Buxar district
Buxar district is one of the 38 districts of Bihar, India. Located in the southwestern part of the state, it is a primarily agricultural district. The district headquarters is at the town of Buxar.
Buxar district
𑂥𑂍𑂮𑂩 | |
|---|---|
 Paddy fields near Buxar | |
 Location of Buxar district in Bihar | |
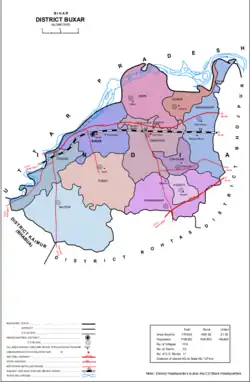 Map divisions of Buxar district | |
| Coordinates (Buxar): 25°33′53″N 83°58′40″E | |
| Country | |
| State | Bihar |
| Division | Patna |
| Established | 1992 |
| Headquarters | Buxar |
| Blocks | Block List (11)
|
| Government | |
| • Member of Parliament | Ashwini Kumar Choubey |
| • District Magistrate | Aman Samir (IAS) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,624 km2 (627 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 1,706,352 |
| • Density | 1,100/km2 (2,700/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 164,499 |
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (IST) |
| Vehicle registration | BR-44 |
| Major Highways | NH-84 |
| Website | buxar |
Etymology
According to local traditions, the name Buxar is derived from a lake in the town named Aghsar (effacer of Sin), which in course of time became Baghsar and took the present form that is Buxar. Another Vedic legend states that, a sage or rishi named Besira transformed himself to take the look of a Tiger to frighten Durvasa rishi, and doomed by him to retain the form of Tiger forever. In order to restore his human form, Bedsira bathed in the holy pond of Aghsar and worshipped Garushankar. To commemorate this event the spot was called Vyaghrasar and later became Baghsar (The Tiger's pond).[1]
History
The Battle of Buxar and Battle of Chausa were fought in this district.[2][3][4]
The present district was created on 17 March 1991, when it was split off from Bhojpur district.[5]
Geography
Buxar district is located in the southwestern part of the state of Bihar, bordered by Rohtas and Kaimur districts to the south, and by Bhojpur district to the east. To the north and west, respectively, the Ganges and Karmanasa Rivers form the boundary with the state of Uttar Pradesh.[5] In Uttar Pradesh, the district of Ballia is to the north and west of Buxar and that of Ghazipur lies to the west.)[6]
Buxar district covers an area of 1,703 km2, roughly 1.8% of the total area of Bihar, making it the 30th largest district in the state by area. Much of the district consists of an alluvial plain, gently sloping downward toward the northeast, with a height ranging from 71m above sea level in the south to 66m in the north. The soil consists of ultisols, ochrepts, orthents, fluvents, and psamments.[5]
The district formerly had large areas of forest cover, but deforestation caused by clearing land for agriculture has significantly reduced its area. This has also caused wildlife in the area to dramatically decline in numbers. Common trees in the forests of Buxar district are mango, seasum, mahua, and bamboo. Their main human use is as firewood. Additionally, long jhalas grass grows near the Ganges and is used to make roofs for kuccha houses.[5]
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1901 | 391,371 | — |
| 1911 | 371,963 | −0.51% |
| 1921 | 362,231 | −0.26% |
| 1931 | 398,022 | +0.95% |
| 1941 | 464,919 | +1.57% |
| 1951 | 536,754 | +1.45% |
| 1961 | 635,988 | +1.71% |
| 1971 | 765,094 | +1.87% |
| 1981 | 916,886 | +1.83% |
| 1991 | 1,087,676 | +1.72% |
| 2001 | 1,402,396 | +2.57% |
| 2011 | 1,706,352 | +1.98% |
| source:[7] | ||
According to the 2011 census, Buxar district has a population of 1,706,352[9] (roughly equal to the nation of The Gambia[10] or the US state of Nebraska[11]). This gives it a ranking of 285th in India (out of a total of 640).[9] With 1.6% of the total population of Bihar, Buxar district is ranked 29th in the state by population.[5] The district has a population density of 1,003 inhabitants per square kilometre (2,600/sq mi) .[9] Its population growth rate over the decade 2001-2011 was 21.67%.[9] Buxar has a sex ratio of 922 females for every 1,000 males,[9] and a literacy rate of 70.14%. 9.64% of the population lives in urban areas. Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes make up 14.75% and 1.57% of the population respectively.[9]
