Sankarabharanam (raga)
Dhīraśankarābharaṇaṃ, commonly known as Śankarābharaṇaṃ, is a rāga in Carnatic music. It is the 29th Melakarta rāga in the 72 Melakarta rāga system of Carnatic music. Since this raga has many Gamakās (ornamentations), it is glorified as "Sarva Gamaka Maaṇika Rakti Rāgaṃ".
| Mela | 29th, Dheera Shankaraabharanam |
|---|---|
| Chakra | Bāṇa |
| Arohanam | S R₂ G₃ M₁ P D₂ N₃ Ṡ |
| Avarohanam | Ṡ N₃ D₂ P M₁ G₃ R₂ S |
| Synonym | Dheera Shankaraabharanam |
| Equivalent |
| Carnatic music |
|---|
 |
| Concepts |
| Compositions |
| Instruments |
|
By scale wise, the Śankarābharaṇaṃ scale corresponds to Bilaval in the Hindustani music system. The Western equivalent is the major scale, or the Ionian mode.[1][2] Hence this rāga is one of the most popular scales across the world, known with different names in different musical styles.
Its nature is mellifluous and smooth. This rāga offers a large scope for compositions. It is ideal for a melodious, but still laid back majestic presentation.
Structure and Lakshana
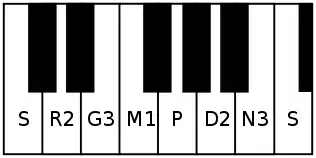
It is the 5th rāga in the 5th Chakra Bāṇa. The mnemonic name is Bāṇa-Ma. The mnemonic phrase is sa ri ga ma pa da ni sa[1] Its ārohaṇa-avarohaṇa structure is as follows (see swaras in Carnatic music for details on below notation and terms):
- ārōhaṇa: S R₂ G₃ M₁ P D₂ N₃ Ṡ[lower-alpha 1]
- avarōhaṇa: Ṡ N₃ D₂ P M₁ G₃ R₂ S[lower-alpha 2]
The notes in this scale are shadjam, chatushruti rishabham, antara gandharam, shuddha madhyamam, paṅchamam, chatushruti dhaivatam and Kakali Nishadam. As it is a Melakarta rāga, by definition it is a Sampurṇa rāga (has all seven notes in ascending and descending scale). It is the Shuddha Madhyamam equivalent of 65th Melakarta rāga Kaḷyāṇi.
Janya Rāgas
Due to the even spacing of svarās, many janya rāgas can be derived from Śaņkarābharaṇaṃ. It is one of the melakarta rāgas that has high number of Janya rāgas (derived scales) associated with it.
Many of the Janya rāgas are very popular on their own, lending themselves to elaboration, interpretation and evoking different moods. Some of them are Arabhi, Atana, Bilahari, Devagaandhaari, Jana Ranjani, Hamsadhvani, Kadanakutuhalam, Niroshta, Shuddha Sāveri, Pahādi, Purnachandrika, Janaranjani, Kedaram, Kurinji, Navroj, Sarasvati-manohari, Naagadhvani etc.
See List of Janya rāgas for full list of rāgas associated with Śaṃkarābharaṇaṃ.
Compositions
Śankarābharaṇaṃ has been decorated with compositions by almost all composers. A few of the compositions are listed here.
- Chalamela,a popular Adathaalavarnam by Maharaja Swathi Thirunal in Telugu
- Nrityati Nrityati By Swati Thirunal in Sanskrit
- Eduṭa Nilacitē, Bhakti Bhikṣamīyave, Maryāda Kādurā, Svararāgasudhārasa, Sundarēśvaruṇi, Manasu Svādhīnamaina and Eṃduku Peddalavalē by Tyagaraja in Telugu.
- Dakṣhiṇāmūrtē, Sadāśivam Upāsmahē, Akṣhayaliṃgavibho and Śrī kamalāmbā by Muthuswami Dikshitar in Sanskrit
- Pogadirēlo Ranga (6th Navaratna Malike), Kande naa kanasinali, Enagu aane by Purandara Dasa in Kannada
- Yenu Olle Hariye By Kanaka Dasa in Kannada
- Sarōjadala Nētri and Dēvī Mīnānētri by Syama Sastri in Telugu
- Devi Jagath Janani,Bhaktha Paraayana by Swathi Thirunal Maharaja in Sanskrit
- Rajeevaksha Baro By Swati Thirunal in Kannada
- Alarulu Kuriyaga Āḍinadē by Annamacharya in Telugu
- Samakarardha Sariirini by Saint Gnanananda Teertha (Ogirala Veeraraghava Sarma) in Telugu
- Rama Ninnuvina by Thyagaraja
- Swara Raga Sudha by Thyagaraja
Muthuswami Dikshitar also has a list of 22 "Nottu Svara" compositions, based on Western Major Scale notes to his credit.
Related rāgas
This section covers the theoretical and scientific aspect of this rāga.
