Outline of ancient Rome
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ancient Rome:
Ancient Rome – former civilization that thrived on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to become one of the largest empires in the ancient world.[1]
Essence of Ancient Rome
Geography of ancient Rome
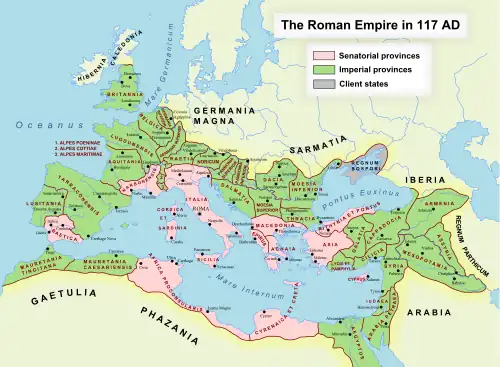
The Roman Empire at its greatest extent, under Trajan (117); imperial provinces are shaded green, senatorial provinces are shaded pink, and client states are shaded gray
- Roman provinces
- Achaia
- Africa
- Alpes Graiae et Poeninae
- Arabia Petraea
- Arcadia Aegypti
- Asia
- Assyria
- Bithynia and Pontus
- Britannia
- Byzacena
- Cappadocia
- Cilicia
- Coele Syria
- Crete and Cyrenaica
- Cyprus
- Dacia
- Dacia Aureliana
- Dalmatia
- Danubian provinces
- Dardania
- Egypt
- Galatia
- Gallia Aquitania
- Gallia Belgica
- Gallia Lugdunensis
- Gallia Narbonensis
- Gaul
- Germania Antiqua
- Germania Inferior
- Germania Superior
- Hispania Baetica
- Hispania Balearica
- Hispania Carthaginensis
- Hispania Citerior
- Hispania Tarraconensis
- Illyricum
- Islands
- Judea
- Lycia et Pamphylia
- Lusitania
- Macedonia
- Mauretania Caesariensis
- Mauretania Tingitana
- Mesopotamia
- Moesia
- Numidia
- Pannonia Inferior
- Pannonia Prima
- Pannonia Savia
- Pannonia Secunda
- Pannonia Superior
- Pannonia Valeria
- Raetia
- Sardinia and Corsica
- Sicilia
- Syria
- Tres Alpes
Government and politics of ancient Rome

Augustus, the first Roman emperor
- Curia
- Forum
- Cursus honorum
- Collegiality
- Emperor
- Legatus
- Dux
- Officium
- Praefectus
- Princeps senatus
- Populares
- Vicarius
- Vigintisexviri
- Lictor
- Magister militum
- Imperator
- Pontifex maximus
- Augustus
- Caesar
- SPQR
- Tetrarch
Political institutions of ancient Rome
Political institutions of ancient Rome
- of ancient Rome in general
- of the Roman Kingdom
- of the Roman Republic
- of the Roman Empire
Magistrates
Ordinary magistrates
Extraordinary magistrates
Roman law
- Constitution (Roman law)
- Roman laws
- Twelve Tables
- Roman citizenship
- Auctoritas
- Imperium
- Status in Roman legal system
- Roman litigation
- Roman Constitution
Military of ancient Rome

The Praetorians Relief, from the Arch of Claudius, Rome
Roman armed forces
- Roman army
- Size of the Roman army
- Troops
 Altar of Domitius Ahenobarbus, c. 122 BC; the altar shows two Roman infantrymen equipped with long scuta and a cavalryman with his horse. All are shown wearing chain mail armour.
Altar of Domitius Ahenobarbus, c. 122 BC; the altar shows two Roman infantrymen equipped with long scuta and a cavalryman with his horse. All are shown wearing chain mail armour. - Roman infantry tactics
.jpg.webp) Roman soldiers in testudo formation
Roman soldiers in testudo formation - Testudo formation
- Military equipment
- Navy
- Decorations and punishments
- Economics of the Roman army
- Roman military clothing
Military history of Rome

Roman Empire at its greatest extent, in AD 117
vassals
Military history of ancient Rome
- Borders of the Roman Empire
- Roman military frontiers and fortifications
- Military engineering of ancient Rome
- Military establishment of the Roman kingdom
- Military establishment of the Roman Republic
- Political history of the Roman military
- Strategy of the Roman military
- Structural history of the Roman military
- Technological history of the Roman military
General history of ancient Rome

