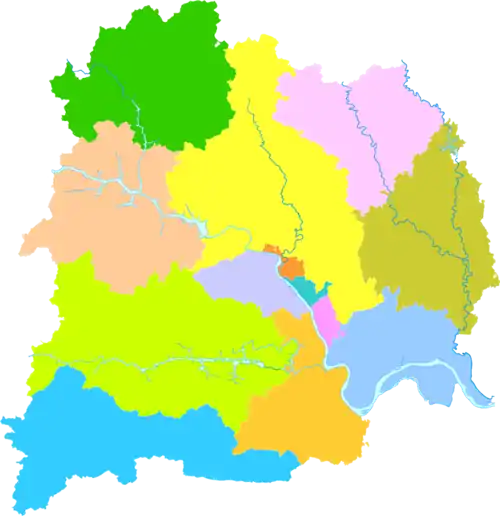
Yichang
Yichang (Chinese: 宜昌), alternatively romanized as Ichang, is a prefecture-level city located in western Hubei province, China. It is the third largest city in the province after the capital, Wuhan and the prefecture-level city Xiangyang, by urban population. The Three Gorges Dam is located within its administrative area, in Yiling District.[3]
Yichang
宜昌市 Ichang | |
|---|---|
Three Gorges Dam, Cool shrimp, Tribe of Three Gorges, Qingjiang Gallery, Sanyou Cave, Three Gorges Waterfall, Xiling Gorge. | |
 Location of Yichang City jurisdiction in Hubei | |
 Yichang Location of the city in Hubei  Yichang Location of the city in China | |
| Coordinates (Yichang municipal government): 30°41′31″N 111°17′13″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Hubei |
| Municipal seat | Xiling District |
| Government | |
| • CPC Party Secretary | Huang Chuping |
| • Mayor | Ma Xuming |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 21,338 km2 (8,239 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 4,234.3 km2 (1,634.9 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 4,192 km2 (1,619 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 58 m (191 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 2,427 m (7,963 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 35 m (115 ft) |
| Population (2020 census)[2] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 4,017,607 |
| • Density | 190/km2 (490/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,604,740 |
| • Urban density | 380/km2 (980/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,536,012 |
| • Metro density | 370/km2 (950/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal codes | 443000 |
| Area code | 0717 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HB-05 |
| Licence plate prefixes | 鄂E |
| Website | en |
| Yichang | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 "Yichang", as written in Chinese | |||||||||||
| Chinese | 宜昌 | ||||||||||
| Postal | Ichang | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
History
In ancient times Yichang was known as Yiling. Historical records indicate that in the year 278 BC, during the Warring States period, the Qin general Bai Qi set fire to Yiling. In 222 AD Yichang was also the site of the Battle of Yiling, during the Three Kingdoms Period.
Under the Qing Guangxu Emperor, Yichang was opened to foreign commerce as a trading port after the Qing and Great Britain agreed to the Chefoo Convention, which was signed by Sir Thomas Wade and Li Hongzhang in Chefoo on 21 August 1876. The imperial government set up a navigation company there and began building facilities. Since 1949, more than 50 wharves (with a total combined length of over 15 kilometers (9.3 mi)) have been constructed at the port.
During the Second Sino-Japanese War, Yichang was a primary supply depot for the defending Chinese army. In October 1938, as the Japanese moved up the Yangtze River towards the strategic city of Chongqing, it became clear that Yichang needed to be evacuated. In 40 days, under the direction of businessman Lu Zuofu, more than 100,000 tons of equipment and 30,000 personnel were transported upstream by steamship or by porters pulling smaller vessels through the Three Gorges rapids to Chongqing.[4][5]
In 1940, the Battle of Zaoyang-Yichang took place in the area.
