This article was co-authored by Marjan Mahallati, RHN, AADP. Marjan Mahallati is a Registered Holistic Nutritionist, board certified through the AADP (American Association of Drugless Practitioners) and a graduate of the Canadian School of Natural Nutrition. She is the owner of Let's Nutrition Weight Loss & Nutrition Center in Irvine, California, where she teaches clients how to lose weight and achieve optimal nutrition and health. Marjan has over 15 years of experience in the weight loss industry and has empowered thousands of people to gain their health back and live their healthiest lives.
There are 17 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 13,274 times.
Your basic metabolism, also known as your basal metabolic rate (BMR), is all of the biochemical reactions that help provide and use up energy. Boosting your metabolism through your diet is achieved by making sure your body has enough energy through a healthy intake of essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals. These are needed to run all your biochemical reactions at the most efficient levels, which will boost your metabolism.[1] Kickstart your metabolism by choosing healthy foods that support these processes, eating at the right times, and making healthy lifestyle choices.
Steps
Changing Your Eating Habits
-
1Eat quality meat proteins. Protein is the main nutrient needed for muscle development. Muscle tissue burns more calories than fat tissue. Increasing your muscle mass helps you not only to lose weight but also improves your metabolism. To get more protein in your diet, incorporate proteins into each meal.[2] These should be high quality lean meats that contain complete proteins, which contain the amino acids necessary for muscle production.[3] Try to get hormone and antibiotic free meat and grass fed beef when possible. Good meats include:[4]
- Lean, skinless poultry, including chicken and turkey
- Lean ground turkey
- Lean ground beef or trimmed cuts of beef
- Buffalo trimmed of excess fat
- Lean pork trimmed of excess fat
- Fish, including tuna, salmon, sardines and mackerel
-
2Consume additional forms of protein. In addition to meat proteins, you can consume protein in many other forms. This is especially helpful if you are a vegetarian or if you have health conditions that require you to limit your meat intake. Plant-based proteins also contain complete amino acids that will help with muscle growth. Incorporate more of these into your diet every day. These foods include:[5]
- Eggs and egg whites
- Nuts and seeds
- Dairy products, such as low-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese
- Soy products, such as tofu and soy milk
- Lentils, peas and beans, falafel
- Hearty grains, such as oats and quinoa
- Skimmed milk powder that can be added into milk shakes, soups, sauces, gravies, casseroles, etc.
- Whey protein powder
- Quorn
Advertisement -
3Incorporate more healthy fats into your diet. The healthiest form of fats you can consume is omega-3 fats. Omega-3 fats reduce inflammation, which helps with excess fat, which is one of the most common types of inflammation. They also help balance blood sugar levels and regulate your overall metabolism.
- Omega-3s are also thought to help regulate the response to certain hormones, such as leptin and adiponectin, that are instrumental to the control of hunger and weight.
- These are found in many fish, including salmon, tuna, herring, mackerel, and sardines. They can also be found in flaxseed oil, walnut oil, and borage oils.[6] [7]
-
4Choose whole foods. Whole foods are foods that are not processed, which are those foods that are found in nature (such as whole fruits and vegetables). These foods are more complex and have more nutrients, which means it takes more energy and burns more calories as you digest them. By choosing whole foods, you force your body to work harder.[8]
- Keep in mind the term "processed" can refer to many things — spinach that is washed and bagged, for instance, is considered processed. Minimal processing like this (or cutting up veggies, etc.) is fine. Just try to avoid highly processed foods such as fast foods or foods that are boxed and contain a lot of preservatives and additives.
-
5Avoid easily digestible foods. Although some easily digestible foods, such as smoothies, are good for you, avoid them if you are trying to kickstart your metabolism. Smoothies are easy for your body to digest, which means it works less to digest them. Instead, eat more complex foods that will make your body work harder to digest them.
- Also avoid other soft foods, such as bananas, yogurt, and pudding.
- These easily digestible foods should be limited to one a day, such as an add on smoothie with your breakfast or a yogurt cup for a snack.
-
6Save most of your calories for the morning hours. The best way to keep your metabolism active all day is to get active in the morning and intake most of your calories before 4 pm. This is so your body can digest your food properly and pep up your metabolism more. If you eat too many calories after this time, you won't burn as many calories because your metabolism slows down as you sleep.
