This article was co-authored by JoAnna Nguyen, MD. Dr. Joanna Nguyen is a Board-Certified Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeon based in Los Angeles, California. Dr. Nguyen holds dual degrees in Psychology and Biology with a Specialization in Neuroscience from Boston University and completed her medical training at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine. She then went on to complete comprehensive training in plastic surgery at the University of Southern California. Dr. Nguyen is a practicing plastic surgeon in Los Angeles, California and specializes in eyelid surgery, labiaplasty and breast augmentation. She is a diplomat of the American Board of Plastic Surgery.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 92% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 65,269 times.
Operating rooms must always remain sterile environments to protect patients from being exposed to harmful bacteria during medical procedures. Being exposed to these bacteria during a medical procedure could lead to an infection. This is why surgeons and all other members of the surgical team need to follow special directions (known as aseptic technique) when scrubbing in. This procedure requires a little bit of prep, attention to detail during the actual scrub, and a special method of drying off. While scrubbing in, you need to decide whether you want to time yourself or count scrubbing strokes. If you're timing yourself, your goal is five minutes for the entire procedure. If you're counting strokes, you'll need to aim for 20 to 30 strokes per side of your hand or arm.
Steps
Prepping
-
1Enter the designated changing room. Regardless of the facility you're operating in, the location must have a designated changing room to reduce the possibility of contamination. Here, you'll change from your street clothes to your scrubs. After surgery, you'll return here to wash up and change back into your street clothes.[1]
-
2Tie up your hair. This applies if your hair is long or medium-length. Pull it back in a topknot or bun. Don't allow any hair to hang over your face. Make sure that your hairdo will easily fit under your head covering.
- You'll need to cover your hair, so take that into consideration when you're deciding how to put it up.[2]
Advertisement -
3Cover your hair. Hair, dandruff, and squamous cells fall from your head without your noticing. Therefore, covering your head is essential for your patients' safety. Wear a standard surgical head cover or hood provided by the hospital. Make sure the material is free of lint and is large enough to fit all of your hair. If you have sideburns and/or facial hair, you should wear a surgical hood to cover these areas.
- Avoid surgeons' skull caps, which do not adequately cover your hair.[3]
-
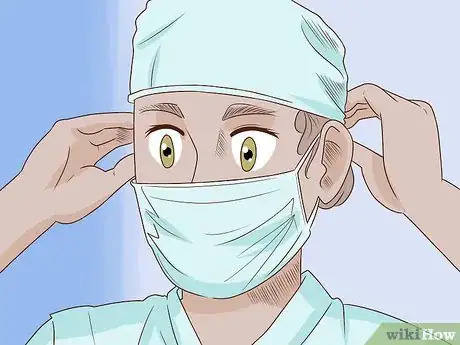
4Put on your surgical mask. This is to prevent bacteria, saliva, or mucous from contaminating your hands as you scrub. It also covers facial hair, which can carry dandruff or contaminating squamous cells. Make sure the fabric covers your nose and mouth. Tie each set of strings behind your head. The mask should be secure without cutting off your air flow.[4]
-
5Remove your jewelry. Jewelry carries microbes that could infect your patient. Take off your watch, bracelets, rings, etc and put them in your locker. Make sure nothing remains on your hands or arms.[5]
-
6Put on your scrub suit. Your suit should consist of a shirt and pants. Put your shirt on first. If you're wearing an undershirt, bra, or camisole, your shirt should cover it completely. Not even the collar or straps should emerge from the neckline of the scrub shirt. After your shirt is on, put on your scrub pants. Tuck your shirt tail into the waistband to prevent billowing or skin shedding into sterile areas.[6]
- Be sure to wear clean scrubs every time you scrub in.[7]
-
