Confidence-Interval.aspx?Tutorial=Stat
About This Article
You can determine a confidence interval by calculating a chosen statistic, such as the average, of a population sample, as well as the standard deviation. Choose a confidence level that best fits your hypothesis, like 90%, 95%, or 99%, and calculate your margin of error by using the corresponding equation. Finally, you can state your confidence interval by calculating its upper and lower bounds. Simply add the margin of error to your chosen statistic to get the upper bound, and subtract the margin of error to get the lower bound. If you want to learn how to calculate any margins of error, keep reading the article!