This article was medically reviewed by Erik Kramer, DO, MPH. Dr. Erik Kramer is a Board-Certified Primary Care Physician at the University of Colorado. With over 15 years of experience, his clinical interests include obesity and weight management, diabetes care, and preventive care, as well as embracing a holistic approach to primary care. He received his Doctorate in Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) from the Touro University Nevada College of Osteopathic Medicine and completed his residency at Central Maine Medical Center. Dr. Kramer is a Diplomate of the American Board of Obesity Medicine.
There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article has 11 testimonials from our readers, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 284,720 times.
Salmonella poisoning most often results from coming into contact with water or food contaminated with salmonella bacteria. It can cause fever, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps, and is often referred to as food poisoning. Symptoms occur within 2 to 48 hours and can last up to 7 days. They usually go away on their own, but complications can arise on rare occasions. The only way to know for sure if you have salmonella is to get a diagnosis from your doctor. The good news is that there are some simple things you can do to start feeling better—and to prevent getting sick again!
Steps
Diagnosis
-
1Look for symptoms like vomiting, diarrhea, and a fever. Salmonella infection is usually caused by eating raw or undercooked eggs or meat products that are contaminated with the bacteria. You may feel symptoms within about 8 hours, or it may take up to 2 days. Salmonella causes inflammation of the stomach and intestines (gastroenteritis).[1] Watch out for common symptoms such as:
- Persistent vomiting and diarrhea
- Nausea
- Chills
- Fever
- Headache
- Blood in the stool
- Cold sweats
-
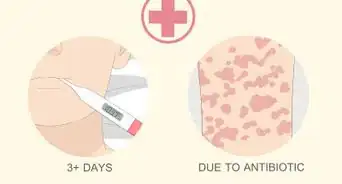
2See a doctor if you have severe symptoms or a weakened immune system. While salmonella usually isn’t dangerous, there’s a higher risk of complications if you have a condition that affects your immune system (such as HIV/AIDS, sickle cell disease, or inflammatory bowel disease). Children and the elderly are also more likely to experience serious complications. If the symptoms don't seem to be going away, and the person experiencing them is in a higher-risk group, it's advisable to see a doctor as soon as possible. Immediate medical attention should also be sought if you or the person you're concerned about experiences the following:[2]
- Dehydration, leading to decreased urine output, decreased tear production, dry mouth, and sunken eyes. If you are losing more fluids (through vomiting or diarrhea) than you’re taking in, see your doctor.
- Signs of a rare, advanced condition known as bacteremia, in which salmonella enters the bloodstream and infects body tissues in the brain, spinal cord, heart, or bone marrow. A sudden high fever, chills, rapid heart rate, and an appearance of serious illness are signs that this may be occurring. Most salmonella can be caught early before this occurs.
Advertisement -
3Get tested for salmonella infection. The doctor will assess your symptoms and, in most cases, advise getting plenty of fluids and resting until the symptoms pass, since they usually go away on their own. If the doctor determines a test is necessary, a stool sample will be tested to determine whether it contains salmonella.[3]
- The doctor may also decide to test a blood sample to determine whether bacteremia has occurred.
- The doctor may prescribe antibiotics if the salmonella infection has spread beyond the digestive system.
- If dehydration becomes severe enough, the patient may need to be admitted to the hospital to take fluids intravenously (through an IV).
Treatment
-
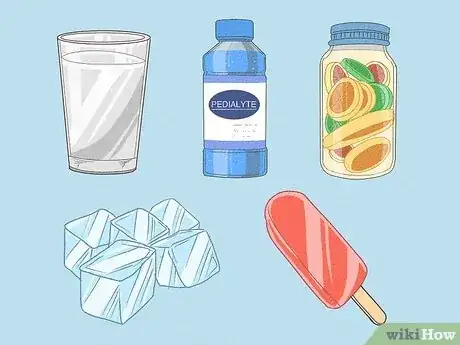
1Drink plenty of fluids, especially water. Loss of fluids through vomiting and diarrhea creates the risk of dehydration. It is important to replace lost fluid and electrolytes by drinking water, herbal tea, juice, and broth. Even if it doesn't feel good to drink, this is the best way to keep up your body's energy and get past the worst of the symptoms.[4]
- Try eating a popsicle, ice chips, or some sorbet as a way to get both water and sugar into your system.
- Drink plenty of water, especially after severe bouts of vomiting or diarrhea.
- Children can drink a rehydration solution like Pedialyte or a flat soda to restore fluids and electrolytes.
-
2Stick to bland foods while recovering from a salmonella infection. Eating hard-to-digest foods can further aggravate your already-sensitive digestive system. While you’re recovering, eat gentle foods such as bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast.[5]
- Stay away from foods that might aggravate your symptoms and make you feel worse, like dairy products or greasy fast food.
- Avoid foods that might reinfect you or make you sicker, like salads or sushi. Wait at least a few days after you’ve recovered so your immune system can bounce back.
-
3Use a heating pad or warm compress to soothe cramps. Warmth can sometimes bring relief from stomach pain. Grab a heating pad or electric blanket and lay it over your abdomen to help relieve any cramps you may be experiencing.[6] A hot water bottle or a hot bath will also do the trick.
- You can also make your own heating pad by filling a sock with uncooked rice and warming it up in the microwave for 1-2 minutes.
