Metenolone acetate
Metenolone acetate, or methenolone acetate, sold under the brand names Primobolan and Nibal, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used mainly in the treatment of anemia due to bone marrow failure.[1][2][3][4][5][6] It is taken by mouth.[5] Although it was widely used in the past, the drug has mostly been discontinued and hence is now mostly no longer available.[4][5][2] A related drug, metenolone enanthate, is given by injection into muscle.[5]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Primobolan, Primobolan S, Primonabol, Nibal |
| Other names | Methenolone acetate; NSC-74226; SH-567; SQ-16496; Methenolone 17β-acetate; 1-Methyl-δ1-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone 17β-acetate; 1-Methyl-δ1-DHT acetate; 1-Methylandrost-1,4-dien-17β-ol-3-one 17β-acetate |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid; Androgen ester |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.453 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
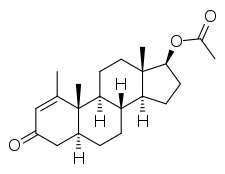
| Formula | C22H32O3 |
| Molar mass | 344.495 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Side effects of metenolone acetate include symptoms of masculinization like acne, increased hair growth, voice changes, and increased sexual desire.[5] The drug is a synthetic androgen and anabolic steroid and hence is an agonist of the androgen receptor (AR), the biological target of androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT).[5][7] It has moderate anabolic effects and weak androgenic effects, as well as no estrogenic effects or risk of liver damage.[5][7] Metenolone enanthate is a metenolone ester and a prodrug of metenolone in the body.[5]
Metenolone acetate was introduced for medical use in 1961.[8][5] In addition to its medical use, metenolone acetate is used to improve physique and performance.[5] The drug is a controlled substance in many countries and so non-medical use is generally illicit.[5] It remains marketed for medical use only in a few countries, such as Japan and Moldova.[4][5]
Side effects
Pharmacology
| Medication | Ratioa |
|---|---|
| Testosterone | ~1:1 |
| Androstanolone (DHT) | ~1:1 |
| Methyltestosterone | ~1:1 |
| Methandriol | ~1:1 |
| Fluoxymesterone | 1:1–1:15 |
| Metandienone | 1:1–1:8 |
| Drostanolone | 1:3–1:4 |
| Metenolone | 1:2–1:30 |
| Oxymetholone | 1:2–1:9 |
| Oxandrolone | 1:3–1:13 |
| Stanozolol | 1:1–1:30 |
| Nandrolone | 1:3–1:16 |
| Ethylestrenol | 1:2–1:19 |
| Norethandrolone | 1:1–1:20 |
| Notes: In rodents. Footnotes: a = Ratio of androgenic to anabolic activity. Sources: See template. | |
| Medication | Form | Major brand names | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Testosterone | Aqueous suspension | Andronaq, Sterotate, Virosterone | 2–3 days |
| Testosterone propionate | Oil solution | Androteston, Perandren, Testoviron | 3–4 days |
| Testosterone phenylpropionate | Oil solution | Testolent | 8 days |
| Testosterone isobutyrate | Aqueous suspension | Agovirin Depot, Perandren M | 14 days |
| Mixed testosterone estersa | Oil solution | Triolandren | 10–20 days |
| Mixed testosterone estersb | Oil solution | Testosid Depot | 14–20 days |
| Testosterone enanthate | Oil solution | Delatestryl | 14–28 days |
| Testosterone cypionate | Oil solution | Depovirin | 14–28 days |
| Mixed testosterone estersc | Oil solution | Sustanon 250 | 28 days |
| Testosterone undecanoate | Oil solution | Aveed, Nebido | 100 days |
| Testosterone buciclated | Aqueous suspension | 20 Aet-1, CDB-1781e | 90–120 days |
| Nandrolone phenylpropionate | Oil solution | Durabolin | 10 days |
| Nandrolone decanoate | Oil solution | Deca Durabolin | 21–28 days |
| Methandriol | Aqueous suspension | Notandron, Protandren | 8 days |
| Methandriol bisenanthoyl acetate | Oil solution | Notandron Depot | 16 days |
| Metenolone acetate | Oil solution | Primobolan | 3 days |
| Metenolone enanthate | Oil solution | Primobolan Depot | 14 days |
| Note: All are via i.m. injection. Footnotes: a = TP, TV, and TUe. b = TP and TKL. c = TP, TPP, TiCa, and TD. d = Studied but never marketed. e = Developmental code names. Sources: See template. | |||
Chemistry
Metenolone acetate, or metenolone 17β-acetate, is a synthetic androstane steroid and a derivative of DHT.[1][2][5] It is the C17β acetate ester of metenolone, which itself is 1-methyl-δ1-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone (1-methyl-δ1-DHT) or 1-methyl-5α-androst-1-en-17β-ol-3-one.[1][2][5]
| Anabolic steroid | Structure | Ester | Relative mol. weight | Relative AAS contentb | Durationc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Moiety | Type | Lengtha | ||||||
| Boldenone undecylenate | C17β | Undecylenic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 11 | 1.58 | 0.63 | Long | ||
| Drostanolone propionate | C17β | Propanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 3 | 1.18 | 0.84 | Short | ||
| Metenolone acetate | C17β | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.14 | 0.88 | Short | ||
| Metenolone enanthate | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.37 | 0.73 | Long | ||
| Nandrolone decanoate | C17β | Decanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 10 | 1.56 | 0.64 | Long | ||
| Nandrolone phenylpropionate | C17β | Phenylpropanoic acid | Aromatic fatty acid | – (~6–7) | 1.48 | 0.67 | Long | ||
| Trenbolone acetate | C17β | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.16 | 0.87 | Short | ||
| Trenbolone enanthated | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.41 | 0.71 | Long | ||
| Footnotes: a = Length of ester in carbon atoms for straight-chain fatty acids or approximate length of ester in carbon atoms for aromatic fatty acids. b = Relative androgen/anabolic steroid content by weight (i.e., relative androgenic/anabolic potency). c = Duration by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection in oil solution. d = Never marketed. Sources: See individual articles. | |||||||||
History
Metenolone acetate was first introduced for medical use in West Germany in 1961 under the brand name Primobolan and in the United States in 1962.[8][5]
Society and culture
Generic names
Metenolone acetate is the generic name of the drug and its INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name, while methenolone acetate is its USANTooltip United States Adopted Name and BANMTooltip British Approved Name.[1][2][3][4][5]
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 784–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. 2000. pp. 659–661. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 178–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- "List of Androgens and anabolic steroids".
- William Llewellyn (2011). Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 625–632. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4.
- J. Larry Jameson; Leslie J. De Groot (25 February 2015). Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 2388–. ISBN 978-0-323-32195-2.
- Kicman AT (2008). "Pharmacology of anabolic steroids". Br. J. Pharmacol. 154 (3): 502–21. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.165. PMC 2439524. PMID 18500378.
- William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 2109–. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3.
External links