This article was co-authored by Jason Shackelford. Jason Shackelford is the Owner of Stingray Auto Repair, a family owned and operated auto repair shop with locations in Seattle and Redmond, Washington. He has over 24 years of experience in auto repair and services, and every single technician on Jason’s team has more than 10 years of experience.
There are 15 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 82,546 times.
The ignition coils in your engine produce an electrical current that’s carried through your ignition cables (spark plug wires) to the spark plug. That current then flows through the plug to detonate the air and fuel mixture inside the cylinder. A faulty ignition coil can result in a misfire or even the engine failing to run.[1] Once you’ve identified which coil is causing the issue, you can test the ignition coil to be sure it’s the problem. Replacing a bad coil can be done in just a few hours with common hand tools.
Steps
Disconnecting the Old Coil
-
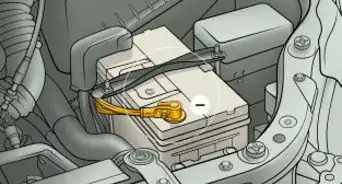
1Disconnect the negative terminal on your battery. Locate your battery in either the engine bay or the trunk of the vehicle. It looks like a rectangular box with two posts (terminals) sticking out of the top of it. The terminals will be labeled with a plus (+) sign on the positive post and a minus (-) sign on the negative one. Use an appropriate sized wrench or socket and ratchet to loosen the bolt securing the cable to the negative terminal, then slide it off.[2]
- Tuck the cable down to the side of the battery to ensure it doesn’t accidentally come back into contact with the battery’s terminal while you work.
- Disconnecting the power will help ensure you can’t get shocked or damage the electrical system of the vehicle while replacing the coil.
- Be careful not to touch the positive and negative terminals at the same time with your wrench or you could get shocked.
-
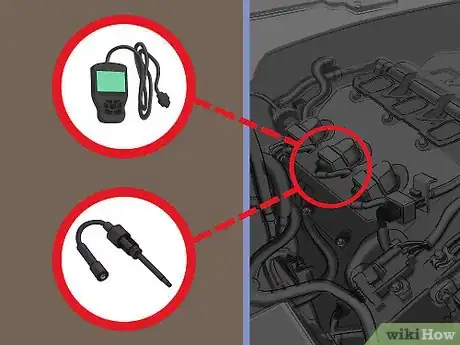
2Locate the ignition coil that needs to be replaced. Some vehicles have a single ignition coil with outlets for each cylinder, while others have individual coils for each cylinder. If you have identified which ignition coil needs to be replaced using an OBD-II code scanner, you can refer to an application-specific repair manual to identify the coil related to the error code your scanner provided. If instead, you identified the bad coil using an ignition spark tester, you’ll already know exactly which coil you need to remove.[3]
- An application-specific repair manual can tell you exactly where to find the ignition coils in your vehicle, as well as which coil relates to different error codes.
- You can purchase these repair manuals at most auto parts stores or online retailers like Amazon.
- You should test the ignition coil before replacing it.
Advertisement -
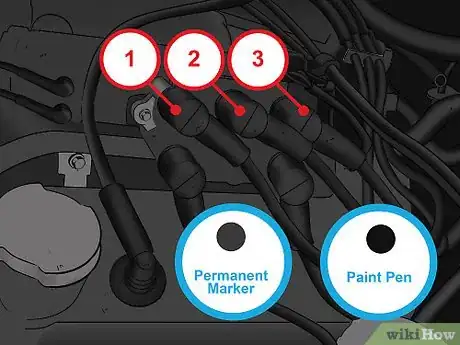
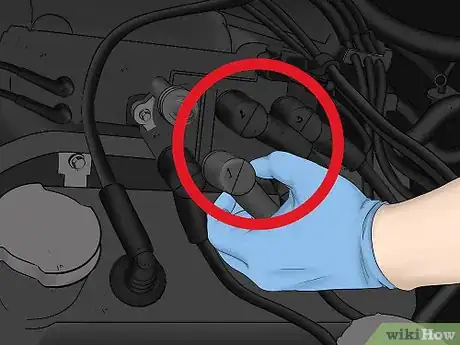
3Label the cables running into the coil, if there are more than one. If the ignition coil in your vehicle supplies an electrical current to multiple cylinders, write numbers on them with a marker to remember which order they connect in. Start from left to right, numbering each ignition cable connected to the coil in order so you can connect them to the new coil in the same way.[4]
- If there are two rows of ignition cables coming from your coil, start at the top left and work your way across, then continue numbering on the next row.
- If the cables are grey, a permanent marker will do the trick. However, if they’re black, use a paint pen to ensure you can read the numbers.