-
4Rest and give your body time to heal. Overdoing it may increase your recovery time. Your body will naturally fight against the salmonella and it will recover more quickly if you do not put undue stress on it. Take it easy and try to get plenty of rest and sleep so you can bounce back faster.[7]
- Salmonella is rarely contagious from person to person.[8] However, it’s still a good idea to take time off work or school for a few days for your own sake, especially if you’re still throwing up or having diarrhea.
Prevention
-
1Cook animal products thoroughly. Don't eat or drink foods that have raw animal products. This is the most common way people get infected with salmonella. Don't hesitate to send undercooked meat, poultry, and eggs back to the kitchen when you're eating out.[9]
- Salmonella is most commonly found in animal products, but vegetables may also get contaminated. Be sure to wash all your vegetables before cooking them.
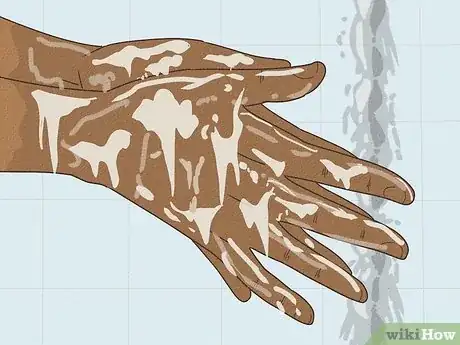
- Wash your hands and work surfaces after they come into contact with raw poultry, meat, or eggs.
-
2Wash your hands after handling animals and their feces. This is another common way that salmonella is spread. Healthy reptiles and birds can carry salmonella on their bodies, and it's also present in cat and dog feces. Any time you handle an animal or its feces, be sure to wash your hands with soapy water.[10]
-
3Don't allow children under 5 to handle reptiles and young birds. Some animals, such as baby chicks, lizards, and turtles, can carry salmonella on their bodies. A child cuddling one of these animals could come into contact with salmonella. Since the infection is harder on a very young child's immune system than an adult's, it's best to forbid children under 5 from getting close to animals that could contaminate them.[11]
- Instruct older children to carefully wash their hands with soap and water after handling any animal, and explain that it is unsafe to kiss the animal or put their hands in their mouth after touching it.
- Adults or older children with weakened immune systems should also avoid touching these animals and things they’ve been in contact with.
Expert Q&A
-
QuestionI have an immune deficiency. What serious complications could result with severe salmonella poisoning?
 Jurdy Dugdale, RNJurdy Dugdale is a Registered Nurse in Florida. She received her Nursing License from the Florida Board of Nursing in 1989.
Jurdy Dugdale, RNJurdy Dugdale is a Registered Nurse in Florida. She received her Nursing License from the Florida Board of Nursing in 1989.
Medical Review Board Your main concern should be diarrhea and a loss of fluids. Stay hydrated as best as you can.
Your main concern should be diarrhea and a loss of fluids. Stay hydrated as best as you can.
Warnings
- Once you have been infected with salmonella, you become a carrier. While salmonella is rarely contagious between people, you can still spread it to others if you don’t practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands after using the bathroom or cleaning up thoroughly after vomiting.[12]⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Do not store fresh fruits and vegetables next to raw meat, as the juice from the meat could contaminate the fruits or vegetables and increase the risk of salmonella bacteria transfer.[13]⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Be careful of cross-contamination from utensils used for handling raw meat and poultry and your food work area. Use separate utensils, plates, and cutting boards when you’re cooking and handling raw meat along with other foods.[14]⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/salmonellosis-salmonella/symptoms.html
- ↑ https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/salmonellosis-salmonella/risks.html
- ↑ https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/salmonella#diagnosed
- ↑ https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/salmonella#diagnosed
- ↑ https://www.ucsfhealth.org/education/diet-modifications-for-nausea-and-vomiting
- ↑ https://reverehealth.com/live-better/should-you-go-to-the-emergency-room-for-your-abdominal-pain/
- ↑ https://www.foodsafety.gov/food-poisoning/bacteria-and-viruses
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/training/SIC_CaseStudy/Infection_Salmonella_ptversion.pdf
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15697-salmonella#management-and-treatmentl
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/general/prevention.html
- ↑ https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15697-salmonella#management-and-treatment
- ↑ http://conditions.health.qld.gov.au/HealthCondition/condition/14/33/124/Salmonella-infection-salmonellosis
- ↑ http://conditions.health.qld.gov.au/HealthCondition/condition/14/33/124/Salmonella-infection-salmonellosis
- ↑ https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/salmonella-(non-typhoidal)
About This Article
If you've noticed symptoms of salmonella, like persistent vomiting and diarrhea, chills, fever, and headache, you should rest for a few days so your body has time to heal. While you're recovering, drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration, and avoid eating food since it can irritate your stomach more. However, you should see a doctor if you have a compromised immune system or if your symptoms aren't going away. Children and the elderly should also see a doctor since they're more likely to experience complications. For advice from our Medical co-author, like how to make yourself more comfortable while you're recovering from salmonella, keep reading.

















-Step-11.webp)














































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...