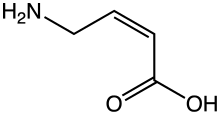
(Z)-4-Amino-2-butenoic acid
(Z)-4-Amino-2-butenoic acid[1] (CACA, cis-4-aminocrotonic acid) is a GABA receptor partial agonist selective for the GABAA-ρ (previously known as GABAC) subtype.[2][3][4]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2Z)-4-Aminobut-2-enoic acid | |
| Other names
(Z)-4-Amino-2-butenoic acid cis-4-Aminocrotonic acid 4-Amino-cis-2-butenoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | CACA |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H7NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 101.105 g·mol−1 |
| 124 mg/mL | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- cis-4-Aminocrotonic acid at Sigma-Aldrich
- Qian, H; Dowling, JE (1996). "Selective agonists for GABAC receptors". Trends in Neurosciences. 19 (5): 190. doi:10.1016/0166-2236(96)85451-8. PMID 8723205. S2CID 208792634.
- Duke, RK; Chebib, M; Balcar, VJ; Allan, RD; Mewett, KN; Johnston, GA (2000). "(+)- and (−)-cis-2-aminomethylcyclopropanecarboxylic acids show opposite pharmacology at recombinant rho(1) and rho(2) GABA(C) receptors". Journal of Neurochemistry. 75 (6): 2602–10. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0752602.x. PMID 11080214.
- Reis, GM; Duarte, ID (2007). "Involvement of chloride channel coupled GABA(C) receptors in the peripheral antinociceptive effect induced by GABA(C) receptor agonist cis-4-aminocrotonic acid". Life Sciences. 80 (14): 1268–73. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2006.12.015. PMID 17316706.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.