Pico de Orizaba
Pico de Orizaba, also known as Citlaltépetl (from Nahuatl citlal(in) = star, and tepētl = mountain), is an active stratovolcano, the highest mountain in Mexico[1] and the third highest in North America, after Denali of Alaska in the United States and Mount Logan of Canada. Pico de Orizaba is also the highest volcanic summit in North America. It rises 5,636 metres (18,491 ft) above sea level in the eastern end of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt, on the border between the states of Veracruz and Puebla.[1] The volcano is currently dormant but not extinct, with the last eruption taking place during the 19th century. It is the second most prominent volcanic peak in the world after Africa's Mount Kilimanjaro.
| Pico de Orizaba | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 5,636 m (18,491 ft)[1][2] |
| Prominence | 4,922 m (16,148 ft)[3] |
| Parent peak | Mount Logan[4] |
| Isolation | 2,690 km (1,670 mi) |
| Listing | |
| Coordinates | 19°01′48″N 97°16′12″W |
| Geography | |
 Pico de Orizaba Mexico | |
| Location | Veracruz, Mexico |
| Geology | |
| Mountain type | Stratovolcano |
| Volcanic arc/belt | Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt |
| Last eruption | 1846 |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | 1848 by F. Maynard & William F. Raynolds |
| Easiest route | moderate snow/ice climb |
Toponymy
Pico de Orizaba overlooks the valley and city of Orizaba, from which it gets its Spanish name. During the colonial era, the volcano was also known as Cerro de San Andrés due to the nearby settlement of San Andrés Chalchicomula at its base.
Its Náhuatl name, Citlaltépetl, comes from citlalli (star) and tepētl (mountain) and thus means "Star Mountain". This name is thought to be based on the fact that the snow-covered peak can be seen year round for hundreds of kilometers throughout the region. This name is not, however, used by Náhuatl speakers of the Orizaba area, who instead call it Istaktepetl (Iztactépetl in the traditional orthography for Classical Nahuatl), meaning 'White Mountain'.
A third name, Poyauhtecatl, which means "the one that colours or illuminates", has also been recorded. This name was given by the Tlaxcaltecs in memory of their lost country.[5]
Topography
The peak of Citlaltépetl rises dramatically to an elevation of 5,636 m (18,491 ft) above sea level; it has a topographic prominence of 4,922 m (16,148 ft). Regionally dominant, Pico de Orizaba is the highest peak in Mexico and the highest volcano in North America; it is also the third highest peak in North America after Denali and Mount Logan. Orizaba is ranked 7th in the world in topographic prominence. It is the second most prominent volcanic peak in the world after Africa's Mount Kilimanjaro, and the volcano is also ranked 16th in the world for topographic isolation. About 110 km (68 mi) to the west of the port of Veracruz, its peak is visible to ships approaching the port in the Gulf of Mexico, and at dawn rays of sunlight strike the Pico while Veracruz still lies in shadow. The topography of Pico de Orizaba is asymmetrical from the center of the crater; the eastern face is the steepest side of the volcano and the northwestern face the most gradual side. The gradual slopes of the northwestern face of the volcano allow for the presence of large glaciers and provide the most traveled route for hikers traveling to the summit.
