Belarusian Arabic alphabet
The Belarusian Arabic alphabet (Belarusian: Беларускі арабскі алфавіт, Biełaruski arabski ałfavit) or Belarusian Arabitsa (بَلاروُسقایا ارابیࢯا, Беларуская Арабіца, Biełaruskaja Arabica)[1] was based on the Arabic script and was developed in the 16th century (possibly 15th). It consisted of twenty-eight graphemes, including several additions to represent Belarusian phonemes not found in the Arabic language.


The Belarusian Arabic alphabet was used by the Lipka Tatars, who had been invited to settle in Belarusian territory, at the time part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. During the 14th–16th centuries they gradually stopped using their own language and started using the Old Belarusian language rendered in the Belarusian Arabic alphabet. Books of that literary tradition are known in Belarusian as Kitab (Belarusian: "Кітаб"), which is Arabic for written material.

Some Polish texts were also written in the Arabic script in the 17th century or later.[2]
Additional graphemes
- For the sounds /ʒ/ (ж), /t͡ʃ/ (ч) and /p/ (п), which are absent from the Arabic language, the following Persian graphemes were used:
- For denoting the soft /d͡zʲ/ (дзь) and /t͡s/ (ц) sounds, the following newly constructed graphemes were used:
- These graphemes were used during the 16th–20th centuries to write Belarusian and Polish.[2]
- و
Equivalence chart
Vowels
 Vowels A and E (initial اَ)
Vowels A and E (initial اَ) Vowels I and Y (initial اِ)
Vowels I and Y (initial اِ) Vowels U and O (initial اُ)
Vowels U and O (initial اُ)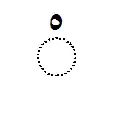 No vowel
No vowel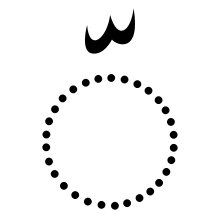 Consonant gemination
Consonant gemination
/a/ is consistently written long (that is, with a mater lectionis), while /e/ is consistently written short.
/o/ is most commonly written long.[3]
Consonants
| Cyrillic | Latin | Arabic | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contextual forms | Isolated | ||||
| Final | Medial | Initial | |||
| Б б | B b | ـب | ـبـ | بـ | ب |
| В в | V v | ـو | و | ||
| Г г | H h | ـه | ـهـ | هـ | ه |
| Ґ ґ | G g | ـغ | ـغـ | غـ | غ |
| Д д | D d | ـد | د | ||
| Дж дж | Dž dž | ـج | ـجـ | جـ | ج |
| Дзь дзь | Dź dź | ـࢮ | ࢮ ( | ||
| Ж ж | Ž ž | ـژ | ژ | ||
| З з | Z z | ـض | ـضـ | ضـ | ض |
| Зь зь | Ź ź | ـز | ز | ||
| Й й | J j | ـى | ـىـ | ىـ | ى |
| К к | K k | ـق | ـقـ | قـ | ق |
| Кь кь | Kj kj | ـك | ـكـ | كـ | ك |
| Л л, Ль ль | Ł ł, L l | ـل | ـلـ | لـ | ل |
| М м | M m | ـم | ـمـ | مـ | م |
| Н н, Нь нь | N n, Ń ń | ـن | ـنـ | نـ | ن |
| П п | P p | ـپ | ـپـ | پـ | پ |
| Р р | R r | ـر | ر | ||
| С с | S s | ـص | ـصـ | صـ | ص |
| Сь сь | Ś ś | ـث | ـثـ | ثـ | ث |
| Т т | T t | ـط | ـطـ | طـ | ط |
| Ў ў | Ŭ ŭ | ـو | و | ||
| Ф ф | F f | ـف | ـفـ | فـ | ف |
| Х х | Ch ch | ـح | ـحـ | حـ | ح |
| Ц ц | C c | ـࢯ | ـࢯـ | ࢯـ | ࢯ ( |
| Ць ць | Ć ć | ـت | ـتـ | تـ | ت |
| Ч ч | Č č | ـچ | ـچـ | چـ | چ |
| Ш ш | Š š | ـش | ـشـ | شـ | ش |
| ’ | — | — | ـعـ | — | — |
| ь | — | — | |||
Ligature
| Cyrillic | Latin | Arabic | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contextual forms | Isolated | ||||
| Final | Medial | Initial | |||
| Ла ла, Ля ля | Ła ła, La la | ـلا | لا | ||
See also
- Belarusian Latin alphabet
- Arebica – modified Arabic script used for Serbo-Croatian
References
- Maxime Seveleu-Dubrovnik, The Belarusian Arabic alphabet initiative at the FIAS. https://arabica.fias.fr/pages/origin-en(Archive)
- Ilya Yevlampiev, Karl Pentzlin and Nurlan Joomagueldinov, N4072 Revised Proposal to encode Arabic characters used for Bashkir, Belarusian, Crimean Tatar, and Tatar languages, ISO/IEC JTC1/SC2/WG2, 20 May 2011.
- "Антон Антановіч. Беларускія тэксты, пісаныя арабскім пісьмом". knihi.com (in Belarusian). Retrieved 2022-05-27.
Further reading
- Akiner, Shirin. Religious Language of a Belarusian Tatar Kitab: A Cultural Monument of Islam in Europe. Otto Harrassowitz, 2009.
- Д-р Я. Станкевіч. Беларускія мусульмане і беларуская літаратура арабскім пісьмом. [Адбітка з гадавіка Беларускага Навуковага Таварыства, кн. I.] – Вільня : Друкарня Я. Левіна, 1933 ; Менск : Беларускае коопэрацыйна-выдавецкае таварыства ″Адраджэньне″, 1991 [факсімільн.]. – 3-е выд.
- Антон Антановіч, "Беларускія тэксты, пісаныя арабскім пісьмом"
External links
 Media related to Belarusian Arabic alphabet at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Belarusian Arabic alphabet at Wikimedia Commons- Kitabs, the unique highlight of the Belarusian language at pravapis.org