Lusutrombopag
Lusutrombopag, sold under the brand name Mulpleta among others, is a medication that has been developed for certain conditions that lead to thrombocytopenia (abnormally low platelet counts) such as thrombocytopenia associated with chronic liver disease in patients prior to elective invasive procedures.[1] It is being manufactured and marketed in Japan by Shionogi.[2][3][4] It was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in July 2018, and NICE in January 2020.[5][6]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | loo" soo trom' boe pag |
| Trade names | Mulpleta, Mulpleo |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a618043 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
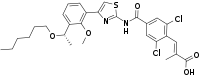
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H32Cl2N2O5S |
| Molar mass | 591.54 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
It was approved for medical use in the European Union in February 2019.[7]
References
- Shirley M, McCafferty EH, Blair HA (October 2019). "Lusutrombopag: A Review in Thrombocytopenia in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Prior to a Scheduled Procedure". Drugs. 79 (15): 1689–1695. doi:10.1007/s40265-019-01197-8. PMID 31529283. S2CID 202574131.
- Shionogi Receives Marketing and Manufacturing Approval in Japan for Mulpleta Tablets 3mg for Improvement of Thrombocytopenia, September 28, 2015
- Shionogi Launches Mulpleta Tablets 3mg In Japan for Improvement of Thrombocytopenia
- Lusutrombopag (Mulpleta) for severe thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic liver disease undergoing an elective invasive procedure
- "FDA approves lusutrombopag for thrombocytopenia in adults with chronic liver disease". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). July 31, 2018.
- "Overview | Lusutrombopag for treating thrombocytopenia in people with chronic liver disease needing a planned invasive procedure | Guidance | NICE".
- "Mulpleo EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Retrieved 17 June 2020.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.