Roman expansion in Italy from 500 BC to 218 BC through the Latin War (light red), Samnite Wars (pink/orange), Pyrrhic War (beige), and First and Second Punic War (yellow and green). Cisalpine Gaul (238-146 BC) and Alpine valleys (16-7 BC) were later added. The Roman Republic in 500 BC is marked with dark red.
- Conflict of the Orders (494-287 BC)
- Punic Wars (264-146 BC) – series of three wars fought between Rome and ancient Carthage
- First Punic War (264-241 BC)
- Second Punic War (218-201 BC) – marked by Hannibal's surprising overland journey and his costly crossing of the Alps, followed by his reinforcement by Gaulish allies and crushing victories over Roman armies in the battle of the Trebia and the giant ambush at Trasimene.
- Hannibal – Punic Carthaginian military commander, generally considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. Hannibal occupied much of Italy for 15 years, but a Roman counter-invasion of North Africa forced him to return to Carthage, where he was decisively defeated by Scipio Africanus at the Battle of Zama.
- Conquests of Hannibal
- Battle of Zama – marked the final and decisive end of the Second Punic War. A Roman army led by Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus defeated a Carthaginian force led by the legendary commander Hannibal. Soon after this defeat on their home ground, the Carthaginian senate sued for peace, which was given to them by the Roman Republic on rather humiliating terms, ending the 17-year war.
- Hannibal – Punic Carthaginian military commander, generally considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. Hannibal occupied much of Italy for 15 years, but a Roman counter-invasion of North Africa forced him to return to Carthage, where he was decisively defeated by Scipio Africanus at the Battle of Zama.
- Third Punic War (149-146 BC) – involved an extended siege of Carthage, ending in the city's thorough destruction. The resurgence of the struggle can be explained by growing anti-Roman agitations in Hispania and Greece, and the visible improvement of Carthaginian wealth and martial power in the fifty years since the Second Punic War.
- Siege of Carthage (c. 149 BC)
- Crisis of the Roman Republic (134 BC-44 BC) – extended period of political instability and social unrest that culminated in the demise of the Roman Republic and the advent of the Roman Empire.
- Assassination of Julius Caesar
 Extent of the Roman Republic on the eve of the assassination of Julius Caesar, 44 BC
Extent of the Roman Republic on the eve of the assassination of Julius Caesar, 44 BC
- Roman Empire
- Principate (27 BC-284 AD) – first period of the Roman Empire, extending from the beginning of the reign of Caesar Augustus to the Crisis of the Third Century, after which it was replaced with the Dominate. During the Principate, the constitution of the Roman Republic was never formally abolished. It was amended in such a way as to maintain a politically correct façade of Republican government. This ended following the Crisis of the Third Century (235–284), during the reign of Diocletian.
- Julio-Claudian dynasty (27 BC-68 AD) – the first five Roman Emperors, including Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula (also known as Gaius), Claudius, and Nero. The dynasty ended when Nero committed suicide.
- Augustus
 Extent of the Roman Empire under Augustus. Yellow shows the extent of the Republic in 31 BC, shades of green represent territories gradually conquered by Augustus, and pink shows client states.
Extent of the Roman Empire under Augustus. Yellow shows the extent of the Republic in 31 BC, shades of green represent territories gradually conquered by Augustus, and pink shows client states. - Tiberius (ruled 14-37 AD) – stepson of Augustus. He was one of Rome's greatest generals, conquering Pannonia, Dalmatia, Raetia, and temporarily Germania; laying the foundations for the northern frontier. But he came to be remembered as a dark, reclusive, and sombre ruler who never really desired to be emperor; Pliny the Elder called him tristissimus hominum, "the gloomiest of men."[2]
- Caligula
- Claudius
- Nero
- Year of the Four Emperors (69 AD) – these four emperors were Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian. Vespasian's rule marked the beginning of the Flavian dynasty.
- Flavian dynasty (69-96 AD)
- Nerva–Antonine dynasty (96-192 AD) – dynasty of seven Roman Emperors who ruled over the Roman Empire from 96 AD to 192 AD. These Emperors were Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, Marcus Aurelius, Lucius Verus, and Commodus.