- This means any excess calories can be turned into fat.
- Never skip breakfast if you are trying to boost your metabolism. It is hard to get the right nutrients and boost your metabolism if you don't eat early in the day.
- Incorporate high quality, lean, and complete protein with your breakfast to ensure that your metabolism is super charged throughout the day, especially if you work out early in the morning. It also helps keep hunger down throughout the day.[9]
-
7Avoid cutting too many calories too quickly. If you are trying to reduce your daily intake of calories, avoid doing so too quickly. When you cut your daily caloric intake too much at one time, your body responds by going into famine mode. This means your body conserves calories and actually lowers your BMR.[10]
- A healthy way around this reaction is to calculate the amount of calories you need to maintain your BMR. Measure the amount of calories you currently eat every day, then cut it by 10% every week or two until you match the caloric intake needed to maintain your BMR.
Using Other Natural Methods
-
1Pair diet with physical activity.[11] The best way to increase body metabolism is to increase exercise levels. To kickstart your metabolism, increase your daily physical activity. This will make your body work more, which will burn more calories and increase your BMR. It also helps you build muscles, which will help your burn even more calories and increase your BMR even more.
- When it comes to exercise, do a combination of cardio, like interval training, and lifting weights.[12]
- When you increase your physical activity along with providing your body with quality nutrients, you help kickstart your metabolism into burning more calories more efficiently.[13] [14] [15] [16]
- Try incorporating more movement into your daily life. For instance, at work you can walk to colleagues to talk instead of emailing or messaging, walk or ride a bike to work, walk on your lunch break, wear a pedometer and set target steps for each day.
-
2Drink more water. Getting the proper amount of water every day is essential to have the optimal BMR and calorie burning potential. Although the daily recommended amount is six to eight 8-oz (237 ml) glasses of water a day, increasing that amount of water to ten to twelve glasses water may help boost your metabolism.[17]
- You should drink half your weight in ounces of water per day. For example, if you weight 160 pounds, you need to drink 80 ounces of water each day.[18]
- It can also help you lose weight because water helps curb hunger.
-
3Drink green tea. In addition to your daily water, drink green tea every day. Studies have shown that the catechins in green tea are thermogenic, which means they help burn calories.
- Drink four to six cups or glasses of green tea, which can be hot or iced, daily.[19]
- This can be used as a base in your morning smoothie or as a snack.
- Avoid drinking it late at night unless you buy decaffeinated tea so you won't disrupt your sleeping patterns.
-
4Work with a dietitian. If you are unsure of exactly how to integrate the needed foods, supplements, or changes into your daily life, think about asking a health professional, such as dietitian, for help. They can help you kickstart your metabolism in a safe, healthy, and effective way.
- If you aren't sure how to find a dietitian, ask your doctor for a recommendation.
-
5Try supplements for an extra boost. There are certain supplements that you can add to your daily routine in addition to your diet to help kickstart your metabolism. This does not mean they should take the place of adequate nutrients in your diet. Make sure you avoid supplements that claim to be for boosting your metabolism that are instead full of caffeine and ephedra derivatives. Always follow manufacturer's instructions as well as those of your doctor. Helpful supplements include:
- Turmeric and ginger, which is thermogenic, meaning it increases heat in the body to boost metabolism. Turmeric also contains antioxidants, which help eliminate harmful by products from the digestive process.[20] [21]
- B-complex vitamins, such as B6 and B12, which are essential for energy production to increase metabolism.[22]
- Zinc and selenium, which are minerals required in many of the biochemical reactions that help with your metabolism. In addition to the supplement, zinc is found in scallops, oysters, dark poultry meat, and beef. Selenium is found in barley, mushrooms, Brazil nuts, and sunflower seeds.
- Chili peppers contain capsaicin, a chemical compound that can boost metabolism.
Understanding Metabolism
-
1Refute common myths about metabolism. It is a common misconception that people will gain weight due to a slow metabolism. Although this does sometimes happen, weight gain is more than likely due to an abundance of bad calories that cannot be used by your metabolism to drive energy and charge your body.
