List of kings of Burgundy
The following is a list of the kings of the two kingdoms of Burgundy, and a number of related political entities devolving from Carolingian machinations over family relations.
Kings of the Burgundians
- Gebicca (late 4th century – c. 407)
- Gundomar I (c. 407 – 411), son of Gebicca
- Giselher (c. 407 – 411), son of Gebicca
- Gunther (c. 407 – 436), son of Gebicca
Flavius Aëtius moves the Burgundians into Sapaudia (Upper Rhône Basin).
- Gunderic/Gundioc (436–473) opposed by
- Chilperic I, brother of Gundioc (443–c. 480)
- division of the kingdom among the four sons of Gundioc:
- Gundobad (473–516 in Lyon, king of all of Burgundy from 480),
- Chilperic II (473–493 in Valence)
- Godomar I (473–486 in Vienna)
- Godegisel (473–500, in Vienne and Geneva)
- Sigismund, son of Gundobad (516–523)
- Godomar or Gundimar, son of Gundobad (523–534)
Burgundy under Frankish kings
Gradually conquered by the Frankish kings Childebert I and Chlothar I from 532–534
Merovingian kings
- Childebert I, 534–558 (central parts)
- Theudebert I, 534–548 (northern parts)
- Chlothar I, 534–561 (southern parts), eventually uniting the entire kingdom
- Guntram (561–592)
- Childebert II, 592–595
- Theuderic II, 595–613
United with Neustria under one king, but a separate administration (613–751)
Carolingian kings
- Pippin the Younger, 751–768
- Carloman, 768–771
- Charlemagne, 771–814
- Louis the Pious, 814–840
- Lothair I, 840–855, king under his father after 817
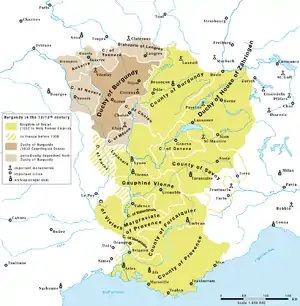
The sons of Louis the Pious divided the Frankish kingdom in the treaty of Verdun in 843. Burgundy was divided between the brothers.
- Charles the Bald received the smaller part, west of the river Saône. This entity was officially called regnum burgundiae (Kingdom of Burgundy), but since the King of France delegated administration to dukes, the territory became known as the Duchy of Burgundy.
- Lothair I received the larger part, east of the river Saône, which retained the name of Kingdom of Burgundy
After Lothair's death in 855, his realm was divided between his sons. The Burgundian territories were divided between:
- Lothair II, who received the north, and
- Charles of Provence, who received the south, including Provence, Lyon and Vienne. His realm was called the regnum provinciae (Kingdom of Provence).
Kingdom of Lower Burgundy
The Kingdom of Lower Burgundy (or Cisjurane Burgundy) was also known as the Kingdom of Provence. Its capital was first Vienne then Arles.
- Charles of Provence (855–863)
On his death, Provence divided between surviving brothers, Lothair II and the Emperor Louis II. The bulk goes to Louis. - Louis II (863–875), also Holy Roman Emperor from 855
On his death, as with his Kingdom of Italy, Louis's Provence goes to his uncle Charles the Bald . - Charles the Bald (875–877), also Holy Roman Emperor from 875
- Louis the Stammerer (877–879)
With the death of Louis the Stammerer, the nobles of Provence refused to elect his two sons and instead elected one of their own, Boso, as king. Boso married Ermengard, daughter of Louis II, to strengthen his and his son's claim. - Boso (879–887)
- Louis the Blind (887–928), also Holy Roman Emperor from 901 to 905
Louis's kingdom did not pass to his children, but instead to his brother-in-law, the husband of his sister, Hugh, who had acted as his regent since 905. Hugh never used the royal title in Provence. - Hugh (911–933)
In 933, Provence ceases to be a separate kingdom as Hugh exchanged it with Rudolph II of Upper Burgundy for the Iron Crown of Lombardy, that is, rule of Italy.