Administrative divisions
Administratively, it is a prefecture-level city; its municipal government has jurisdiction over five counties, five urban districts, and three satellite county-level cities (Yidu, Dangyang, Zhijiang).[1][6][7]
- Xiling District (西陵区) - includes the city center
- Wujiagang District (伍家岗区) - southeastern parts of the urban area and suburbs
- Dianjun District (点军区) - the part of the urban area southwest of the Yangtze (across from the city center) and suburbs
- Xiaoting District (猇亭区)
- Yiling District (夷陵区) - northern part of the urban area and suburbs
- Zhijiang City (枝江市)
- Yidu City (宜都市)
- Dangyang City (当阳市)
- Yuan'an County (远安县)
- Xingshan County (兴山县)
- Zigui County (秭归县) - a county whose seat (Maoping) is some 50 kilometers (31 mi) west of downtown Yichang, next to the Three Gorges Dam
- Changyang Tujia Autonomous County (长阳土家族自治县)
- Wufeng Tujia Autonomous County (五峰土家族自治县)
Administrative map
The prefecture-level city of Yichang has direct jurisdiction over 14 divisions: 5 districts (区; qū), 3 county-level cities (县级市; xiànjí shì), 3 counties (县; xiàn), and 3 autonomous counties (自治县; zìzhì xiàn).:
| Map | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Hanzi | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2010 census) [8] |
Area (/km2) [9] |
Density (/km2) | |
| Districts | ||||||
| Xiling District | 西陵区 | Xīlíng Qū | 512,074 | 68.14 | 7,515.03 | |
| Wujiagang District | 伍家岗区 | Wǔjiāgǎng Qū | 214,194 | 84.03 | 2549.02 | |
| Dianjun District | 点军区 | Diǎnjūn Qū | 103,696 | 533.23 | 194.47 | |
| Xiaoting District | 猇亭区 | Xiāotíng Qū | 61,230 | 130.40 | 469.55 | |
| Yiling District | 夷陵区 | Yílíng Qū | 520,186 | 3,416.57 | 152.25 | |
| County-level cities | ||||||
| Yidu | 宜都市 | Yídū Shì | 384,598 | 1,354.83 | 283.87 | |
| Dangyang | 当阳市 | Dāngyáng Shì | 468,293 | 2,148.82 | 217.93 | |
| Zhijiang | 枝江市 | Zhījiāng Shì | 644,835 | 2,010.00 | 321 | |
| Counties | ||||||
| Yuan'an County | 远安县 | Yuǎn'ān Xiàn | 184,532 | 1,741.06 | 105.99 | |
| Xingshan County | 兴山县 | Xīngshān Xiàn | 231,536 | 480.20 | 73.69 | |
| Zigui County | 秭归县 | Zǐguī Xiàn | 367,107 | 2,273.80 | 161.45 | |
| Autonomous counties | ||||||
| Changyang Tujia Autonomous County |
长阳土家族自治县 | Chángyáng Tǔjiāzú Zìzhìxiàn |
388,228 | 3418.82 | 113.56 | |
| Wufeng Tujia Autonomous County |
五峰土家族自治县 | Wǔfēng Tǔjiāzú Zìzhìxiàn |
188,923 | 2,370.41 | 79.70 | |
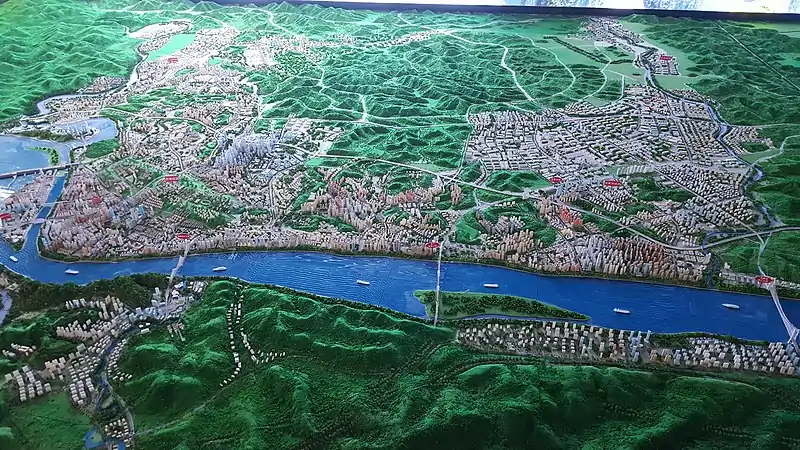
Geography
Like most prefecture-level cities, Yichang includes both an urban area (which is labeled on less detailed maps as "Yichang") and the surrounding country area. It covers 21,084 square kilometers (8,141 sq mi) in Western Hubei Province, on both sides of the Yangtze River. The Xiling Gorge, the easternmost of the Three Gorges on the Yangtze, is located within the prefecture-level city.