Mythology
It is said that Ahilya, the wife of Gautam Rishi restored her human body from that of stone and got salvation by a mere touch of the feet of Lord Rama. This place is now known as Ahirauli, and is situated six kilometers away from Buxar. The Kanwaldah Pokhara, also known as VyaghraSar, is today a tourist destination. It is in this district that sage Vishwamitra's Hermitage was situated. Chaitra Van, the forest where demoness Tadaka lived and was killed by Shri Ram, is also situated in Buxar.[13]
Politics
| District | No. | Constituency | Name | Party | Alliance | Remarks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buxar | 199 | Brahampur | Shambhu Nath Yadav | RJD | MGB | |||
| 200 | Buxar | Sanjay Kumar Tiwari | INC | MGB | ||||
| 201 | Dumraon | Ajit Kumar Singh | CPI(ML)L | MGB | ||||
| 202 | Rajpur | Vishwanath Ram | INC | MGB | ||||
Divisions
Buxar district is divided 11 community development blocks, grouped together into 2 subdivisions based at Buxar and Dumraon.[6]
- Buxar subdivision
- Dumraon subdivision
Of these, the most populous is Buxar and the least populous is Kesath.[5]
There are 1,133 villages and 142 gram panchayats in Buxar district.[5]
The district contains the following towns:[5]
| Town name | Block | Class | Population (in 2011) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buxar | Buxar | Nagar parishad | 102,861 |
| Dumraon | Dumraon | Nagar parishad | 53,618 |
| Sarimpur | Buxar | Census town | 8,020 |
Economy
Buxar district is mainly agricultural. Major crops include rice (especially winter rice), wheat, barley, and pulses, the most important of which is gram. Arhar, khesari, and masur are other pulses grown in Buxar. Other important crops include oil seed and sugar cane.[5]
Industry and commerce are mainly concentrated in the cities of Buxar and Dumraon, which both have soap and furniture manufacturers as well as the main wholesale markets in the district.[6]
Notable people
- Bismillah Khan (Bharat Ratna)
- Gupteshwar Pandey (IPS)
- Ananda Prasad
- Harihar Singh, Former Chief Minister of Bihar and Bhojpuri Poet
- Lallan Prasad Singh (IAS)
- Ravindra Kishore Sinha
- Vimlanand Saraswati
- Hemant (DSP)
See also
References
- Bihar And Orissa Gazetteers Shahabad. p. 163. ISBN 8172681224.
- "Battle of Buxar : Venue, Date, Reasons, Winner, Loser, Aftermath, Significance". www.mapsofindia.com. Retrieved 22 January 2018.
- "Battle of Buxar | Summary". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 22 January 2018.
- "The new battles of Buxar". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 27 October 2015. Retrieved 22 January 2018.
- "Census of India 2011: Bihar District Census Handbook - Buxar, Part A (Village and Town Directory)". Census 2011 India. pp. 19–20, 23–98, 681–82, 730–746. Retrieved 3 July 2020.
- "About District/". Buxar. National Informatics Centre. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- "Table A-02 Decadal Variation in Population Since 1901: Bihar" (PDF). census.gov.in. Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India.
- "Population by Religious Community – 2011". Census of India, 2011. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India.
- "District Census Handbook: Buxar" (PDF). Census of India. Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India. 2011.
- US Directorate of Intelligence. "Country Comparison:Population". Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 1 October 2011.
Gambia, The 1,797,860 July 2011 est.
- "2010 Resident Population Data". U. S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 30 September 2011.
Nebraska 1,826,341
- "Table C-16 Population by Mother Tongue: Bihar". censusindia.gov.in. Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India. 2011.
- ""Buxar history"". Archived from the original on 23 February 2012. Retrieved 14 November 2009.