Glaciers
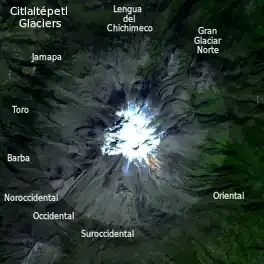
Pico de Orizaba is one of only three volcanoes in México that continue to support glaciers and is home to the largest glacier in Mexico, Gran Glaciar Norte. Orizaba has nine known glaciers: Gran Glaciar Norte, Lengua del Chichimeco, Jamapa, Toro, Glaciar de la Barba, Noroccidental, Occidental, Suroccidental, and Oriental. The equilibrium line altitude (ELA) is not known for Orizaba. Snow on the south and southeast sides of the volcano melts quickly because of solar radiation, but lower temperatures on the northwest and north sides allow for glaciers. The insolation angle and wind redeposition on the northwest and north sides allow for constant accumulation of snow providing a source for the outlet glaciers. On the north side of Orizaba, the Gran Glaciar Norte fills the elongated highland basin and is the source for seven outlet glaciers. The main glacier extends 3.5 km (2.2 mi) north of the crater rim, has a surface area of about 9.08 km2 (3.51 sq mi) descending from 5,650 m (18,540 ft) to about 5,000 m (16,000 ft). It has a slightly irregular and stepped profile that is caused in part by the configuration of the bedrock. Most crevasses show an ice thickness of approximately 50 m (160 ft).[6]

Below the 5,000 m (16,000 ft) in elevation on the north side of the volcano, the outlet glaciers Lengua del Chichimeco and Jamapa extend north and northwest another 1.5 km (0.93 mi) and 2 km (1.2 mi), respectively. The terminal lobe of Lengua del Chichimeco at 4,740 m (15,550 ft), having a gradient of only 140 m/km (740 ft/mi), is a low, broad ice fan that has a convex-upward profile, a front typical of almost all Mexican glaciers. The most distinct glacier is Glaciar de Jamapa, which leaves Gran Glaciar Norte at about 4,975 m (16,322 ft) and, after 2 km (1.2 mi) with a gradient of 145 m/km (770 ft/mi), divides into two small tongues that end at 4,650 m (15,260 ft) and 4,640 m (15,220 ft). Both tongues terminate in broad convex-upward ice fans thinning along their edges. The retreat of these tongues prior to 1994 produced much erosion downstream and buried their edges by ablation rock debris.[6]
The west side of Gran Glaciar Norte generates five outlet glaciers. From north to south, the first two, Glaciar del Toro and Glaciar de la Barba, are hanging cliff or icefall glaciers, reaching the tops of giant lava steps at 4,930 m (16,170 ft) and 5,090 m (16,700 ft), respectively. They then descend 200 to 300 m (660 to 980 ft) farther down into the heads of stream valleys as huge ice blocks but are not regenerated there. About 1 km (0.62 mi), Glaciar Noroccidental, a small outlet glacier 300 m (980 ft) long, drains away from the side of Gran Glaciar Norte at about 5,100 m (16,700 ft) and draws down the ice surface a few tens of meters over a distance of 500 m (1,600 ft), descending to 4,920 m (16,140 ft) with a gradient of 255 m/km (1,350 ft/mi). Another 1 km (0.62 mi) still farther south, Glaciar Occidental breaks away from Gran Glaciar Norte west of the summit crater at about 5,175 m (16,978 ft) as a steep, 1 km (0.62 mi) long glacier having a gradient of 270 m/km (1,400 ft/mi) that ends at 4,930 m (16,170 ft). From the southwest corner of the mountain, another outlet glacier, Glaciar Suroccidental, 1.6 km (0.99 mi) long, flows from Gran Glaciar Norte at 5,250 m (17,220 ft) with a gradient of 200 m/km (1,100 ft/mi), which also ends at 4,930 m (16,170 ft) in a long smooth surface.[6]
East of the summit cone, a separate steep niche glacier, Glaciar Oriental, 1.2 km (0.75 mi) long and having a gradient of 440 m/km (2,300 ft/mi), flows down the mountainside from about 5,600 to 5,070 m (18,370 to 16,630 ft); it contains many crevasses and seracs and is the most difficult glacier to climb. Glacier Oriental had a surface area of about 420,000 m2 (4,500,000 sq ft) in 1958, which makes the total area of glaciers and firn field on Citlaltépetl about 9.5 km2 (3.7 sq mi). No earlier historical record of glacier tongue activity (advance or recession) is known for Citlaltépetl's glaciers. Although the Gran Glaciar Norte ice cap is covered with snow, it is possible to see the seven outlet glaciers on the irregular west margin of the ice cap, especially Glaciar de Jamapa and Glaciar Occidental.[6]
Climate


The climate of Pico de Orizaba, like the Sierra Madre Oriental, varies greatly due to the change of elevation and prevailing winds. Due to the latitude and the extreme rugged terrain the volcano experiences many microclimates. Vegetation varies from tropical at the lower elevations on the eastern face to alpine forests in the higher elevations.
Large amounts of precipitation fall on the eastern face of the volcano due to adiabatic cooling and condensation from the trade winds that bring moisture off the Gulf of Mexico. The eastern face is frequently covered by fog and low cloud cover. The climate of the eastern face varies from tropical (Af) at the lower elevations to subtropical highland (Cwb) at the higher elevations, with mild variation in temperatures and an average annual rainfall of 1,600 mm (63 in).