7Open the packaging of a new scrub brush. Each brush is individually packaged to remain sterile. Tear the backing away from the plastic packaging. As you open it, look for an enclosed nail file. Take the file in your dominant hand. Keep the scrub brush in the packaging for now.[8]
-
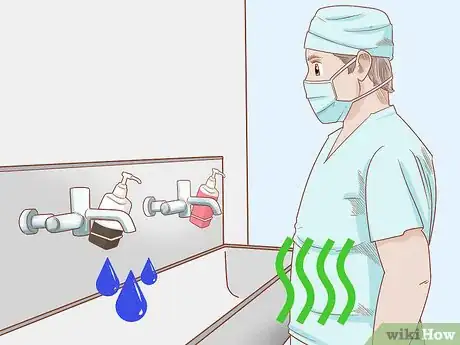
8Adjust the water temperature to a warm setting. Antimicrobial soap works most efficiently in warm water. Avoid excessively hot water, which could lead to dry and irritated skin. Cold water should also be avoided because it keeps soap from lathering properly.[9]
Washing
-
1Keep your surgical attire dry. Make sure that no water splashes on it at any time during the scrubbing procedure. If you get your attire wet, you'll risk contamination. This means you must change clothes and start scrubbing all over again.[10]
-
2Clean beneath your nails. Remove the nail file from the scrub brush packaging. Hold the file in your dominant hand. Place the other hand under the water. Allow the water to flow between your fingertip and fingernail as you remove dirt with the file. Repeat this process with each finger on both hands. Make sure you've removed all dirt and debris. Discard the file when you're finished.[11]
-
3Remove the scrub brush from the packaging. Hold the plastic side of the packaging in one hand. Allow the brush to fall into the other hand. Discard the packaging. Aim carefully to prevent the brush from falling on the floor or other unsanitary surface.
- Keep in mind that some facilities use a brushless scrub technique because some studies have shown that the brushless technique results in a lower bacterial count.[12]
-
4Pump iodine or antimicrobial soap onto the scrub brush. You should find at least two dispensers above the sink within easy reach. The iodine has a brownish tint. Soaps will have a pink or blue hue. Use your elbow to do pump the iodine/soap. About two pumps should do the trick. Make sure the iodine/soap falls onto the rough side of the brush.[13]
-
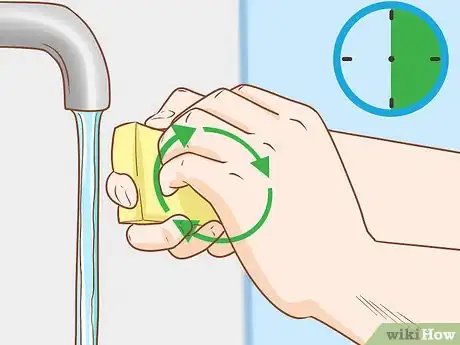
5Scrub your fingertips. Move the scrub brush in a circular motion. Try to scrub beneath your fingernails to pick up any lingering dirt you might have missed with the file. Scrub for 30 seconds to one minute on each hand. Discard the brush when you're finished with this step.[14]
- If you're counting strokes, as opposed to keeping time, scrub for 30 circular strokes on each hand.[15]
-
6Wash your hands. Use chlorhexidine or iodine for this step. Continue to move in a circular motion over your hands. Get in between your fingers. Scrub the front and back sides of your hands to remove bacteria. Do this for two minutes. If you take too long with this step, bacteria will have a chance to grow on your arms.[16]
- If you're counting strokes, go for 20 circular strokes on each side of your hand.[17]
-
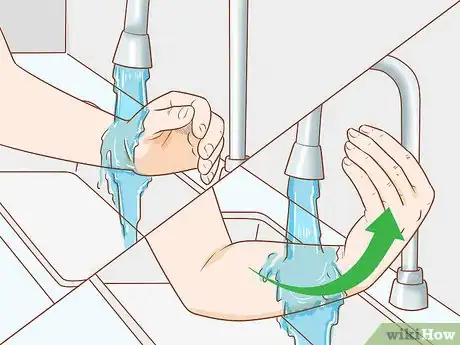
7Scrub your arms. Move in one direction from the base of your palm toward your elbow. Wash up to 2 to 3 inches (5.1 to 7.6 cm) above your elbow. Do this for one minute. Continue to keep your hands elevated to prevent contaminated soap from reaching your clean hands. Keep your hands held higher than your arms during the entire process. This prevents contaminated soap and bacteria from soiling your hands. If contaminated soap hits your hands, you'll have to repeat the process.[18]
- For the counted stroke method, scrub for 20 strokes on each side of your forearm.[19]
-
8Rinse your hands and arms. Avoid moving them back and forth through the water. Work your way up from your fingertips to your elbows. Aim for one swift movement of your arm in one direction. This should only take about three seconds per arm. Let the excess water drip from your hands and arms. Don't shake them.[20]
Drying
-
1Wait until you enter the operating room. You will not dry your hands until you enter the OR. When you do enter the OR, you will dry your hands and arms thoroughly using the aseptic technique. Make sure to dry your hands and arms before donning your sterile gown.
