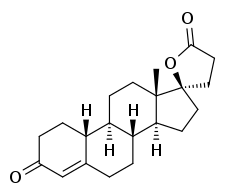
SC-8109
SC-8109 is a steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group which was never marketed.[1][2] It is a potent antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor and is more potent than the related drug SC-5233 (of which SC-8109 is the 19-nor analogue).[1][3] However, SC-8109 was found to have relatively low oral bioavailability and potency,[1][4] though it nonetheless produced a mild diuretic effect in patients with congestive heart failure.[2] Spironolactone (SC-9420; Aldactone), another spirolactone, followed and had both good oral bioavailability and potency, and was the first antimineralocorticoid to be marketed.[1][5]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 19-Norspirolactone; 19-Nor-17α-(2-carboxyethyl)testosterone γ-lactone; 3-Oxo-17β-hydroxyestr-4-ene-17-propanoic acid lactone; 17-Hydroxy-3-oxo-19-Nor-17α-pregn-4-ene-21-carboxylic acid γ-lactone |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H28O3 |
| Molar mass | 328.452 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
In addition to its antimineralocorticoid activity, SC-8109 shows potent progestogenic activity, with similar potency relative to that of progesterone.[6] Its analogue, SC-5233, possesses similar but less potent progestogenic activity.[6] In addition, SC-5233 has been assessed and found to possess some antiandrogenic activity, antagonizing the effects of testosterone in animals, and SC-8109 may as well.[7]
| Compound | PRTooltip Progesterone receptor | ARTooltip Androgen receptor | ERTooltip Estrogen receptor | GRTooltip Glucocorticoid receptor | MRTooltip Mineralocorticoid receptor | SHBGTooltip Sex hormone-binding globulin | CBGTooltip Corticosteroid binding globulin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progesterone | 100 | 3–10 | <1 | <1 | 3–10 | ? | ? |
| SC-8109 | 191 | 25–50 | <1 | <1 | 15–25 | ? | ? |
| Values are percentages (%). Reference ligands (100%) were progesterone for the PRTooltip progesterone receptor, testosterone for the ARTooltip androgen receptor, estradiol for the ERTooltip estrogen receptor, DEXATooltip dexamethasone for the GRTooltip glucocorticoid receptor, and aldosterone for the MRTooltip mineralocorticoid receptor. | |||||||
See also
References
- Bentley PJ (1980). "The Adrenal Gland". Endocrine Pharmacology: Physiological Basis and Therapeutic Applications. CUP Archive. pp. 160–. ISBN 978-0-521-22673-8.
- Buchborn E, Bock KD (14 December 2013). Diuresis and Diuretics / Diurese und Diuretica: An International Symposium Herrenchiemsee, June 17th–20th, 1959 Sponsored by CIBA / Ein Internationales Symposium Herrenchiemsee, 17.–20. Juni 1959 Veranstaltet mit Unterstützung der CIBA. Springer-Verlag. pp. 224, 261. ISBN 978-3-642-49716-2.
- Ussing HH, Kruhoffer P, Thaysen HJ, Thorn NH (8 March 2013). The Alkali Metal Ions in Biology: I. The Alkali Metal Ions in Isolated Systems and Tissues. II. The Alkali Metal Ions in the Organism. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 418–. ISBN 978-3-642-49246-4.
- Brandon ML (1 January 1962). Corticosteroids in medical practice. Thomas. ISBN 9780398002152.
- Cokkinos DV (6 November 2014). Introduction to Translational Cardiovascular Research. Springer. pp. 61–. ISBN 978-3-319-08798-6.
- Dorfman RI (5 December 2016). Steroidal Activity in Experimental Animals and Man. Elsevier Science. pp. 371–. ISBN 978-1-4832-7299-3.
- Kagawa CM, Sturtevant FM, Van Arman CG (June 1959). "Pharmacology of a new steroid that blocks salt activity of aldosterone and desoxycorticosterone". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 126 (2): 123–130. PMID 13665517.
[SC-5233] (total dose of 5 mg/rat) partially blocked the effects of testosterone propionate on the seminal vesicles and prostate in similar animals.
- Raynaud JP, Ojasoo T, Bouton MM, Philibert D (1979). "Receptor Binding as a Tool in the Development of New Bioactive Steroids". Drug Design. pp. 169–214. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-060308-4.50010-X. ISBN 9780120603084.