Within the prefecture-level city of Yichang, the Yangtze is joined by a number of tributaries, including the Qing River (right), Xiang Xi and Huangbo Rivers (left).
The central urban area of Yichang is split between several districts. On the right (northeastern) bank of the Yangtze are located Xiling District (where the city center is located), Yiling District (neighborhoods north of the center) and Wujiagang District (southern area). The city area on the opposite (southeastern) bank of the river is included into Dianjun District. All these districts, with the exception of the central Xiling, also include a fair amount of suburban/rural area outside of the city urban core.
Climate
Yichang has a four-season, monsoon-influenced, humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cwa), with cool, damp and generally overcast winters, and hot, humid summers. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from 5.0 °C (41.0 °F) in January to 27.7 °C (81.9 °F) in July, while the annual mean is 17.08 °C (62.7 °F). Close to 70% of the annual precipitation of 1,160 mm (46 in) occurs from May to September. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 24% in January to 49% in August, the city receives 1,568 hours of bright sunshine annually, and summer is the sunniest season.
| Climate data for Yichang (1991–2013 normals, extremes 1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.5 (72.5) |
27.6 (81.7) |
33.0 (91.4) |
36.7 (98.1) |
38.7 (101.7) |
39.9 (103.8) |
40.7 (105.3) |
41.4 (106.5) |
39.2 (102.6) |
35.7 (96.3) |
29.8 (85.6) |
24.6 (76.3) |
41.4 (106.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.8 (47.8) |
11.8 (53.2) |
16.6 (61.9) |
23.0 (73.4) |
27.3 (81.1) |
30.5 (86.9) |
32.7 (90.9) |
32.1 (89.8) |
28.2 (82.8) |
23.0 (73.4) |
17.2 (63.0) |
11.2 (52.2) |
21.9 (71.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.0 (41.0) |
7.6 (45.7) |
11.7 (53.1) |
17.7 (63.9) |
22.2 (72.0) |
25.8 (78.4) |
28.1 (82.6) |
27.4 (81.3) |
23.6 (74.5) |
18.3 (64.9) |
12.7 (54.9) |
7.3 (45.1) |
17.3 (63.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.2 (36.0) |
4.6 (40.3) |
8.1 (46.6) |
13.6 (56.5) |
18.2 (64.8) |
22.1 (71.8) |
24.5 (76.1) |
23.9 (75.0) |
20.1 (68.2) |
14.9 (58.8) |
9.5 (49.1) |
4.4 (39.9) |
13.8 (56.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −9.8 (14.4) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
0.4 (32.7) |
8.8 (47.8) |
14.7 (58.5) |
18.4 (65.1) |
17.2 (63.0) |
11.4 (52.5) |
3.7 (38.7) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
−5.4 (22.3) |
−9.8 (14.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 24.4 (0.96) |
38.7 (1.52) |
54.8 (2.16) |
92.3 (3.63) |
139.4 (5.49) |
141.8 (5.58) |
211.0 (8.31) |
191.3 (7.53) |
107.2 (4.22) |
73.8 (2.91) |
46.7 (1.84) |
18.7 (0.74) |
1,140.1 (44.89) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 7.7 | 9.2 | 11.0 | 12.5 | 13.3 | 12.6 | 14.7 | 13.7 | 10.5 | 10.4 | 8.3 | 7.7 | 131.6 |
| Average snowy days | 4.3 | 3.0 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 1.4 | 10 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74 | 73 | 72 | 73 | 73 | 76 | 79 | 78 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 73 | 75 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 65.9 | 71.9 | 103.1 | 125.8 | 132.8 | 134.1 | 157.2 | 168.4 | 126.8 | 118.6 | 103.8 | 81.1 | 1,389.5 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 20 | 23 | 28 | 32 | 31 | 32 | 37 | 41 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 26 | 31 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[10][11] | |||||||||||||
Transport
By Plane
Yichang Sanxia Airport is located in the Xiaoting District of Yichang City, 26 km (16 mi) away from the city center and 55 km (34 mi) from the Three Gorges Dam site. The airport is conveniently located, which borders Yihuang Highway in the north, Long River Golden Waterway in the south and Jiaozhi Railway in the east.