- Severan dynasty (193-235 AD)
- Crisis of the Third Century (235-284 AD) – period in which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed under the combined pressures of invasion, civil war, plague, and economic depression. The Crisis began with the assassination of Emperor Alexander Severus at the hands of his own troops, initiating a fifty-year period in which 20–25 claimants to the title of Emperor, mostly prominent Roman army generals, assumed imperial power over all or part of the Empire.
 During the Crisis of the Third Century, the Roman Empire suffered internal schisms, forming the Palmyrene Empire and the Gallic Empire
During the Crisis of the Third Century, the Roman Empire suffered internal schisms, forming the Palmyrene Empire and the Gallic Empire- Barracks emperor – any Roman Emperor who seized power by virtue of his command of the army. Barracks emperors were especially common in the period from 235 through 284, during the Crisis of the Third Century.
- Gallic Empire (260-274 AD) – modern name for a breakaway realm of the Roman Empire, founded by Postumus in 260 in the wake of barbarian invasions and instability in Rome, and at its height included the territories of Germania, Gaul, Britannia, and (briefly) Hispania.
- Palmyrene Empire (260-273) – splinter empire, that broke away from the Roman Empire during the Crisis of the Third Century. It encompassed the Roman provinces of Syria Palaestina, Egypt and large parts of Asia Minor.
- Julio-Claudian dynasty (27 BC-68 AD) – the first five Roman Emperors, including Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula (also known as Gaius), Claudius, and Nero. The dynasty ended when Nero committed suicide.
- Dominate (284-476 AD) – 'despotic' latter phase of government in the ancient Roman Empire from the conclusion of the Third Century Crisis until the collapse of the Western Empire. The Emperor Diocletian abandoned the appearances of the Republic for the sake of control, and introduced a novel system of joint rule by four monarchs known as the Tetrarchy.
- Decline of the Roman Empire – process spanning many centuries; there is no consensus when it might have begun but many dates and time lines have been proposed by historians.
- Tetrarchy (293-313 AD) – Diocletian designated the general Maximian as co-emperor, first as Caesar (junior emperor) in 285, and then promoted him to Augustus in 286. Diocletian took care of matters in the Eastern regions of the Empire while Maximian similarly took charge of the Western regions. In 293, feeling more focus was needed on both civic and military problems, Diocletian, with Maximian's consent, expanded the imperial college by appointing two Caesars (one responsible to each Augustus). The tetrarchy collapsed, however, in 313 and a few years later Constantine I reunited the two administrative divisions of the Empire as sole Augustus.[3]
 Map of the Roman Empire under the Tetrarchy, showing the dioceses and the four Tetrarchs' zones of influence.
Map of the Roman Empire under the Tetrarchy, showing the dioceses and the four Tetrarchs' zones of influence.- First Tetrarchy – created by Diocletian with Maximian's consent in 293 by the appointment of two subordinate Caesars.
- Diocletian (Augustus)
- Galerius (Caesar)
- Maximian (Augustus)
- Constantius Chlorus (Caesar)
- Diocletian (Augustus)
- Second Tetrarchy – in 305, the senior emperors jointly abdicated and retired, elevating Constantius and Galerius to the rank of Augusti. They in turn appointed two new Caesars.
- Galerius (Augustus)
- Maximinus (Caesar)
- Constantius Chlorus (Augustus)
- Flavius Valerius Severus (Caesar)
- Galerius (Augustus)
- Civil wars of the Tetrarchy – series of conflicts between the co-emperors of the Roman Empire, starting in 306 AD with the usurpation of Maxentius and the defeat of Severus, and ending with the defeat of Licinius at the hands of Constantine I in 324 AD.
- First Tetrarchy – created by Diocletian with Maximian's consent in 293 by the appointment of two subordinate Caesars.
- Constantinian dynasty – informal name for the ruling family of the Roman Empire from Constantius Chlorus (†305) to the death of Julian in 363. It is named after its most famous member, Constantine the Great who became the sole ruler of the empire in 324. It is also called the Neo-Flavian dynasty.
- First phase of the Migration Period
