Chandpur District
Chandpur District (চাঁদপুর) is a district located in Chattogram Division, Bangladesh.[3] It was a part of the Comilla District until 15 February 1984.[4]
Chandpur District
চাঁদপুর জেলা | |
|---|---|
     Clockwise from top-left: Aerial view of Chandpur bridge, Rupsha Zamindar Bari, Chandpur Port, Lohagor Math, Meghna River, Hajiganj Boro Masjid | |
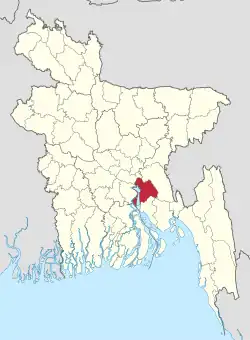 Location of Chandpur District within Bangladesh | |
Expandable map of Chandpur District | |
| Coordinates: 23.2139°N 90.6361°E | |
| Country | |
| Division | Chittagong Division |
| Formed (Mahkuma) | 1878 |
| Formed (City) | 1894 |
| Established as District | 15 February 1984 (split from Comilla) |
| Parliamentary seat | 5 |
| Government | |
| • Deputy Commissioner | Kamrul Hasan |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,704.06 km2 (657.94 sq mi) |
| Population (2022 census)[1] | |
| • Total | 2,635,748 |
| • Density | 1,500/km2 (4,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+06:00 (BST) |
| ISO 3166-2 | BD-09 |
| HDI (2018) | 0.614[2] medium · 7th of 21 |
| Calling code | 0841 |
| Website | www |
History
During the ruling of the Baro-Bhuiyans, this region was occupied by Chand Ray, the Zamindar of Bikrampur and son of Kedar Ray. According to historian J. M. Sengupta, the region was named Chandpur, following the name of Chand Ray. On the other hand, others say that the name of this region comes from Chand Faqir of Purindapur mahalla of Chandpur, Bangladesh. It is said that an administrator named Shah Ahmed Chand came here from Delhi in the fifteenth century and established a river port.
In 1779 AD, Major James Rennel, a British surveyor, drew a map of Bengal during the British rule and included an obscure town called Chandpur. At that time, there were offices and courts at a place called Narsinghpur (which has now sunk) south of Chandpur. The confluence of the Padma and the Meghna was about 60 miles south-west of the present place. This area has now disappeared due to the game of breaking the Meghna river.
The first Chandpur subdivision was formed in 1878 as a result of administrative reorganization during the British rule. On 1 October 1896, Chandpur city was declared as a municipality. It was declared as Chandpur district on 15 February 1984.[5]
Geography
The Geological formation of Chandpur was taken place in Pleistocene and Holocene Era. Geographical history of Chandpur was found in the East-Indian country-map of Perguitar. In the map, south to Bangladesh, Sagornooper, to the north Pragjyotish and the Eastern plain beside hills was known as ‘Kiratas.’ The then Red River (Brammhaputra of today) borne alluvial soil contributed the formation of ‘Kiratas’ and Comilla was under it. That is Chandpur was under ‘Kiratas.’ In the map of Tomas Water, a land named ‘Srikhetra’ was shown to the south of the combined course of both the Titas and Gomati (probably). It is guessed that Chandpur and the west part of Noakhali were under ‘Srikhetra.’ In the map of Jean de Brosse in 1560, ‘Tropo’ was shown by river banks. This ‘Tropo’ was actually Tripura or Comilla region. That is, Chandpur was a part of Tripura. In the map of Portuguese sailor Sanson de Abevil in 1652, Bander, a place was marked where there was a big river port. This port was actually Chandpur. In 1779, English surveyor Major James Rennel drew a map where not only Tripura, but also Chandpur and Comilla were rightly spotted.[6]
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1974 | 1,543,183 | — |
| 1981 | 1,796,777 | +2.20% |
| 1991 | 2,032,449 | +1.24% |
| 2001 | 2,271,229 | +1.12% |
| 2011 | 2,416,018 | +0.62% |
| 2022 | 2,635,748 | +0.79% |
| Sources:[1][7] | ||
According to the 2022 Census of Bangladesh, Chandpur District had 635,458 households and a population of 2,635,748, 26.2% of whom lived in urban areas. The population density was 1,602 people per km2. The literacy rate (age 7 and over) was 78.1%, compared to the national average of 74.7%.[1]