Subtropical climates are found between 2,200 and 3,200 m (7,200 and 10,500 ft) above sea level with a regular rainfall all year long. Autumn and winter come with frequent freezes and light snow, but the snow on the south and southeast sides melt quickly due to solar radiation. The northern face is dominated by subtropical highland (Cwb). The southern face mostly experiences a humid subtropical climate, (Cwa) with the highest annual temperatures in the month of April.
Due to katabatic winds the western side is dominated by steppe (BSk) creating a rain shadow below 2,600 m (8,500 ft) above sea level. Although there are some areas on the western side that experience (Cfa) most of the area is semi-dry with temperate to warm temperatures and an annual precipitation average of 550 mm (22 in). Vegetation here is grass and shrubs with few alpine species.
Between 3,200 and 4,300 m (10,500 and 14,100 ft), where temperatures usually are between 2 and 5 °C (36 and 41 °F), continental subarctic climate (Dfc) predominates. Over 4,300 m (14,100 ft) with an annual average low of −2 °C (28 °F), alpine tundra (ET) prevails to the summit; heavy snowfalls and blizzards are common throughout the year. Snow on the south and southeast melts due to solar radiation, but continually remains on the north and northwestern faces. Extreme cold dominates a surface area of approximately 31 km2 (12 sq mi).
Geology
Pico de Orizaba evolved in three stages, the most recent initiated about 16,000 years ago during the late Pleistocene and Holocene. Citlaltépetl consists of three superimposed stratovolcanoes and dome intrusions: Torrecillas (650–250 ka), Espolón de Oro (210– 16 ka), and Citlaltépetl (16 ka to present). The volcano was formed by thick andesitic and dacitic lavas that followed repetitive explosive eruptions and lava effusions that created the iconic cone structure. The volcano is currently dormant but not extinct. The latest eruption of the volcano occurred in 1846 with a magnitude of VEI 2. Previous eruptions occurred in: 1687, 1613, 1589–1569, 1566, 1555–1545,1539–1533, 1351, 1260, 1187, 1175, 1157, 220 AD, 140 AD, 90 AD, 40 AD, ~780 BC, ~1500 BC, ~2110 BC, ~2300 BC, ~2500 BC, ~2780 BC, ~4690 BC, ~6220 BC, ~6710 BC, ~7030 BC, and ~7530 BC.[7] The most violent eruption in the volcano's history is thought to have occurred around 6710 BC, reaching a magnitude of VEI 5, characterized by lava dome extrusion and pyroclastic flow.
The volcano's crater is elliptical with a transverse diameter measuring 478 m (1,568 ft) and a conjugate diameter measuring 410 m (1,350 ft). The crater has an estimated 154,830 m2 (1,666,600 sq ft) with a maximum depth of 300 m (980 ft). Pico de Orizaba is constantly covered by an ice cap consisting of several glaciers. An outlet glacier, known as Jamapa Glacier, is located on the north-eastern side of the peak; it has been a powerful force in shaping the volcano. The Jamapa Glacier is responsible for a significant portion of the geomorphologic evolution of the region surrounding the volcano.[8]
Geography


Pico de Orizaba is located at 19°1′48″N 97°16′12″W, about 110 kilometres (68 mi) west of the Gulf of Mexico and 200 kilometres (120 mi) east of Mexico City, on the border between the states of Veracruz and Puebla. The volcano is approximately 480 kilometres (300 mi) south of the Tropic of Cancer. Orizaba anchors the south-eastern end of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt, a volcanic chain that runs from west to east across Central Mexico. A companion peak lying about six km to the southwest of Pico de Orizaba is the Sierra Negra, at 4,640 metres (15,223 ft). This subsidiary peak is significantly lower than its massive neighbour, but the road to the observatory on its summit is the highest road in North America.
Pico de Orizaba, as part of the Sierra Madre Oriental, forms a barrier between the coastal plains of the Gulf of Mexico and the Mexican Plateau. The volcano blocks the moisture from the Gulf of Mexico from saturating central Mexico and influences the climates of both areas. Both the state of Veracruz and Puebla depend on Pico de Orizaba for supplying fresh water. The largest river originating on the volcano is the Jamapa River.
History


Pico de Orizaba was important in pre-Hispanic cultures, such as those of the Nahuatl-speaking Aztecs and the Totonacs. The volcano is part of many native mythologies.
