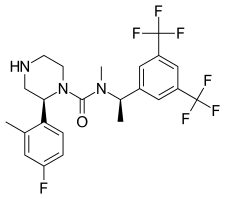
Vestipitant
Vestipitant (INN)[1]: 98 is a drug developed by GlaxoSmithKline which acts as a selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor. It is under development as a potential antiemetic and anxiolytic drug,[2][3] and as a treatment for tinnitus[4] and insomnia.[5]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H21F10N3O |
| Molar mass | 545.425 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
References
- "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names: List 53" (PDF). World Health Organization. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- Reddy GK, Gralla RJ, Hesketh PJ (April 2006). "Novel neurokinin-1 antagonists as antiemetics for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced emesis". Supportive Cancer Therapy. 3 (3): 140–2. doi:10.3816/SCT.2006.n.011. PMID 18632487.
- Brocco M, Dekeyne A, Mannoury la Cour C, Touzard M, Girardon S, Veiga S, et al. (October 2008). "Cellular and behavioural profile of the novel, selective neurokinin1 receptor antagonist, vestipitant: a comparison to other agents". European Neuropsychopharmacology. 18 (10): 729–50. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2008.06.002. PMID 18657401. S2CID 8258896.
- Clinical trial number NCT00394056 for "Vestipitant Or Vestipitant/Paroxetine Combination In Subjects With Tinnitus And Hearing Loss" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Ratti E, Carpenter DJ, Zamuner S, Fernandes S, Squassante L, Danker-Hopfe H, et al. (December 2013). "Efficacy of vestipitant, a neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist, in primary insomnia". Sleep. 36 (12): 1823–30. doi:10.5665/sleep.3208. PMC 3825431. PMID 24293756.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.