ACTA2
ACTA2 (actin alpha 2) is an actin protein with several aliases including alpha-actin, alpha-actin-2, aortic smooth muscle or alpha smooth muscle actin (α-SMA, SMactin, alpha-SM-actin, ASMA). Actins are a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments. ACTA2 is one of 6 different actin isoforms and is involved in the contractile apparatus of smooth muscle. ACTA2 (as with all the actins) is extremely highly conserved and found in nearly all mammals.
| ACTA2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | ACTA2, AAT6, ACTSA, MYMY5, actin, alpha 2, smooth muscle, aorta, actin alpha 2, smooth muscle | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 102620 MGI: 87909 HomoloGene: 133938 GeneCards: ACTA2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In humans, ACTA2 is encoded by the ACTA2 gene located on 10q22-q24.[5][6] Mutations in this gene cause a variety of vascular diseases, such as thoracic aortic disease, coronary artery disease, stroke, Moyamoya disease, and multisystemic smooth muscle dysfunction syndrome.[5]
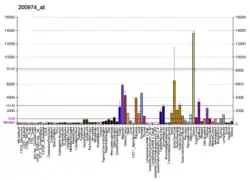
ACTA2 (commonly referred to as alpha-smooth muscle actin or α-SMA) is often used as a marker of myofibroblast formation.[7] Studies have shown that ACTA2 is associated with TGF-β pathway that enhances contractile properties of hepatic stellate cells leading to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.[8]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000107796 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000035783 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: ACTA2 actin, alpha 2, smooth muscle, aorta".
- Ueyama H, Bruns G, Kanda N (June 1990). "Assignment of the vascular smooth muscle actin gene ACTSA to human chromosome 10". Jinrui Idengaku Zasshi. The Japanese Journal of Human Genetics. 35 (2): 145–50. doi:10.1007/BF01876459. PMID 2398629.
- Nagamoto T, Eguchi G, Beebe DC (April 2000). "Alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in cultured lens epithelial cells". Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 41 (5): 1122–9. PMID 10752950.
- Hassan, Sobia; Shah, Hussain; Shawana, Summayya (2020). "Dysregulated epidermal growth factor and tumor growth factor-beta receptor signaling through GFAP-ACTA2 protein interaction in liver fibrosis". Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences. 36 (4): 782–787. doi:10.12669/pjms.36.4.1845. PMC 7260937. PMID 32494274.
Further reading
- Snásel J, Pichová I (1997). "The cleavage of host cell proteins by HIV-1 protease". Folia Biologica. 42 (5): 227–30. doi:10.1007/BF02818986. PMID 8997639. S2CID 7617882.
- Adams LD, Tomasselli AG, Robbins P, Moss B, Heinrikson RL (February 1992). "HIV-1 protease cleaves actin during acute infection of human T-lymphocytes". AIDS Research and Human Retroviruses. 8 (2): 291–5. doi:10.1089/aid.1992.8.291. PMID 1540415.
- Harris DE, Warshaw DM, Periasamy M (March 1992). "Nucleotide sequences of the rabbit alpha-smooth-muscle and beta-non-muscle actin mRNAs". Gene. 112 (2): 265–6. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(92)90388-6. PMID 1555776.
- Tomasselli AG, Hui JO, Adams L, Chosay J, Lowery D, Greenberg B, Yem A, Deibel MR, Zürcher-Neely H, Heinrikson RL (August 1991). "Actin, troponin C, Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein and pro-interleukin 1 beta as substrates of the protease from human immunodeficiency virus". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 266 (22): 14548–53. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)98721-1. PMID 1907279.
- Jahoda CA, Reynolds AJ, Chaponnier C, Forester JC, Gabbiani G (July 1991). "Smooth muscle alpha-actin is a marker for hair follicle dermis in vivo and in vitro". Journal of Cell Science. 99 ( Pt 3) (3): 627–36. doi:10.1242/jcs.99.3.627. PMID 1939373.