- In order to avoid this, eat proteins, whole foods, and good fats to provide your body with sufficient nutrients that will help your burn the ingested calories more efficiently.[23]
-
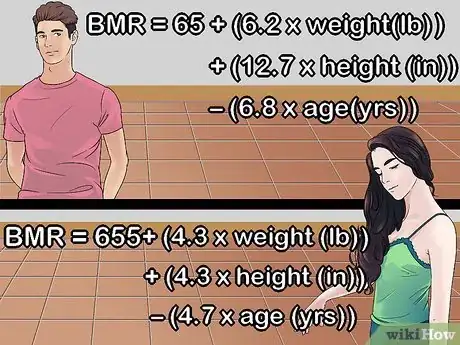
2Determine how your BMR works. There is no strict guide to determine your exact BMR. It will vary depending on your body size and composition, which is measured through your weight and muscle mass. Your age and gender also play a major role in BMR levels.
- Your BMR uses about 70% of the calories you ingest on a daily basis and this portion of your metabolic rate cannot change; however, the remaining 30% of your metabolic rate can change. Diet is one way, and increasing your physical activity and building up more muscle mass also help burn calories and increase your metabolic rate.[24]
-
3Check your thyroid. The thyroid is a gland that plays a major role in metabolism. If you have an underactive thyroid condition, called hypothyroidism, you will have a low functioning metabolism. If you are worried about your metabolic rate or have the symptoms of hypothyroidism, consider having your doctor check your thyroid. These symptoms include:[25]
- Unexplained weight gain
- Fatigue
- Lack of energy
- Increase sensitivity to cold
- Hair loss
- Dry skin
- Muscle weakness or aches
- Abnormally heavy periods
- Constipation
- Depression
-
4See your doctor. Before you start any diet change, consult your doctor. You want to let them know what you are planning so they can let you know if you are making healthy choices. They may want to run tests for any conditions that might deter you from or limit how quickly you can go through the kickstart process.
- Also let them know that you plan to change your diet. Make sure any new food items will not interact with any existing conditions you have.
- Your doctor can also refer you to a registered dietitian who can help you plan meals and choose the best foods for your metabolism.
References
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/metabolism/art-20046508
- ↑ Marjan Mahallati, RHN, AADP. Registered Holistic Nutritionist. Expert Interview. 21 July 2020.
- ↑ http://www.fitday.com/fitness-articles/nutrition/proteins/incomplete-vs-complete-proteins.html
- ↑ http://authoritynutrition.com/20-delicious-high-protein-foods/
- ↑ http://authoritynutrition.com/20-delicious-high-protein-foods/
- ↑ http://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/other-nutrients/essential-fatty-acids
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24129365
- ↑ http://www.jillianmichaels.com/fit/lose-weight/metabolism-boosting-foods
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/expert-answers/food-and-nutrition/faq-20058449
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3673773/
- ↑ Marjan Mahallati, RHN, AADP. Registered Holistic Nutritionist. Expert Interview. 21 July 2020.
- ↑ Marjan Mahallati, RHN, AADP. Registered Holistic Nutritionist. Expert Interview. 21 July 2020.
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/metabolism/art-20046508
- ↑ http://www.news-medical.net/life-sciences/What-is-Metabolism.aspx
- ↑ http://www.womenshealthmag.com/weight-loss/boost-your-metabolism
- ↑ http://www.mensfitness.com/training/pro-tips/best-ways-increase-your-metabolism
- ↑ http://press.endocrine.org/doi/full/10.1210/jc.2003-030780
- ↑ Marjan Mahallati, RHN, AADP. Registered Holistic Nutritionist. Expert Interview. 21 July 2020.
- ↑ Hursel R, Westerterp-Plantenga MS. Catechin- and caffeine-rich teas for control of body weight in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013 Dec;98(6 Suppl):1682S-1693S
- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15507147
- ↑ http://www.webmd.com/food-recipes/antioxidants-topic-overview
- ↑ Marjan Mahallati, RHN, AADP. Registered Holistic Nutritionist. Expert Interview. 21 July 2020.
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/metabolism/art-20046508
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/weight-loss/in-depth/metabolism/art-20046508
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hypothyroidism/symptoms-causes/dxc-20155382

































































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...