| Religion | Population (1941)[8]: 102–103 | Percentage (1941) | Population (2011)[7] | Percentage (2011) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Islam |
855,937 | 79.99% | 2,269,246 | 93.93% |
| Hinduism |
213,022 | 19.91% | 145,551 | 6.02% |
| Others [lower-alpha 2] | 1,069 | 0.10% | 1,221 | 0.05% |
| Total Population | 1,070,028 | 100% | 2,416,018 | 100% |
Muslims make up 93.93% of the population, while Hindus are 6.02% of the population. The Hindu population has decreased from 1981.[7]
Administrative subdivisions
Education
- Chandpur Science & Technology University
- Chandpur Government College
- Chandpur Polytechnic Institute
- Chandpur Medical College
- Hasan Ali Government High School
- Al-AMIN Academy School And College
- Matlabganj J. B. Pilot High School
- Sojatpur Degree College
- Nandalalpur Samadia High School
Notable residents
- Mohammad Abdullah, politician and academic
- Wahiduddin Ahmed, academic
- Shamsul Alam, State Minister of Planning
- Abul Kalam Azad, businessman, got his start trading coconuts from village to village in the district when he was a child.[13]
- Kabir Bakul, lyricist and journalist
- Amena Begum, a former Member of Parliament of East Pakistan
- Nurjahan Begum, the first female journalist in Bangladesh
- Abidur Reza Chowdhury (1872–1961), politician and educationist
- Mizanur Rahman Chowdhury, former Prime Minister
- Humayun Kabir Dhali, author and journalist
- Dildar, actor
- Sabnam Faria, film and drama actress and model
- G. M. Fazlul Haque, politician
- Mohammad Anwar Hossain, army officer
- Neamat Imam, author
- Monirul Islam, artist
- Burhanuddin Khan Jahangir, academic and writer
- Mahmudul Hasan Joy, cricketer
- Shantanu Kaiser, poet and essayist
- Janab Ali Majumdar, Bengali politician
- Abu Naser Muhammad Ehsanul Haque Milan, politician
- Dipu Moni, Education Minister
- Mohammad Nasiruddin, journalist
- Tania Sultana Popy, actress
- Rezaul Karim Reza, footballer
- Nurul Amin Ruhul, also known as Ruhul Bhai, politician
- Shykh Seraj, journalist, media personality and agriculture development activist
- Farida Zaman, artist and illustrator
See also
Notes
- Chandpur subdivision of Tippera district
- Including Jainism, Christianity, Buddhism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Ad-Dharmis, or not stated
References
- Population and Housing Census 2022: Preliminary Report. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics. August 2022. pp. viii, 29, 38, 45. ISBN 978-984-35-2977-0.
- "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2020-03-18.
- Khan, Abul Khaer (2012). "Chandpur District". In Sirajul Islam; Miah, Sajahan; Khanam, Mahfuza; Ahmed, Sabbir (eds.). Banglapedia: the National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh (Online ed.). Dhaka, Bangladesh: Banglapedia Trust, Asiatic Society of Bangladesh. ISBN 984-32-0576-6. OCLC 52727562. OL 30677644M. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- Musa, Muhammad. Brahmanbariar Itibrittyo, Shetu Prokashoni, Brahmanbaria,1998.
- "Naming of Chandpur". chandpur.gov.bd. Retrieved 30 October 2020.
- "Chandpur Geological Structure". chandpur.gov.bd. Retrieved 31 October 2020.
- "Bangladesh Population and Housing Census 2011 Zila Report – Chandpur" (PDF). bbs.gov.bd. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
- "Census of India, 1941 Volume VI Bengal Province" (PDF).
- "Home". Matripith Government Girls' High School. Archived from the original on 16 November 2015.
- "Matripith Govt. Girls High School - Sohopathi | সহপাঠী". 4 May 2018.
- "搞淫五月天伊人,2021天天操,天天干,天天射,天天操Bb,精品人人视屏".
- "Home". aaac.comillaboard.gov.bd.
- Ahmed, Jashim Uddin; Shimul, Anwar Sadat; Hossain, Shahid (January 2017). "Azad Products (Pvt.) Ltd: The Challenges Ahead". Business Perspectives and Research. 5 (1): 102. doi:10.1177/2278533716671634.