Histidine methyl ester
Histidine methyl ester (HME) is an irreversible histidine decarboxylase inhibitor.[1][2][3] It is the methyl ester of histidine.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Methyl L-histidinate, HME | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 957974 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.645 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H11N3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 169.184 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
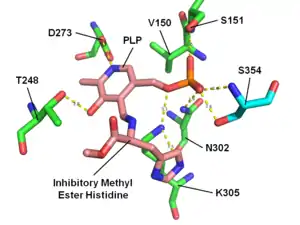
HME bound to histidine decarboxylase
References
- Lane, Roger S; Manning, James M; Snell, Esmond E (2002). "Histidine decarboxylase of lactobacillus 30a: inactivation and active-site labeling by L-histidine methyl ester". Biochemistry. 15 (19): 4180–5. doi:10.1021/bi00664a008. PMID 963031.
- Alston, Theodore A; Abeles, Robert H (2002). "Reaction of Lactobacillus histidine decarboxylase with L-histidine methyl ester". Biochemistry. 26 (13): 4082–5. doi:10.1021/bi00387a051. PMID 3651438.
- Komori, H; Nitta, Y; Ueno, H; Higuchi, Y (2012). "Structural Study Reveals That Ser-354 Determines Substrate Specificity on Human Histidine Decarboxylase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 287 (34): 29175–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.381897. PMC 3436558. PMID 22767596.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.