Roads and bridges

- China National Highway 318 runs east–west through most of the prefecture-level city, south of the center city
- China National Highway 209 passes through the northwestern corner of the prefecture-level city (Xingshan County)
Several provincial highways connect Yichang center city with most counties.
Several bridges span the Yangtze River within the prefecture-level city of Yichang, including (upstream to downstream):
- Xiling Bridge, connecting Letianxi and Sandouping in Yiling District, a few km downstream from the Three Gorges Dam.
- Yiling Bridge, downtown Yichang (a few km downstream from the Gezhouba Dam). It connects the urban Xiling and Dianjun Districts.
- Yichang Yangtze Highway Bridge, on the Hu-Rong Expressway, downstream of Yichang center city
- Yiwan Bridge: A Railway Bridge for Yiwan Railway which connects Yichang to Chongqing by high speed trains, almost 5 km (3.1 mi)downstream from the Yiling Bridge.
There are several ferry crossings as well.
Waterways

Yichang is an important river port on the Yangtze river. Maoping Town (the county seat of Zigui County), has an active passenger wharf as well.
The Qing River in the southern part of the prefecture, with its cascade of dams, is an important waterway as well.
Railway
Yichang is served by several railway lines.
Yichang Railway Station, located in downtown Yichang, opened in 1971, was the city's first railway station. In 2012 it closed for a renovation project.[12]
The Yichang East Railway Station, opened in the late 2010 in the eastern suburbs of Yichang,[13] is presently the city's main train station. It is the junction point of two segments of the Shanghai-Wuhan-Chengdu Passenger Dedicated Line, one of China's new east–west rail mainlines. To the east, the Hanyi Railway[14] (opened June 29, 2012) provides frequent service to Wuhan, with some trains continuing to Nanjing and Shanghai. To the west, the Yiwan Railway (Yichang-Wanzhou; opened December 2010) serves as the gateway to Hubei's southwestern panhandle (Enshi), with some service continuing to Chongqing and Chengdu.
The Jiaozuo–Liuzhou Railway, a north–south line, crosses the eastern part of the prefecture-level city. It crosses the Yangtze at Zhicheng in Yidu County-level City.
Demographics

As of the 2020 census, its population was 4,017,607 inhabitants of whom 1,536,012 lived in the built-up (or metro) area consisting of Yiling, Xiling, Wujiagang and Dianjun urban districts. The Xiaoting District has not yet been urbanized. Yichang prefecture-level city, is home to many members of the Tujia ethnic group, who mostly live in several counties in the south-west of the prefecture.
Yichang also formed the border between the cultures of Ba in the west (an ancient state in the eastern part of what is now Sichuan Province) and the Chu State in the east (an ancient state in what is now Hubei Province and northern Hunan Province).
Education
Since 2002, Yichang City has been home of the China Three Gorges University (the result of the merger of the University of Hydraulic & Electric Engineering, Yichang and of Hubei Sanxia University), the largest comprehensive university in Hubei Province outside Wuhan, with over 20,400 full-time students.
- China Three Gorges University
- Three Gorges Vocational College of Electric Power
There are 170 secondary schools in Yichang enrolling 150,700 students. 53,900 of the citizens in Yichang hold a secondary school degree. There are 282 elementary schools being located in Yichang enrolling 156,900. 27,600 of the citizens hold secondary school degrees. 383 kindergartens located in Yichang with 78,500 children.
Economy
Yichang has long been a major transit port and distribution center of goods, and serves as the economic hub of western Hubei province and an intermediary between the major cities of Chongqing and Wuhan. Its primary industries are shipping and shipbuilding, taking advantage of its location on the Yangtze River.
