X
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, volunteer authors worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 57,729 times.
Learn more...
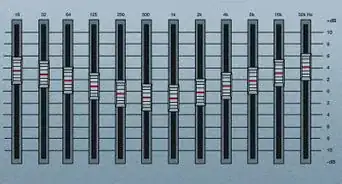
Parametric equalizers are effective when shaping the tone of an audio signal. The controls allow for the user to be precise in selecting a frequency to boost or cut, which is helpful if the signal is feeding back or has an unpleasant overtone. Parametric equalizers are found on mixing boards, amps and most commonly in audio editing software programs. Here's some information on using a parametric equalizer for tone shaping and feedback protection.
Steps
Method 1
Method 1 of 2:
Parametric Equalizer Tone Shaping
-
1Use the hi-pass and low-pass filter.
- On many software programs, there is a high-pass and a low-pass function. The high-pass button will generally cut any frequencies below 100Hz and sometimes 80Hz.
- The low-pass button will generally cut any frequencies above around 10kHz. Many live mixing boards have a high-pass button which serves the same purpose as the software version.
- These buttons allow the user to cut out any unwanted high and low harmonics that can be troublesome in the mix.
-
2Determine frequency. Software programs make it possible for the user to cut or boost 3 to 7 frequencies simultaneously. These are called bands. Start by with just 1 band at a time. Turn on the bandwidth by clicking on the frequency spectrum screen.Advertisement
-
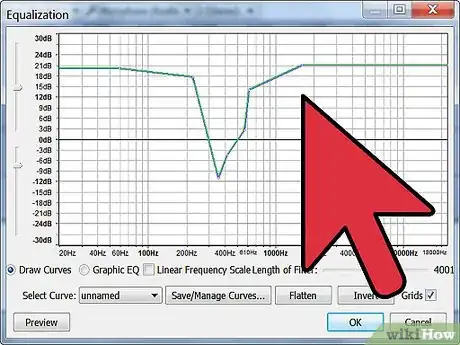
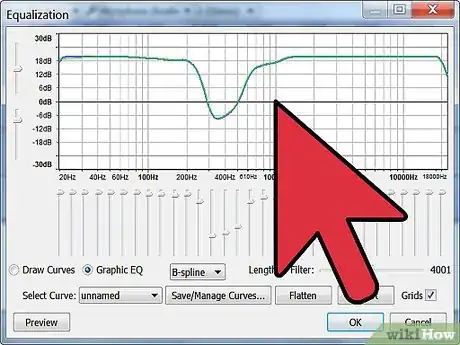
3Determine the bandwidth.
- The bandwidth is the frequency range in which the band will boost or cut. The bandwidth is also referred to as the "Q". The higher the Q the skinnier the bandwidth.
- The Q can be set to as little as 1/30 of an octave up to 3 octaves. By having a wider Q you can get more of basic tone shaping out of the band.
- By making the Q more narrow you can cut frequencies that may be an issue, such as an unpleasant sound or overtone.
- Widen or narrow the Q by lowering or raising the number, respectively.
-
4Cut or boost the band. Once you have set your frequency and Q width you can cut or boost the bandwidth. Use the gain function on the parametric and cut the band by lowering the gain below zero or boost the gain by raising the gain above zero. Make very minimal adjustments until the desired sound is achieved.
Advertisement
Method 2
Method 2 of 2:
Parametric Equalizer Feedback Elimination
-
1Set the Q. This step is only relevant if the board has a Q knob on the channel strip. In a live situation you can set the Q as high as it can go to make precision cut.
-
2Raise the gain on the channel. Boost the channels gain up until you start hearing the channel feedback.
-
3Find the frequency that is feeding back. Turn the frequency knob until the feed back is most apparent.
-
4Cut out the feedback. Lower the gain level on the EQ until the feedback stops.
Advertisement
References
About This Article
Advertisement