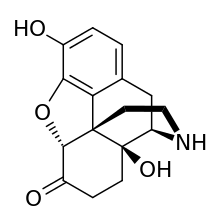
Noroxymorphone
Noroxymorphone is an opioid[1] which is both a metabolite of oxymorphone and oxycodone and is manufactured specifically as an intermediate in the production of narcotic antagonists such as naltrexone and others. It is a potent agonist of the μ-opioid receptor, but is poorly able to cross the blood-brain-barrier into the central nervous system, and for this reason, has only minimal analgesic activity.[2][3][1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | intravenous, intramusucular, subcutaneous, oral, rectal, intranasal |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.046.859 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H17NO4 |
| Molar mass | 287.315 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
In the United States, noroxymorphone is controlled as a Schedule II Narcotic controlled substance with an ACSCN of 9637 and in 2014 the DEA set annual aggregate manufacturing quotas of 17 500 kilogrammes for conversion and 1262.5 kg for sale.[4] In other countries, it may be similarly controlled, controlled at a lower level, or regulated in another way.
See also
- Oxymorphone hydrazone
- Oxymorphol - a metabolite of oxymorphone and an intermediate in the creation of hydromorphone
- Hydromorphone
- Oxycodone
- Norbuprenorphine
References
- Lemberg KK, Siiskonen AO, Kontinen VK, Yli-Kauhaluoma JT, Kalso EA (February 2008). "Pharmacological characterization of noroxymorphone as a new opioid for spinal analgesia". Anesthesia and Analgesia. 106 (2): 463–70, table of contents. doi:10.1213/ane.0b013e3181605a15. PMID 18227301. S2CID 16524280.
- Preedy VR (25 April 2016). Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse Volume 3: General Processes and Mechanisms, Prescription Medications, Caffeine and Areca, Polydrug Misuse, Emerging Addictions and Non-Drug Addictions. Elsevier Science. pp. 462–464. ISBN 978-0-12-800677-1.
- Smith H, Passik S (25 April 2008). Pain and Chemical Dependency. Oxford University Press, USA. pp. 195–. ISBN 978-0-19-530055-0.
- Drug Enforcement Administration (August 25, 2014). "Final Adjusted Aggregate Production Quotas for Schedule I and II Controlled Substances and Assessment of Annual Needs for the List I Chemicals Ephedrine, Pseudoephedrine, and Phenylpropanolamine for 2014". Federal Register. Vol. 79, no. 164. pp. 50700–50704.