Yichang prefecture is the site of many major hydroelectricity projects. The best known of them are the two huge dams on the Yangtze River: the Gezhouba Dam (located just upstream of Yichang central city) and Three Gorges Dam, which is 40 kilometers (25 mi) upstream. The Geheyan Dam and Gaobazhou Dam on the Qing River are important as well. Besides those, a huge number of medium-sized and small power plants operate on smaller rivers and streams within the prefecture.
Picture gallery

 Wenfo mountain
Wenfo mountain Yangtze River
Yangtze River Qing River
Qing River Guanzhuang Reservoir
Guanzhuang Reservoir Huangbo River
Huangbo River Tribe of Three Gorges
Tribe of Three Gorges Three Gorges Waterfall
Three Gorges Waterfall Boats on the Yangtze River, upstream from the Three Gorges
Boats on the Yangtze River, upstream from the Three Gorges Christianity in Yichang
Christianity in Yichang Roman Catholic Diocese of Yichang
Roman Catholic Diocese of Yichang Yichang Yangtze River Railway Bridge
Yichang Yangtze River Railway Bridge Zhenjiang Pavilion
Zhenjiang Pavilion Tianran Pagoda
Tianran Pagoda Statue of Quyuan
Statue of Quyuan Three Gorges University
Three Gorges University Yiling High School
Yiling High School
References
- 宜昌市历史沿革 [Yichang City Historical Development] (in Simplified Chinese). XZQH. 14 July 2014. Retrieved 5 October 2018.
1996年,宜昌市面积21338平方千米,{...}2010年第六次人口普查,宜昌市常住总人口4059686人,其中:西陵区512074人,伍家岗区214194人,点军区103696人,猇亭区61230人,夷陵区520186人,远安县184532人,兴山县170630人,秭归县367107人,长阳土家族自治县388228人,五峰土家族自治县188923人,宜都市384598人,当阳市468293人,枝江市495995人。
- "China: Húbĕi (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map".
- "Yichang Information". Archived from the original on 2009-02-26. Retrieved 2009-12-06.
- 'Yichang Evacuation Monument'; http://easternjourney.com/2009/10/yichang-evacuation-monument/ retvd 12 7 17
- 抗战中的宜昌大撤退:保留中国抗战工业命脉的壮举. 15 April 2015.
- 2017年统计用区划代码和城乡划分代码:宜昌市 [2017 Statistical Area Numbers and Rural-Urban Area Numbers: Yichang City]. National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. 2017. Retrieved 5 October 2018.
统计用区划代码 名称 420501000000 市辖区 420502000000 西陵区 420503000000 伍家岗区 420504000000 点军区 420505000000 猇亭区 420506000000 夷陵区 420525000000 远安县 420526000000 兴山县 420527000000 秭归县 420528000000 长阳土家族自治县 420529000000 五峰土家族自治县 420581000000 宜都市 420582000000 当阳市 420583000000 枝江市
- 吴月, ed. (21 May 2018). 宜昌概况 [Description of Yichang] (in Simplified Chinese). Yichang People's Government. Retrieved 5 October 2018.
【行政区划】2016年,宜昌市辖13个县市区,即远安县、兴山县、秭归县、长阳土家族自治县、五峰土家族自治县、宜都市、枝江市、当阳市、夷陵区、西陵区、伍家岗区、点军区、猇亭区,共设20个乡、67个镇、23个街道。2016年,全市行政区划及其名称未作调整。
- 宜昌市2010年第六次全国人口普查主要数据公报 (in Simplified Chinese). Yichang Statistics Bureau. May 30, 2011. Retrieved 5 December 2013.
- 宜昌市土地利用总体规划(2006-2020年) (in Simplified Chinese). Yichang Bureau of Land Resources. Nov 18, 2013. Retrieved 5 December 2013.
- 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 11 June 2023.
- 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 May 2023.
- 3个月后宜昌火车站可进出动车 低站台改造成高站台. huochepiao.com. October 2012.
- "Yichang". Discover China. Retrieved 2020-01-25.
- Construction of Hanyi Railway to Kick off, Wuhan City Government web site, 2008-07-10
External links
- Official website of Yichang Government - English version Archived 2019-10-21 at the Wayback Machine