-
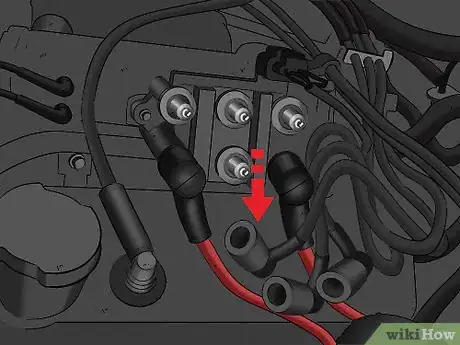
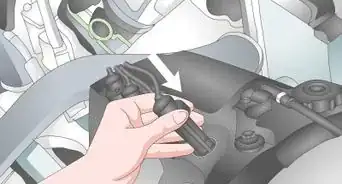
4Disconnect each cable leading into the coil. Grip the ignition cables as close to the coil itself as you can. Squeeze firmly and pull the cable’s boot (the connector portion of the cable) off of the ignition coil. You may need to squeeze and pull rather hard to disconnect each wire.[5]
- If there’s only one cable going to your ignition coil, you only need to disconnect that one.
- Do not pull on the ignition cables anywhere other than low on the boot; otherwise, you could damage the internal wiring of the cable.
-
5Tuck the ignition cables to the side. Once the ignition cable or cables have been disconnected from the coil, they may be hanging in the way of accessing the coil itself. Tuck them behind the coil or anything else nearby so you can easily access the ignition coil.[6]
- The cables are numbered, so you don’t have to worry about mixing them up.
-
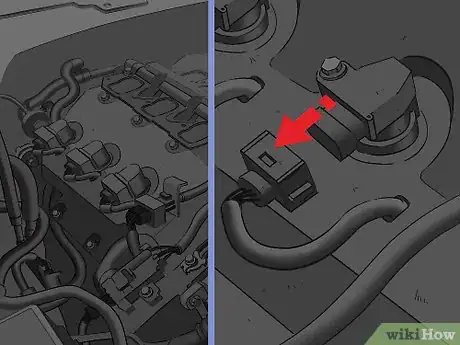
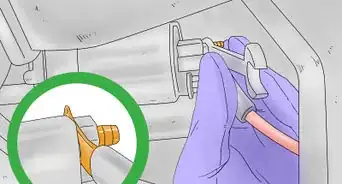
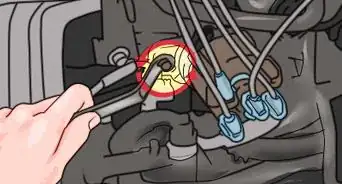
6Release the clip on the plug running into the side of the coil. There will be a single electrical plug going into the side of the ignition coil. It may be larger or smaller, depending on the style of the coil, but removing it is usually the same. Press the plastic clip on the plug that releases it from the ignition coil, and then pull the plug backward to disconnect it.[7]
- In some applications, you may need to use a flat head screwdriver to pry the release up, instead of pressing it down with your thumb.
- If you have trouble determining how to release the connection, refer to an application-specific repair manual or the manufacturer’s website for further guidance.
Swapping in the New Coil
-
1Unscrew the bolts holding the coil in place using a wrench. Depending on the size of the ignition coil, it may be held on with anywhere from 1 to 4 bolts on most applications. Locate each bolt securing the coil in place and then use a socket of the appropriate size with a ratchet to loosen and remove the bolts.[8]
- Set each bolt aside somewhere safe to reuse with the new ignition coil.
- Do not attempt to use a socket or wrench that is too large for the bolt. If you strip the head of the bolt, you will not be able to remove the coil.
-
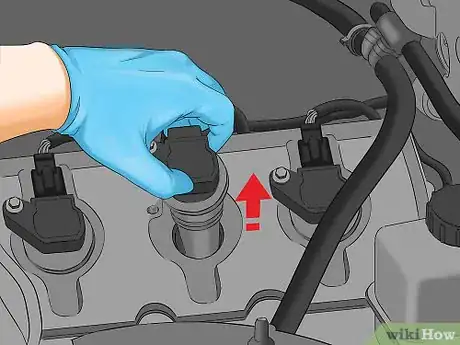
2Remove the coil from the engine bay. With the bolts removed from the coil, grip the coil with one hand and pull it away from where it was mounted in the engine bay. If it doesn’t come out easily, look around for any bolts you may have missed and remove them.[9]
- The ignition coil may be a little stuck on the engine with dirt and grime but should otherwise come out easily.
-
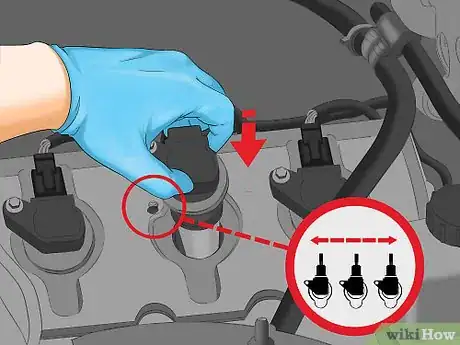
3Compare the new coil to the old one before installing it. Remove your new ignition coil from the box and set it on a table next to your old one. Make sure the new coil has the same number of ports for ignition cables, that the connectors look identical, and that the bolts pass through in the same places. If they aren’t matches, you’ll need to return your new coil for the right part.[10]
- Because parts can change in a vehicle based on the year it was manufactured and the trim package, it’s not uncommon to receive the wrong part, even if it was listed for the right vehicle.