During the Spanish Conquest of Mexico, Hernán Cortés passed through the foothills of Pico de Orizaba; the volcano and the surrounding mountains made his journey to Tenochtitlan more difficult and delayed him for many days. During the 1600s, the Spanish Crown financed several roads to be built that would circumvent Citlaltépetl. One of the roads was routed south of the volcano through the cities of Orizaba and Fortín de las Flores, which became the main trade route between Mexico City and Veracruz on the Gulf Coast. A short road was later built by Jesuits to establish settlements at the base of Pico de Orizaba. The Spanish used the volcano as a landmark to guide themselves to the port of Veracruz. Many battles were fought near this volcano throughout Mexico's struggle for independence.
In 1839, Henri Galeotti was the first European to explore the volcano, but did not hike to the summit. During the American occupation of Mexico in 1848, two American soldiers, F. Maynard and William F. Raynolds, were the first known hikers to reach the summit of Pico de Orizaba.[9] In 1851, the French explorer Alejandro Doignon also reached the summit and found the flagpole left behind by the Americans in 1848. During the mid-19th century Citlaltépetl was explored by many scientists, including the German botanist Hugo Fink, who was the first to record the numerous species of flora found on the volcano. In 1873, Martin Tritschler raised the Mexican flag at the summit.
Pico de Orizaba National Park
On December 16, 1936, President Lázaro Cárdenas, in an effort to protect the natural beauty of Pico de Orizaba, created a national park with an area of 19,750 hectares (48,800 acres) that included the volcano with the surrounding area and the settlements of Tlachichuca, Ciudad Serdán, La Perla, Mariano Escobedo, and Calcahualco. The federal decree became federal law on January 4, 1937.
Climbing and recreation


Pico de Orizaba attracts a large number of international climbers every year. There are multiple routes for approaching and climbing the volcano, and many people attempt it. Most people climb the mountain during the period from October to March when the weather is favorable; temperatures do not vary much month to month due to being in the tropics and April through September are rainy months in the region. The most frequented route begins from the base camp Piedra Grande Hut ("refugio") via the Jamapa Glacier, located at an elevation of 4,270 m (14,010 ft) above sea level.
Another option as a starting point is high camp located at the base of the glacier about 4,900 m (16,100 ft) above sea level. For a more technical challenge for the experienced climber, there is a technical ice climb called the Serpents Head, which involves 10 pitches of grade 3 ice. Additionally, the southern side offers another challenging option; although the trail is shorter, it is also steeper and more difficult. No glaciers are found on the southern side. The final ascent to the summit is via a normally straightforward and crevasse-free glacier route. The caldera can be circumnavigated with relative ease, although at one point this requires a short, exposed traverse of steep rock and ice above the Glacier Este.
See also
Footnotes
- Brown, Stephen (2003). "Orizaba" (PDF). Sombrilla. University of Texas at San Antonio. p. 23. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 30, 2005.
- The elevation given by INEGI mapping is 5,611 m. Higher elevations are given by various other authorities (including 5,747 m by the National Geographic Society).
- "Mexico Ultras". See also Note #1. Peaklist.org. Retrieved 2012-10-20.
- "Pico de Orizaba". Peakbagger.com.
- Map of Cuauhtinchan 2 Vol 2. Keiko Yoneda. p 239
- White, Sidney E. (March 7, 2002). "Glaciers of North America: Glaciers of México" (PDF). U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved 2011-02-20.
- Simkin, T.; Siebert, L. (2002). "Pico de Orizaba". Global Volcanism Program. The Smithsonian Institution.
- Palacios, D.; Vázquez-Selem, L. (1996). "The Geomorphic Effects of the Retreat of Jamapa Glacier, Pico de Orizaba Volcano". Vol. 78. Scandinavian University Press. pp. 19–34. JSTOR 521132.
- Ortenburger, Leigh N.; Jackson, Reynold G. (November 1996). A climber's guide to the Teton Range. Mountaineers Books. p. 374. ISBN 0-89886-480-1.
References
- "Pico de Orizaba". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution.
- Yarza de la Torre, Esperanza (1971). Volcanes de México. Aguilar. pp. 237 pp. (in Spanish)
- Secor, R. J. (2001). Mexico's Volcanoes: A Climbing Guide (3rd ed.). Mountaineers Books. pp. 160 pp. ISBN 0-89886-798-3.

