3-APPA
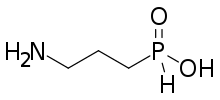
3-Aminopropylphosphinic acid, also known in the literature as 3-APPA or CGP 27492,[1] is a compound used in scientific research which acts as an agonist at the GABAB receptor. It is part of a class of phosphinic acid GABAB agonists,[2] which also includes SKF-97,541. It has a binding affinity (pKi) to the GABAB receptor of 8.30 (i.e. ~3nM).[3]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C3H10NO2P |
| Molar mass | 123.092 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- "3-APPA". IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology. Retrieved March 23, 2021.
- Lacey G, Curtis DR (1994). "Phosphinic acid derivatives as baclofen agonists and antagonists in the mammalian spinal cord: an in vivo study". Experimental Brain Research. 101 (1): 59–72. doi:10.1007/BF00243217. PMID 7843303. S2CID 19055950.
- Froestl W, Mickel SJ, von Sprecher G, Diel PJ, Hall RG, Maier L, et al. (August 1995). "Phosphinic acid analogues of GABA. 2. Selective, orally active GABAB antagonists". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 38 (17): 3313–31. doi:10.1021/jm00017a016. PMID 7650685.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.