1q21.1 duplication syndrome
1q21.1 duplication syndrome or 1q21.1 (recurrent) microduplication is a rare aberration of chromosome 1.
| 1q21.1 duplication syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 1q21.1 (recurrent) microduplication |
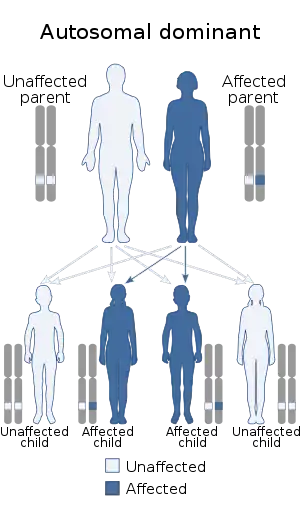 | |
| 1q21.1 duplication syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
In a common situation a human cell has one pair of identical chromosomes on chromosome 1. With the 1q21.1 duplication syndrome one chromosome of the pair is over complete, because a part of the sequence of the chromosome is duplicated twice or more. In 1q21.1, the '1' stands for chromosome 1, the 'q' stands for the long arm of the chromosome and '21.1' stands for the part of the long arm in which the duplication is situated.
Next to the duplication syndrome, there is also a 1q21.1 deletion syndrome. While there are two or three copies of a similar part of the DNA on a particular spot with the duplication syndrome, there is a part of the DNA missing with the deletion syndrome on the same spot. Literature refers to both the deletion and the duplication as the 1q21.1 copy-number variations (CNV).
The CNV leads to a very variable phenotype and the manifestations in individuals are quite variable. Some people who have the syndrome can function in a normal way, while others have symptoms of developmental delays and various physical anomalies.
Symptoms and signs
Currently recognized symptoms include:
- Autism or autistic behaviors
- ADHD
- Learning disability
- Large head
- Dysmorphic facial appearance - mild
- Prominent forehead
- Wide-set eyes (hypertelorism)
- Loose joints
- GERD
- Sleep disturbances
- Sleep Apnea
- Underdeveloped parts of brain - corpus callosum and cerebellar vermis
- Speech & developmental delays
- Chiari malformation of the brain
- Congenital heart defects
- Hypotonia
It is not clear whether the list of symptoms is complete. Very little information is known about the syndrome. The symptomology may be different among individuals, even in the same family.
Cause
Meiosis is the process of dividing cells in humans. In meiosis, the chromosome pairs splits and a representative of each pair goes to one daughter cell. In this way the number of chromosomes will be halved in each cell, while all the parts on the chromosome (genes) remain, after being randomized. Which information of the parent cell ends up in the daughter cell is purely decided by chance. Besides this random process, there is a second random process. In this second random process the DNA will be scrambled in a way that pieces are omitted (deletion), added (duplication), moved from one place to another (translocation) and inverted (inversion). This is a common process, which leads to about 0.4% variation in the DNA. It explains why even identical twins are not genetically 100% identical.
The second random process can give rise to genetic mistakes. In the deletion and duplication process, the chromosomes that come together in a new cell may be shorter or longer. The result of this spontaneous change in the structure of DNA is a copy number variation. Due to the copy number variation chromosomes of different sizes can be combined in a new cell. If this occurs around conception, there is the first cell of a human with a genetic variation. This can be either positive or negative. In positive cases this new human will be capable of a special skill that is assessed positively, for example, sports or science. In negative cases, you have to deal with a syndrome or a severe disability, as in this case the 1q21.1 duplication syndrome.
Based on the meiotic process, the syndrome may occur in two ways.
- 1. a spontaneous deviation (a 'de novo' situation): two chromosomes come together, of which one has a copy number variation as a result of the meiosis process.
- 2. a parent is unknowingly carrier of a chromosome with a copy number variation and passes it through at conception to the child, with different consequences for the child.
Due to this genetic misprint the embryo may experience problems in the development during the first months of pregnancy. Approximately 20 to 40 days after fertilization, something goes wrong in the construction of the body parts and brain, which leads to a chain reaction.[1]
Structure of 1q21.1

The structure of 1q21.1 is complex. The area has a size of approximately 6 Megabase (Mb) (from 141.5 Mb to 147.9 Mb). Within 1q21.1 there are two areas where a duplication or deletion can be found: the TAR-area for the TAR syndrome and the distal area for other anomalies. The 1q21.1 duplication syndrome will commonly be found in the distal area, but an overlap with the TAR-area is possible. 1q21.1 has multiple repetitions of the same structure (areas with the same color in the picture have equal structures) Only 25% of the structure is unique. There are several gaps in the sequence. There is no further information available about the DNA-sequence in those areas up until now. The gaps represent approximately 700 Kilobase. New genes are expected in the gaps. Because the gaps are still a topic of research, it is hard to find the exact start and end markers of a deletion. The area of 1q21.1 is one of the most difficult parts of the human genome to map.
Related genes
Genes related to 1q21.1 deletion in the TAR area are HFE2, TXNIP, POLR3GL, LIX1L, RBM8A, PEX11B, ITGA10, ANKRD35, PIAS3, NUDT17, POLR3C, RNF115, CD160, PDZK1, and GPR89A
Genes related to 1q21.1 deletion in the distal area are HYDIN2, PRKAB2, FMO5, CHD1L, BCL9, ACP6, GJA5, GJA8, and GPR89B.
Diagnostics
A 'de novo'-situation appears in about 75% of the cases. In 25% of the cases, one of the parents is carrier of the syndrome, without any effect on the parent. Sometimes adults have mild problems with the syndrome. To find out whether either of the parents carries the syndrome, both parents have to be tested. In several cases, the syndrome was identified with the child, because of an autism disorder or another problem, and later it appeared that the parent was affected as well. The parent never knew about it until the moment that the DNA-test proved the parent to be a carrier.
In families where both parents have been tested negative on the syndrome, chances on a second child with the syndrome are extremely low. If the syndrome was found in the family, chances on a second child with the syndrome are 50%, because the syndrome is autosomal dominant. The effect of the syndrome on the child cannot be predicted.
The syndrome can be detected with fluorescence in situ hybridization and Affymetrix GeneChip Operating Software.For parents with a child with the syndrome, it is advisable to consult a physician before a next pregnancy and to do prenatal screening.
Management
Research
Several researchers around the world are studying on the subject of 1q21.1 duplication syndrome. The syndrome was identified for the first time in people with heart abnormalities. The syndrome was later observed in patients who had autism or schizophrenia.
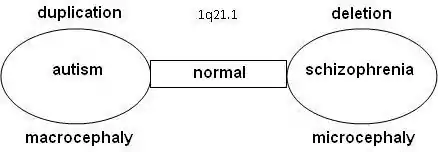
It appears that there is a relation between autism and schizophrenia. Literature shows that nine locations have been found on the DNA where the syndromes related to autism or schizophrenia can be found, the so-called "hotspots": 1q21.1, 3q29, 15q13.3, 16p11.2, 16p13.1, 16q21, 17p12, 21q11.2 and 21q13.3. With a number of hotspots, either autism and schizophrenia were observed depending on the copy-number variation (CNV) at that location.
Statistical research showed that schizophrenia is significantly more common in combination with 1q21.1 deletion syndrome. On the other side, autism is significantly more common with 1q21.1 duplication syndrome. Similar observations were done for chromosome 16 on 16p11.2 (deletion: autism/duplication: schizophrenia), chromosome 22 on 22q11.21 (deletion (Velo-cardio-facial syndrome): schizophrenia/duplication: autism) and 22q13.3 (deletion (Phelan-McDermid syndrome): schizophrenia/duplication: autism). Further research confirmed that the odds on a relation between schizophrenia and deletions at 1q21.1, 3q29, 15q13.3, 22q11.21 en Neurexin 1 (NRXN1) and duplications at 16p11.2 are at 7.5% or higher.[2][3]
Common variations in the BCL9 gene, which is in the distal area, confer risk of schizophrenia and may also be associated with bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder.[4]
Research is done on 10-12 genes on 1q21.1 that produce DUF1220-locations. DUF1220 is an unknown protein, which is active in the neurons of the brain near the neocortex. Based on research on apes and other mammals, it is assumed that DUF1220 is related to cognitive development (man: 212 locations; chimpanzee: 37 locations; monkey: 30 locations; mouse: 1 location). It appears that the DUF1220-locations on 1q21.1 are in areas that are related to the size and the development of the brain. The aspect of the size and development of the brain is related to autism (macrocephaly) and schizophrenia (microcephaly). It is assumed that a deletion or a duplication of a gene that produces DUF1220-areas might cause growth and development disorders in the brain [5]
Another relation between macrocephaly with duplications and microcephaly with deletions has been seen in research on the HYDIN Paralog or HYDIN2. This part of 1q21.1 is involved in the development of the brain. It is assumed to be a dosage-sensitive gene. When this gene is not available in the 1q21.1 area it leads to microcephaly. HYDIN2 is a recent duplication (found only in humans) of the HYDIN gene found on 16q22.2.[6]
GJA5 has been identified as the gene that is responsible for the phenotypes observed with congenital heart diseases on the 1q21.1 location. In case of a duplication of GJA5 tetralogy of Fallot is more common. In case of a deletion other congenital heart diseases than tetralogy of Fallot are more common.[7]
References
- A. Ploeger; 'Towards an integration of evolutionary psychology and developmental science: New insights from evolutionary developmental biology'
- Levinson DF, Duan J, Oh S, et al. (March 2011). "Copy number variants in schizophrenia: confirmation of five previous findings and new evidence for 3q29 microdeletions and VIPR2 duplications". Am J Psychiatry. 168 (3): 302–16. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.10060876. PMC 4441324. PMID 21285140.
- Ikeda M, Aleksic B, Kirov G, et al. (February 2010). "Copy number variation in schizophrenia in the Japanese population". Biol. Psychiatry. 67 (3): 283–6. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.08.034. PMID 19880096. S2CID 26047827.
- Li J, Zhou G, Ji W, et al. (March 2011). "Common variants in the BCL9 gene conferring risk of schizophrenia". Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 68 (3): 232–40. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1. PMID 21383261.
- Dumas L, Sikela JM (2009). "DUF1220 domains, cognitive disease, and human brain evolution". Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 74: 375–82. doi:10.1101/sqb.2009.74.025. PMC 2902282. PMID 19850849.
- Doggett NA, Xie G, Meincke LJ, et al. (Dec 2006). "A 360-kb interchromosomal duplication of the human HYDIN locus". Genomics. 88 (6): 762–71. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2006.07.012. PMID 16938426.
- Soemedi, R.; et al. (2011). "Phenotype-Specific Effect of Chromosome 1q21.1 Rearrangements and GJA5 Duplications in 2436 Congenital Heart Disease Patients and 6760 Controls". Hum. Mol. Genet. 21 (7): 1513–1520. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr589. PMC 3298277. PMID 22199024.
Further reading
- Mefford HC, Sharp AJ, Baker C, et al. (October 2008). "Recurrent rearrangements of chromosome 1q21.1 and variable pediatric phenotypes". N. Engl. J. Med. 359 (16): 1685–99. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0805384. PMC 2703742. PMID 18784092.
- Brunetti-Pierri N, Berg JS, Scaglia F, et al. (December 2008). "Recurrent reciprocal 1q21.1 deletions and duplications associated with microcephaly or macrocephaly and developmental and behavioral abnormalities". Nat. Genet. 40 (12): 1466–71. doi:10.1038/ng.279. PMC 2680128. PMID 19029900.
- Crespi B, Stead P, Elliot M (January 2010). "Evolution in health and medicine Sackler colloquium: Comparative genomics of autism and schizophrenia". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107 (Suppl 1): 1736–41. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107.1736C. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906080106. PMC 2868282. PMID 19955444.
External links
- 1q21.1 microduplications
- DECIPHER database entry for 1q21.1 duplication syndrome