- Comparing the parts before you start the installation can save a great deal of time if it turns out you got the wrong part.
-
4Orient the new coil in the same direction as the old one. Different vehicles utilize different shaped ignition coils, but each will only install one way. Set the new ignition coil where it needs to be mounted so the holes for the bolts line up just as they did with the original.[11]
- If you try to put the coil in backward or upside down, the bolt holes won’t line up.
- If you have trouble figuring out the right way to place the coil inside the car, refer to an application-specific repair manual for guidance.
-
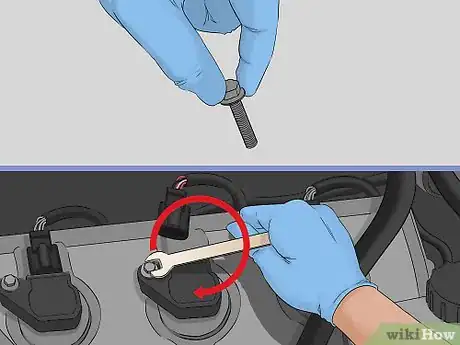
5Insert the bolts to hold the coil in place. Put each bolt in and turn them clockwise by hand to ensure they don’t cross-thread. Once you’ve tightened them a bit by hand, switch to a socket and ratchet to finish tightening them up.[12]
- Cross-threading is when a bolt is forced in at an angle, ruining the threads of the bolt and whatever it’s being screwed into.
- Tighten the bolts until they’re snug and the coil can’t move around at all.
Connecting the New Ignition Coil
-
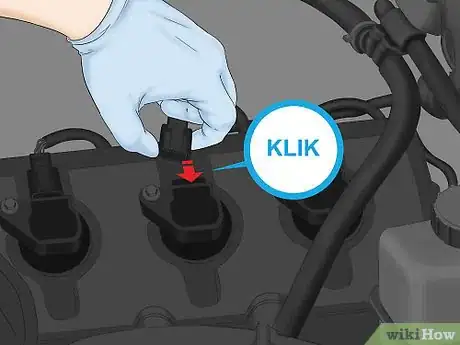
1Connect the plug into the side of the ignition coil. Slide the plug into its port on the new ignition coil until you hear the release click. If you don’t hear a click, it means the connector isn’t pushed in far enough and the coil may not function.[13]
- If you don’t hear a click, pull the connector back off and look inside it to make sure there’s no debris in the way. Then try again.
- Don’t force the connection or you may break it.
-
2Plug each ignition cable into the coil using the order written on them. If there was only a single cable running to the ignition coil, press that cable directly onto the new coil’s cable port until you hear it pop on. If there were multiple cables, start with the cable labeled with a number 1, and connect it to the top left port. Then proceed in order.[14]
- Each cable should produce an audible pop when it’s properly connected.
- You may want to add a dab of dielectric grease to the ports before connecting them to ensure you have a strong connection.
- You can purchase dielectric grease at your local auto parts store.
-
3Reconnect the battery. Slide the cable you removed previously back onto the negative (-) terminal of the battery. Use an open-ended wrench or socket and ratchet to tighten the bolt and secure the cable in place on the terminal.[15]
- The positive cable should still be in place.
- Be careful as you connect the negative cable to the terminal. It may produce a spark.
-
4Start the vehicle to test the new coil. Insert the key into the ignition and turn it to start the engine. If the engine does not turn over at all, the battery is not connected or may be dead. If it attempts to turn over but fails to, check the connections on the ignition coil before trying again.[16]
- Use an OBD-II code scanner to clear any engine error codes. Then allow the engine to run for a few minutes to see if the check engine light begins to flash.
- A flashing check engine light indicates a misfire. Check the connections on your new coil and then try again.
References
- ↑ Jason Shackelford. Auto Technician. Expert Interview. 11 June 2019.
- ↑ https://www.popularmechanics.com/cars/how-to/a1454/4213127/
- ↑ https://youtu.be/b0rmDLSa854?t=80
- ↑ https://youtu.be/5aVDcufzrBw?t=37
- ↑ https://youtu.be/5aVDcufzrBw?t=68
- ↑ https://youtu.be/mgxRlUFcWxU?t=81
- ↑ https://youtu.be/b0rmDLSa854?t=129
- ↑ https://youtu.be/5aVDcufzrBw?t=116
- ↑ https://youtu.be/b0rmDLSa854?t=171