- Ueyama H, Ohsugi R (March 1990). "TaqI polymorphism in the 3' flanking region of the human aortic smooth muscle actin gene". Nucleic Acids Research. 18 (5): 1318. doi:10.1093/nar/18.5.1318. PMC 330483. PMID 1969628.
- Shoeman RL, Kesselmier C, Mothes E, Höner B, Traub P (January 1991). "Non-viral cellular substrates for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease". FEBS Letters. 278 (2): 199–203. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(91)80116-K. PMID 1991513. S2CID 37002682.
- Nakano Y, Nishihara T, Sasayama S, Miwa T, Kamada S, Kakunaga T (March 1991). "Transcriptional regulatory elements in the 5' upstream and first intron regions of the human smooth muscle (aortic type) alpha-actin-encoding gene". Gene. 99 (2): 285–9. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(91)90140-7. PMID 2022339.
- Reddy S, Ozgur K, Lu M, Chang W, Mohan SR, Kumar CC, Ruley HE (January 1990). "Structure of the human smooth muscle alpha-actin gene. Analysis of a cDNA and 5' upstream region". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 265 (3): 1683–7. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)40070-7. PMID 2295650.
- Kamada S, Nakano Y, Kakunaga T (December 1989). "Structure of 3'-downstream segment of the human smooth muscle (aortic-type) alpha-actin-encoding gene and isolation of the specific DNA probe". Gene. 84 (2): 455–62. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(89)90520-9. PMID 2612915.
- Kamada S, Kakunaga T (February 1989). "The nucleotide sequence of a human smooth muscle alpha-actin (aortic type) cDNA". Nucleic Acids Research. 17 (4): 1767. doi:10.1093/nar/17.4.1767. PMC 331843. PMID 2701935.
- Kedes L, Ng SY, Lin CS, Gunning P, Eddy R, Shows T, Leavitt J (1986). "The human beta-actin multigene family". Transactions of the Association of American Physicians. 98: 42–6. PMID 3842206.
- Ueyama H, Hamada H, Battula N, Kakunaga T (June 1984). "Structure of a human smooth muscle actin gene (aortic type) with a unique intron site". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 4 (6): 1073–8. doi:10.1128/MCB.4.6.1073. PMC 368875. PMID 6330528.
- Strauch AR, Rubenstein PA (June 1984). "A vascular smooth muscle alpha-isoactin biosynthetic intermediate in BC3H1 cells. Identification of acetylcysteine at the NH2 terminus". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 259 (11): 7224–9. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)39861-7. PMID 6725286.
- Ueyama H, Inazawa J, Ariyama T, Nishino H, Ochiai Y, Ohkubo I, Miwa T (March 1995). "Reexamination of chromosomal loci of human muscle actin genes by fluorescence in situ hybridization". The Japanese Journal of Human Genetics. 40 (1): 145–8. doi:10.1007/BF01874078. PMID 7780165.
- Arora PD, McCulloch CA (April 1994). "Dependence of collagen remodelling on alpha-smooth muscle actin expression by fibroblasts". Journal of Cellular Physiology. 159 (1): 161–75. doi:10.1002/jcp.1041590120. PMID 8138584. S2CID 84214215.
- Iwata Y, Pan Y, Yoshida T, Hanada H, Shigekawa M (February 1998). "Alpha1-syntrophin has distinct binding sites for actin and calmodulin". FEBS Letters. 423 (2): 173–7. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00085-4. PMID 9512352. S2CID 26209999.
- Comer KA, Dennis PA, Armstrong L, Catino JJ, Kastan MB, Kumar CC (March 1998). "Human smooth muscle alpha-actin gene is a transcriptional target of the p53 tumor suppressor protein". Oncogene. 16 (10): 1299–308. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201645. PMID 9546431.
External links
- GeneReviews/NIH/NCBI/UW entry on Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms and Aortic Dissections
- Human ACTA2 genome location and ACTA2 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.