-
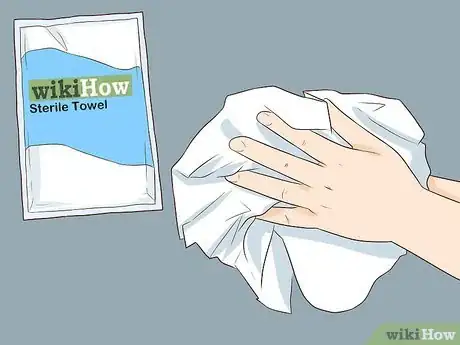
2Pick up a towel. A special sterile towel pack should be included at the top of the package with your surgical gown. Lean forward slightly to pick up the towel pack. Retrieve it and step away from the table to keep your gown sterile. Open the pack so that the towel is folded lengthwise as you open it. Keep the towel away from anything that might be unsterile. Return your hands to the elevated position above your forearms. Make sure your arms don't come into contact with your body.[21]
-
3Dry your hands and arms. Hold one end of the towel in your dominant hand. Dry your other hand and arm by blotting in a circular motion. Start at your fingertips and end at your elbow. Make sure you dry every part of your hand and forearm. Don't go back over any areas you've already dried.[22]
-
4Take the other end of the towel in your non-dominant hand. Repeat the process on your dominant hand and arm, being careful not to retrace your strokes. Discard the towel when you're finished.[23]
- Once your hands are clean and dry, don't touch anything at all until you have on your gown and gloves.[24]
Expert Q&A
Did you know you can get expert answers for this article?
Unlock expert answers by supporting wikiHow
-
QuestionHow do you scrub before surgery?
 JoAnna Nguyen, MDDr. Joanna Nguyen is a Board-Certified Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeon based in Los Angeles, California. Dr. Nguyen holds dual degrees in Psychology and Biology with a Specialization in Neuroscience from Boston University and completed her medical training at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine. She then went on to complete comprehensive training in plastic surgery at the University of Southern California. Dr. Nguyen is a practicing plastic surgeon in Los Angeles, California and specializes in eyelid surgery, labiaplasty and breast augmentation. She is a diplomat of the American Board of Plastic Surgery.
JoAnna Nguyen, MDDr. Joanna Nguyen is a Board-Certified Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeon based in Los Angeles, California. Dr. Nguyen holds dual degrees in Psychology and Biology with a Specialization in Neuroscience from Boston University and completed her medical training at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine. She then went on to complete comprehensive training in plastic surgery at the University of Southern California. Dr. Nguyen is a practicing plastic surgeon in Los Angeles, California and specializes in eyelid surgery, labiaplasty and breast augmentation. She is a diplomat of the American Board of Plastic Surgery.
