Phaclofen
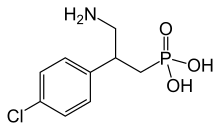
Phaclofen, or phosphonobaclofen, is a selective antagonist for the GABAB receptor.[1] It was the first selective GABAB antagonist discovered, but its utility was limited by the fact that it does not cross the blood brain barrier.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[3-amino-2-(4-chlorophenyl)propyl]phosphonic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H13ClNO3P | |
| Molar mass | 249.631 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- David I.B. KerrCorresponding author contact information, Jennifer Ong, Rolf H. Prager, Bruce D. Gynther, David R. Curtis (3 March 1987). "Phaclofen: a peripheral and central baclofen antagonist". Brain Research. 405 (1): 150–154. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(87)90999-1. PMID 3032346. S2CID 29595421.
{{cite journal}}:|author=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Froestl W, Mickel SJ, von Sprecher G, Diel PJ, Hall RG, Maier L, Strub D, Melillo V, Baumann PA, Bernasconi R, et al. (August 18, 1995). "Phosphinic acid analogues of GABA. 2. Selective, orally active GABAB antagonists". J Med Chem. 38 (17): 3313–3331. doi:10.1021/jm00017a016. PMID 7650685.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.