Corey–Nicolaou macrolactonization
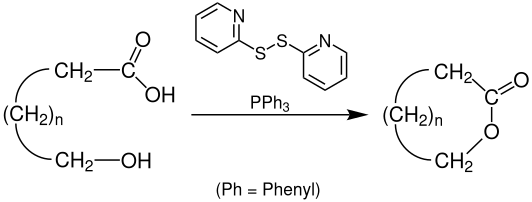
Corey–Nicolaou macrolactonization is a named reaction of organic chemistry, for the synthesis of lactones from hydroxy acids, found in 1974.[1][2] The reaction should take place in a polar aprotic solvent with mild conditions,[3] with the use of 2,2'-Dipyridyldisulfide and triphenylphosphine.
| Corey–Nicolaou macrolactonization | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Elias James Corey K. C. Nicolaou |
| Reaction type | Name reaction |
Mechanism
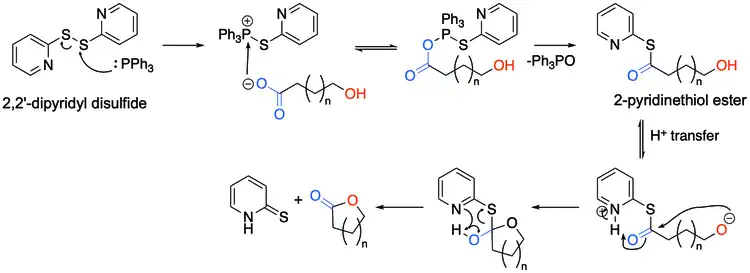
The hydroxy acid first reacts with the 2,2'-Dipyridyldisulfide to form the corresponding 2-pyridinethiol ester, and after a proton transfer, the alkoxide attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming a tetrahedral transition state, before resolving back to the desired lactone and 2-pyridinethione.[4][5]
References
- Corey, Elias James; Nicolaou, Kyriacos Costa (1974-08-01). "Efficient and mild lactonization method for the synthesis of macrolides". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 96 (17): 5614–5616. doi:10.1021/ja00824a073.
- Corey, Elias James; Nicolaou, Kyriacos Costa; Melvin, Lawrence S., Jr. (1975). "Synthesis of novel macrocyclic lactones in the prostaglandin and polyether antibiotic series". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 97 (3): 653–654. doi:10.1021/ja00836a036. PMID 1133366.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Meng, Qingchang; Hesse, Manfred (1992). "Ring-closure methods in the synthesis of macrocyclic natural products". Topics in Current Chemistry. 161: 107–176. doi:10.1007/3-540-54348-1_9. ISBN 978-3-540-54348-0.
- Corey, Elias James; Brunelle, Daniel J.; Stork, Philip J. (1976). "Mechanistic studies on the double activation method for the synthesis of macrocyclic lactones". Tetrahedron Letters. 17 (38): 3405–3408. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)93056-9.
- Behinpour, Kevian; Hopkins, Andrew; Williiams, Andrew (1981). "Macrolide ring closuke: "Double activation" mechanism". Tetrahedron Letters. 22 (4): 275–278. doi:10.1016/0040-4039(81)80074-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.