Board Certified Plastic Surgeon & Reconstructive Surgeon Change into clean scrubs and be sure your hair is up and covered. Wash your hands for at least 2 minutes using a surgical scrub, making sure to clean under your nails and all the way up to your elbows. Then, proceed to the operating room and the surgical technician will assist you in putting on your gown and gloves. Take care not to touch anything until you are fully gowned and gloved to prevent contamination, and once you are fully gowned and gloved, be sure to only touch things in the designated sterile zone.
Change into clean scrubs and be sure your hair is up and covered. Wash your hands for at least 2 minutes using a surgical scrub, making sure to clean under your nails and all the way up to your elbows. Then, proceed to the operating room and the surgical technician will assist you in putting on your gown and gloves. Take care not to touch anything until you are fully gowned and gloved to prevent contamination, and once you are fully gowned and gloved, be sure to only touch things in the designated sterile zone.
Warnings
- Be careful not to touch anything that is not sterile after finishing your scrub in. You will have to repeat the entire process if you touch something that is unsterile.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ http://www.ast.org/uploadedFiles/Main_Site/Content/About_Us/Standard_Surgical_Attire_Surgical_Scrub.pdf
- ↑ JoAnna Nguyen, MD. Board Certified Plastic Surgeon & Reconstructive Surgeon. Expert Interview. 29 July 2020.
- ↑ http://www.ast.org/uploadedFiles/Main_Site/Content/About_Us/Standard_Surgical_Attire_Surgical_Scrub.pdf
- ↑ http://www.ast.org/uploadedFiles/Main_Site/Content/About_Us/Standard_Surgical_Attire_Surgical_Scrub.pdf
- ↑ http://www.infectioncontroltoday.com/articles/2001/05/how-to-perform-surgical-hand-scrubs.aspx
- ↑ http://www.ast.org/uploadedFiles/Main_Site/Content/About_Us/Standard_Surgical_Attire_Surgical_Scrub.pdf
- ↑ JoAnna Nguyen, MD. Board Certified Plastic Surgeon & Reconstructive Surgeon. Expert Interview. 29 July 2020.
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YsAE7h9-0CQ
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK144036/
- ↑ http://www.infectioncontroltoday.com/articles/2001/05/how-to-perform-surgical-hand-scrubs.aspx
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YsAE7h9-0CQ
- ↑ http://www.ast.org/uploadedFiles/Main_Site/Content/About_Us/Standard_Surgical_Attire_Surgical_Scrub.pdf
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YsAE7h9-0CQ
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YsAE7h9-0CQ
- ↑ http://www.brooksidepress.org/Products/Scrub_Gown_and_Glove_Procedures/lesson_1_Section_4.htm
- ↑ http://www.infectioncontroltoday.com/articles/2001/05/how-to-perform-surgical-hand-scrubs.aspx
- ↑ http://www.brooksidepress.org/Products/Scrub_Gown_and_Glove_Procedures/lesson_1_Section_4.htm
- ↑ http://www.brooksidepress.org/Products/Scrub_Gown_and_Glove_Procedures/lesson_1_Section_4.htm
- ↑ http://www.brooksidepress.org/Products/Scrub_Gown_and_Glove_Procedures/lesson_1_Section_4.htm
- ↑ http://www.brooksidepress.org/Products/Scrub_Gown_and_Glove_Procedures/lesson_1_Section_4.htm
- ↑ http://www.brooksidepress.org/Products/Scrub_Gown_and_Glove_Procedures/lesson_1_Section_4.htm
- ↑ http://www.brooksidepress.org/Products/Scrub_Gown_and_Glove_Procedures/lesson_1_Section_4.htm
- ↑ http://www.brooksidepress.org/Products/Scrub_Gown_and_Glove_Procedures/lesson_1_Section_4.htm
- ↑ JoAnna Nguyen, MD. Board Certified Plastic Surgeon & Reconstructive Surgeon. Expert Interview. 29 July 2020.