- Division of the Roman Empire – in order to maintain control and improve administration, various schemes to divide the work of the Roman Emperor by sharing it between individuals were tried between 285 and 324, from 337 to 350, from 364 to 392, and again between 395 and 480. Although the administrative subdivisions varied, they generally involved a division of labour between East and West. Each division was a form of power-sharing (or even job-sharing), for the ultimate imperium was not divisible and therefore the empire remained legally one state—although the co-emperors often saw each other as rivals or enemies rather than partners.
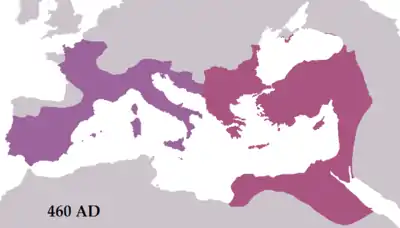 The Roman Empire during the reigns of Leo I (east) and Majorian (west) in 460 AD.
The Roman Empire during the reigns of Leo I (east) and Majorian (west) in 460 AD.- Western Roman Empire – In 285, Emperor Diocletian (r. 284–305) divided the Roman Empire's administration into western and eastern halves.[4] In 293, Rome lost its capital status, and Milan became the capital.
- Byzantine Empire (Eastern Roman Empire) – term used by modern historians to distinguish the Constantinople-centered Roman Empire of the Middle Ages from its earlier classical existence.
- Nicomedia – Nicomedia was the metropolis of Bithynia under the Roman Empire, and Diocletian made it the eastern capital city of the Roman Empire in 286 when he introduced the Tetrarchy system.
- Constantinople – founded in AD 330, at ancient Byzantium as the new capital of the entire Roman Empire by Constantine the Great, after whom it was named.
- Decline of the Roman Empire – process spanning many centuries; there is no consensus when it might have begun but many dates and time lines have been proposed by historians.
- Fall of the Western Roman Empire (476 AD) – the two halves of the Roman Empire ended at different times, with the Western Roman Empire coming to an end in 476 AD (the end of Ancient Rome). The Eastern Roman Empire (referred to by historians as the Byzantine Empire) survived for nearly a thousand years more, and eventually engulfed much of the Western Roman Empire's former territory.
 The Western and Eastern Roman Empires by 476
The Western and Eastern Roman Empires by 476- Fall of the Western Roman Empire – this was not sudden, and took over a hundred years. By 476, when Odoacer deposed the Emperor Romulus, the Western Roman Empire wielded negligible military, political, or financial power and had no effective control over the scattered Western domains that still described themselves as Roman.
- Byzantine Empire (Byzantium) – after the Western Roman Empire fragmented and collapsed, the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantium) continued to thrive, existing for nearly another thousand years until it fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453. Its citizens referred to it as the Roman Empire, and saw it as a direct continuation of it. Historians consider it to be a distinctly different empire, with some overlap, but generally not included in the period referred to as Ancient Rome. Byzantium differed in major ways, including its primary language, which was Greek rather than Latin. It also differed religiously, with Roman mythology being replaced by Christianity.
 For comparison, the Byzantine Empire at its greatest extent under Justinian I, in 555 AD
For comparison, the Byzantine Empire at its greatest extent under Justinian I, in 555 AD
- Principate (27 BC-284 AD) – first period of the Roman Empire, extending from the beginning of the reign of Caesar Augustus to the Crisis of the Third Century, after which it was replaced with the Dominate. During the Principate, the constitution of the Roman Republic was never formally abolished. It was amended in such a way as to maintain a politically correct façade of Republican government. This ended following the Crisis of the Third Century (235–284), during the reign of Diocletian.
- Legacy of the Roman Empire – what the Roman Empire passed on, in the form of cultural values, religious beliefs, as well as technological and other achievements, and through which it continued to shape other civilizations, a process which continues to this day.
- Cultural heritage of the Roman Empire
- History of the Romans in Arabia
- Legacy of Byzantium
- Third Rome
Roman historiography
Works on Roman history
- Ab urbe condita by Titus Livius (around 59 BC-17 AD), a monumental history of Rome, from its founding (traditionally dated to 753 BC).
- Annals and Histories by Tacitus
- De re militari by Vegetius
- Res Gestae by Ammianus Marcellinus
- The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire by Edward Gibbon
Culture of ancient Rome
.jpg.webp)
The Colosseum, the largest amphitheatre ever built

