37th parallel north
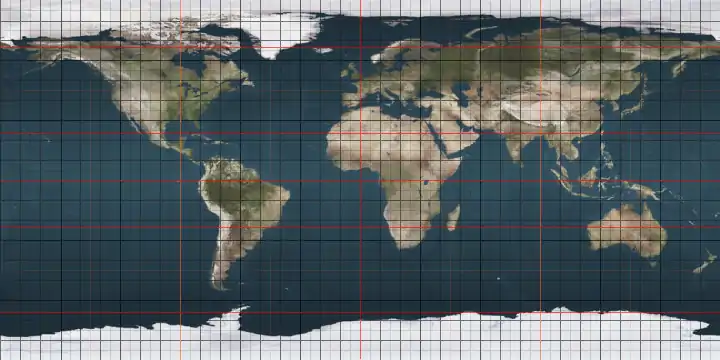
The 37th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 37 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Africa, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
.svg.png.webp)
At this latitude the Sun is visible for 14 hours, 42 minutes during the summer solstice and 9 hours, 37 minutes during the winter solstice.[1]
The 37th parallel north is roughly the northern limit of the visibility of Canopus, the second-brightest star of the night sky. Along with the 37th parallel south, it is the latitude at which solar irradiance is closest to the planetary average,[2] with higher solar irradiance equatorward and lower poleward.
Around the world
Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastward, the parallel 37° north passes through:
United States
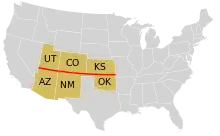
In the United States, the parallel defines the southern borders of Utah, Colorado, and Kansas, and the northern borders of Arizona, New Mexico, and Oklahoma. It dates to the Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854 when Congress divided Unorganized Territory into Kansas and Nebraska north of the 37th parallel and a remainder Indian Territory to the south. Before that the line had been thought to be the boundary between the Cherokee and Osage reservations - the 2.46 miles (3.96 km) discrepancy resulting in the creation of the Cherokee Strip. Congress extended the line west to New Mexico Territory, thus defining which states and territories would constitute The South between the Colorado and Mississippi Rivers, and creating what later became the Oklahoma Panhandle.[3]
Landmarks on the 37th parallel include Santa Cruz, California; Gilroy, California; Madera, California; Ubehebe Crater in Death Valley; Colorado City, Arizona; the Four Corners at the intersection with the 32nd meridian west from Washington (the only place where four U.S. states meet at a point); Cairo, Illinois; Bowling Green, Kentucky; and Newport News, and Hampton, Virginia. It enters the Chesapeake Bay at the northernmost tunnel entrance / exit of the Hampton Roads Bridge Tunnel and the southernmost point of Old Point Comfort on the former Army base, Ft. Monroe.
The parallel 37° north formed the southern boundary of the historic and extralegal Territory of Jefferson.
References
- "Duration of Daylight/Darkness Table for One Year". U.S. Naval Observatory. 2019-09-24. Archived from the original on 2019-10-12. Retrieved 2021-03-10.
- See Nadeau, Alice and McGhee, Richard; ‘A simple formula for a planet's mean annual insolation by latitude’; Icarus, volume 291, 15 July 2017, pp. 46-50
- Hubbard, Bill (2009). American Boundaries: The Nation, the States, the Rectangular Survey. University of Chicago Press. p. 158. ISBN 978-0-226-35591-7. Retrieved 27 September 2012.