Kingdom of Upper Burgundy
- Lothair II, 855–869
Lothair subsumed his portion of Burgundy into the Kingdom of Lotharingia and at his brother Charles of Provence's death, gained some northern districts from his kingdom. When Lothair II died in 869, his realm was divided between his uncles Charles the Bald and Louis the German in the Treaty of Mersen.
On the death in 888 of Emperor Charles the Fat, who until 884 had united all Frankish kingdoms except for Kingdom of Provence, the nobles and leading clergy of Upper Burgundy assembled at St Maurice and elected Rudolph, count of Auxerre, from the Elder Welf family, as king. At first, he tried to reunite the realm of Lothair II, but opposition by Arnulf of Carinthia forced him to focus on his Burgundian territory.
- Rudolf I (888–912)
- Rudolf II (912–937) In 933 Rudolph ceded his claims to the Kingdom of Italy to Hugh of Arles in return for the Kingdom of Provence, thus reuniting the two territories.
- Conrad I (937–993)
- Rudolph III (993–1032) [1]
In 1032, the Kingdom of Burgundy was incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire as a third kingdom, with the Roman-German King as King of Burgundy. From the 12th century it was often referred to as Kingdom of Arles.
Kingdom of Burgundy (Arelat) as part of the Holy Roman Empire
Salian (Frankish) dynasty
Supplinburger
- Lothar III, king 1125–1137, emperor 1133–1137
Staufen (or Hohenstaufen dynasty)
- Conrad III, king 1138–1152
- Frederick I Barbarossa, king 1152, emperor 1155–1190
- Henry VI, king 1190, emperor 1191–1197
- Philip of Swabia, king 1198–1208
- Otto IV of Brunswick (House of Welf), king 1208–1215, emperor 1209–1215
- Frederick II, king 1212, emperor 1220–1250
- Conrad IV, king 1237–1254 (until 1250 under his father)
Rectorate of Burgundy
Under the kings Conrad I and Rudolph III, royal power weakened while local nobles, such as the counts of Burgundy, gained prominence.
After the early death of Emperor Henry III, his widow Agnes of Poitou acted as regent for his young son Henry IV. She made Rudolf von Rheinfelden duke of Swabia and also conferred on him the regal powers over Burgundy. However, when Rudolf was elected anti-king, Henry IV in 1079 stripped him of his powers and delegated them to the Prince-bishops of Lausanne and Sitten.
When William III, Count of Burgundy was assassinated in February 1127, Lothar III supported the claims of William's uncle Duke Conrad of Zähringen, grandson of Rudolf von Rheinfeld, to the countship, and conferred on him the regal powers over Burgundy.
Lacking a proper title, the Zähringer called themselves dukes and rectors of Burgundy, to give themselves the status of the dukes of Burgundy. The royal chancellory however consistently avoided this term and the effective power of the rector (in Roman law, a generic term for provincial governor) was restricted to the possessions of the Zähringer east of the Jura.
Any attempts to enforce the Zähringer's claims and to extend royal authority into the western and southern parts of the kingdom failed, most notably a military campaign in 1153. After these failures, Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa gained a firm hold of the western districts in 1156 by marrying Beatrice, heiress to the countship of Burgundy. This confined the Zähringer between Jura and Alps, where they used their regal powers to expand their possessions. In 1218, Berthold V, Duke of Zähringen died without issue.
After this, King Frederick II conferred the title of the rector of Burgundy on his young son Henry, to keep the Zähringer heirs from the regal powers associated with that title. This appointment was of only momentary importance, and after Henry had been elected King of Germany in April 1220, the title disappeared for good.
Also, the decline of royal power inside the Kingdom of Burgundy remained irreversible.
See also
References
- Britannica (1922). The Encyclopædia Britannica: A Dictionary of Arts, Sciences, Literature. Original from Harvard University: Encyclopædia Britannica. p. 821.