Pont du Gard, a Roman aqueduct built circa 40–60 AD

Back side of the Roman temples of Sbeitla, Tunisia

The ancient theatre of Taormina

.jpg.webp)
Theatrical masks of Tragedy and Comedy, Roman mosaic, 2nd century AD

Ancient Roman earrings

Roman cage cup, ca. 400 AD (Collection Staatliche Antikensammlung, Munich)

Museum of Roman Civilization, a museum in Rome devoted to aspects of the Ancient Roman civilization
_d%C3%A9tail.jpg.webp)
Sundial at the Temple of Apollo (Pompeii)
Architecture of ancient Rome
Types of buildings and structures
Art in ancient Rome
- Art collection in ancient Rome
- Decorative arts of ancient Rome
- Literature
- Music of ancient Rome
- Painting of ancient Rome
- Sculpture of ancient Rome
- Theatre of ancient Rome
- Bathing in ancient Rome
- Calendar
- Cuisine of ancient Rome
- Education in ancient Rome
- Fashion in ancient Rome
- Festivals
- Fiction set in ancient Rome
- Roman folklore
- Roman jokes
- Legacy of the Roman Empire
- Medicine in ancient Rome
- Naming conventions
- People in ancient Rome
- Philosophy in ancient Rome
- Public entertainment
- Sexuality in ancient Rome
- Technology
Social order in ancient Rome

Augustus, possibly the most famous example of adoption in Ancient Rome

Mosaic depicting two female slaves (ancillae) attending their mistress (Carthage National Museum)
Religion in ancient Rome


Jupiter holding a staff, with eagle and globe, a fresco from the Casa dei Dioscuri, Pompeii
Roman mythology
Roman religious institutions

Portrait of the emperor Antoninus Pius in ritual attire
Roman religious practices
Language in ancient Rome
- Romance languages
- History of Latin
- Latin alphabet
- Roman numerals
- Latin phrases
- Latin-script calligraphy
Economy of ancient Rome


Solidus of Constantine I, minted in AD 335
Scholars
Ancient
Modern
Ancient Roman lists
- Adjectival and demonymic forms of regions in Greco-Roman antiquity
- Alphabetized list of notable ancient Romans
- Glossary of ancient Roman religion
- Ancient monuments in Rome
- Ancient Roman fasti
- Ancient Roman temples
- Ancient Romans
- Aqueducts in the city of Rome
- Aqueducts in the Roman Empire
- Censors of the Roman Republic
- Cities founded by the Romans
- Civil wars and revolts
- Condemned Roman emperors
- Governors of Roman Britain
- Late Roman provinces
- Monuments of the Roman Forum
- Roman amphitheatres
- Roman aqueducts by date
- Roman army unit types
- Roman auxiliary regiments
- Roman basilicas
- Roman bridges
- Roman canals
- Roman cisterns
- Roman consuls
- Roman dams and reservoirs
- Roman deities
- Roman dictators
- Roman dynasties
- Roman domes
- Roman emperors
- Roman generals
- Roman gentes
- Roman imperial victory titles
- Roman laws
- Roman legions
- Roman moneyers during the Republic
- Roman praetors
- Roman public baths
- Roman taxes
- Roman theatres
- Roman tribunes
- Roman triumphal arches
- Roman usurpers
- Roman wars and battles
- Thirty Tyrants
See also
References
- Chris Scarre, The Penguin Historical Atlas of Ancient Rome (London: Penguin Books, 1995).
- Pliny the Elder, Natural Histories XXVIII.5.23.
- Bury 1923, p. 1; Kuhoff 2002, pp. 177–178.
- Treadgold 1997, p. 847.
- "Odoacer was the first barbarian who reigned over Italy, over a people who had once asserted their just superiority above the rest of mankind." Edward Gibbon, The Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire, Chapter XXXVI
External links
- Ancient Rome resources for students from the Courtenay Middle School Library.
- History of Ancient Rome OpenCourseWare from the University of Notre Dame providing free resources including lectures, discussion questions, assignments and exams.
- Ancient Rome portal at Encarta Encyclopedia
- Gallery of the Ancient Art: Ancient Rome
- Lacus Curtius
- Livius.Org Archived 2017-07-01 at the Wayback Machine
- Nova Roma - Educational Organization about "All Things Roman"
- The Private Life of the Romans by Harold Whetstone Johnston
- United Nations of Roma Victrix (UNRV) History
- Water and Wastewater Systems in Imperial Rome
- Ancient Rome at The History Channel
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.