Śaṃkarābharaṇaṃ's notes when shifted using Graha bhedam, yields 5 other major Melakarta rāgas, namely, Kalyāṇi, Hanumatodi, Natabhairavi, Kharaharapriya and Harikambhoji. Graha bhedam is the step taken in keeping the relative note frequencies same, while shifting the shadjam to the next note in the rāga. Refer table below for illustration of this concept.
| Rāga | Mela # | C | D | E | F | G | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | A | B | C | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Śaṃkarābharaṇaṃ | 29 | S | R2 | G3 | M1 | P | D2 | N3 | S' | R2' | G3' | M1' | P' | D2' | N3' | S' ' | ||||||||||
| Kharaharapriya | 22 | S | R2 | G2 | M1 | P | D2 | N2 | S' | |||||||||||||||||
| Hanumatodi | 08 | S | R1 | G2 | M1 | P | D1 | N2 | S' | |||||||||||||||||
| Kaḷyāṇi | 65 | S | R2 | G3 | M2 | P | D2 | N3 | S' | |||||||||||||||||
| Harikambhoji | 28 | S | R2 | G3 | M1 | P | D2 | N2 | S' | |||||||||||||||||
| Natabhairavi | 20 | S | R2 | G2 | M1 | P | D1 | N2 | S' | |||||||||||||||||
| Not a Melakarta | -- | S | R1 | G2 | M1 | M2 | D1 | N2 | S' | |||||||||||||||||
| Shankarābharanam | 29 | S | R2 | G3 | M1 | P | D2 | N3 | S' |
Notes on above table
C as the base for Śaṃkarābharaṇaṃ is chosen for above illustration only for convenience, as Carnatic music does not enforce strict frequency/note structure. The shadjam (S) is fixed by the artist as per the vocal range or the instrument's base frequency. All the other svarams are relative to this shadjam, falling into a geometric progression-like frequency pattern.
The 7th Graha bhedam of Śaṃkarābharaṇaṃ has both madhyamams (Ma) and no panchamam (Pa) and hence will not be considered a valid melakarta (rāga having all 7 swarams and only 1 of each). This is only a classification issue with respect to melakarta scales, while this structure could be theoretically used well to create good music.
Interesting features
The swaras are regularly spaced in these ragas. Hence these six ragas give very good melody, scope for elaboration, experimentation and exploration of phrases. In practice, Natabhairavi is not elaborated extensively much. Harikambhoji is taken up for elaboration, but not as much as the rest of the 4 ragas, namely, Śaṃkarābharaṇaṃ, Todi, Kaḷyāṇi and Kharaharapriya. One of these 4 rāgas is sung as the main rāga in a concert quite often.
As can be seen in the illustration, these rāgas can be played using just the white keys of a piano/ organ/ keyboard (rāga in simplified fashion).
Film Songs: Tamil
Janya 1: Ragam Pahadi/Pahari
Ascending: S R2 G3 P D2 P D2 S’
Descending:N3 D2 P G3 M1 G3 R2 S N3 D2 P D2 S
Film Songs: Tamil
Janya 2: Ragam Maand
Ascending: S G3 M1 D2 N3 S
Descending:S N3 D2 P M1 G3 R2 S
Carnatic Compositions
- Maand Thillana by Lalgudi Jayaraman
- Paindhaane Hanuman by Arunachala Kavi
- Ramanai Bhajithaal by Papanasam Sivan
- Aadugindraan Kannan by Suddhanandha Bharathi
- Muralidhara Gopala by Periyasamy Thooran popularised by ML Vasanthakumari
- Aarumo Aaval by Kannan Iyengar, another song popularised by MLV
- Neeraja Dhala Nayana by Sambasiva Iyer popularised by Maharajapuram Santhanam
- Vaanathin Meedhu Mayilaada by Ramalinga Adigal popularised by MS Subbulakshmi
Film Songs: Tamil
Janya 3: Ragam Begada
Ascending: S G3 R2 G3 M1 P D2 P S
Descending: S N3 D2 P M1 G3 R2
Carnatic Compositions
- Naadopasana by Tyagaraja
- Thyagaraja Namasthe and Vallabha Nayakasya by Dikshitar
- Varuvar Azhaithu Vaadi, by Ramalinga Adigal
- Ganarasamudaniin Bhuvaneshwari by Papanasam Sivan
- Vaa Muruga Vaa by Spencer Venugopal
- Nandri Kooruvame by T Lakshmana Pillai
- Shankari Neeve by Subbaraya Sastri
- Kalayami Raghuramam by Swati Thirunal
- Kadaikkan vaithennai by Ramasamy Sivan
- Abimanamennadu Galgu by Patnam Subramaniya Iyer
- Elle Ilangiliye, a Thiruppavai
Film Songs: Tamil
| Song | Movie | Composer | Singer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nijama Idhu Nijama | Haridas | Papanasam Sivan | M. K. Thyagaraja Bhagavathar |
Notes
- Alternate notations:
- Hindustani: S R G M P D N Ṡ
- Western: C D E F G A B C
- Alternate notations:
- Hindustani: Ṡ N D P M G R S
- Western: C B A G F E D C
References
- Ragas in Carnatic music by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications
- Raganidhi by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras