Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist.[1] The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus.
| Forearm | |
|---|---|
 The forearm is highlighted in magenta | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | antebrachium |
| MeSH | D005542 |
| TA98 | A01.1.00.024 |
| TA2 | 146 |
| FMA | 9663 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna,[2] forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface.
The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow (brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the forearm can be divided into two fascial compartments. The posterior compartment contains the extensors of the hands, which are supplied by the radial nerve. The anterior compartment contains the flexors and is mainly supplied by the median nerve. The flexor muscles are more massive than the extensors because they work against gravity and act as anti-gravity muscles. The ulnar nerve also runs the length of the forearm.[3]
The radial and ulnar arteries and their branches supply the blood to the forearm. These usually run on the anterior face of the radius and ulna down the whole forearm. The main superficial veins of the forearm are the cephalic, median antebrachial and the basilic vein. These veins can be used for cannularisation or venipuncture, although the cubital fossa is a preferred site for getting blood.
Structure
Bones and joints
The bones of the forearm are the radius (located on the lateral side) and the ulna (located on the medial side)

Radius
Proximally, the head of the radius articulates with the capitulum of the humerus and the radial notch of the ulna at the elbow. The articulation between the radius and the ulna at the elbow is known as the proximal radioulnar joint.
Distally, it articulates with the ulna again at the distal radioulnar joint. It forms part of the wrist joint by articulating with the scaphoid at its lateral aspect and with the lunate at its medial aspect.
Ulna
Proximally, the trochlear notch of the ulna articulates with the trochlea of the humerus and the radial notch articulates with the head of the radius at the elbow.[4]
Distally it forms part of the distal radioulnar joint and also articulates with the wrist.[5]
Muscles
| Compartment | Level | Muscle | E/I | Nerve |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior | superficial | flexor carpi radialis | E | median |
| Anterior | superficial | palmaris longus | E | median |
| Anterior | superficial | flexor carpi ulnaris | E | ulnar |
| Anterior | superficial | pronator teres | I | median |
| Anterior | superficial (or intermediate) | flexor digitorum superficialis (sublimis) | E | median |
| Anterior | deep | flexor digitorum profundus | E | ulnar + median |
| Anterior | deep | flexor pollicis longus | E | median |
| Anterior | deep | pronator quadratus | I | median |
| Posterior | (see below) | brachioradialis | I | radial |
| Posterior | superficial | extensor carpi radialis longus | E | radial |
| Posterior | superficial | extensor carpi radialis brevis | E | radial |
| Posterior | intermediate | extensor digitorum (communis) | E | radial |
| Posterior | intermediate | extensor digiti minimi (proprius) | E | radial |
| Posterior | superficial | extensor carpi ulnaris | E | radial |
| Posterior | deep | abductor pollicis longus | E | radial |
| Posterior | deep | extensor pollicis brevis | E | radial |
| Posterior | deep | extensor pollicis longus | E | radial |
| Posterior | deep | extensor indicis (proprius) | E | radial |
| Posterior | deep | supinator | I | radial |
| Posterior | deep | anconeus | I | radial |
- "E/I" refers to "extrinsic" or "intrinsic". The intrinsic muscles of the forearm act on the forearm, meaning, across the elbow joint and the proximal and distal radioulnar joints (resulting in pronation or supination, whereas the extrinsic muscles act upon the hand and wrist. In most cases, the extrinsic anterior muscles are flexors, while the extrinsic posterior muscles are extensors.
- The brachioradialis, flexor of the forearm, is unusual in that it is located in the posterior compartment, but it is actually in the anterior portion of the forearm.
- The anconeus is considered by some as a part of the posterior compartment of the arm.[6]
Nerves
- See separate nerve articles for details on divisions proximal to the elbow and distal to the wrist; see Brachial plexus for the origins of the median, radial and ulnar nerves.
- Median nerve – interior nerve of the anterior compartment (PT, FCR, PL, FDS).
- anterior interosseous nerve (supplies FPL, lat. 1/2 of FDP, PQ).
- Radial nerve – supplies muscles of the posterior compartment (ECRL, ECRB).
- Superficial branch of radial nerve
- Deep branch of radial nerve, becomes Posterior interosseus nerve and supplies muscles of the posterior compartment (ED, EDM, ECU, APL, EPB, EPL, EI).
- Ulnar nerve – supplies some medial muscles (FCU, med. 1/2 of FDP).
Vessels

Other structures
Function
The forearm can be brought closer to the upper arm (flexed) and brought away from the upper arm (extended) due to movement at the elbow. The forearm can also be rotated so that the palm of the hand rotates inwards (pronated) and rotated back so that the palm rotates outwards (supinated) due to movement at the elbow and the distal radioulnar joint.[5]
Clinical significance

A fracture of the forearm can be classified as to whether it involves only the ulna (ulnar fracture), only the radius (radius fracture), or both radioulnar fracture.
For treatment of children with torus fractures of the forearm splinting appears to work better than casting.[7] Genetically determined disorders like hereditary multiple exostoses can lead to hand and forearm deformities. Hereditary multiple exostoses is due growth disturbance of the epiphyses of the radius and ulna, the two bones of the forearm.[8]
Additional images
 Superficial muscles of the forearm
Superficial muscles of the forearm Deep muscles of the anterior forearm
Deep muscles of the anterior forearm Deep muscles of the posterior forearm
Deep muscles of the posterior forearm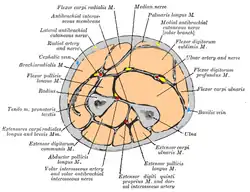 Cross-section through the middle of the forearm.
Cross-section through the middle of the forearm. Bones of the forearm - ulna (right) and radius (left)
Bones of the forearm - ulna (right) and radius (left)
See also
References
- WebMD (2009). "forearm". Webster's New World Medical Dictionary (3rd ed.). Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. p. 166. ISBN 978-0-544-18897-6.
- "Forearm". The Lecturio Medical Concept Library. Retrieved 2021-06-22.
- Mitchell, Brittney; Whited, Lacey (2020-08-15). "Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Forearm Muscles". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine. StatPearls Publishing LLC. Retrieved 22 June 2021.
- "Structure of The Forearm". The Lecturio Medical Concept Library. Retrieved 2021-06-22.
- Standring, Susan (2016). Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice (Forty-first ed.). [Philadelphia]. ISBN 9780702052309. OCLC 920806541.
- "Dissector Answers — Axilla & Arm". The University of Michigan. Archived from the original on 3 January 2008. Retrieved 2008-01-17.
- Jiang N, Cao ZH, Ma YF, Lin Z, Yu B (November 2016). "Management of Pediatric Forearm Torus Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". Pediatric Emergency Care. 32 (11): 773–778. doi:10.1097/pec.0000000000000579. PMID 26555307. S2CID 25796224.
- El-Sobky TA, Samir S, Atiyya AN, Mahmoud S, Aly AS, Soliman R (2018). "Current paediatric orthopaedic practice in hereditary multiple osteochondromas of the forearm: a systematic review". SICOT-J. 4: 10. doi:10.1051/sicotj/2018002. PMC 5863686. PMID 29565244.