Myoma
A myoma is a type of tumor that involves muscle cells.[1] There are two main types of myoma:
- Leiomyomas which occur in smooth muscle.[1] They most commonly occur as uterine fibroids, but may also form in other locations.
- Rhabdomyomas which occur in striated muscle.[1][2][3] They are rare tumors, occur in childhood and often become malignant.
| Myoma | |
|---|---|
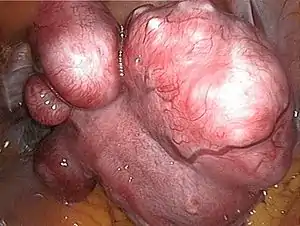 | |
| Uterine fibroids | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
Whether or not angiomyomas are a type of leiomyoma or a separate entity is disputed as of 2014.[3]
Myomas are benign tumors of the uterus that can affect the fertility of a woman depending mainly on three factors:
- Size (cut off value 4-5 cm)
- Number
- Location (they can be intramural, subserous or submucous). Submucous ones are worst from a fertility point of view, while subserous are less dangerous.
Some of the most common symptoms are: abundant menstrual bleeding, longer menstrual periods, pelvic pressure, constipation, a need to urinate continuously.
References
- Ziegler, Ernst (1883). A Text-book of pathological anatomy and pathogenesis pt. 1, 1883. William Wood & Company. p. 210.
- "MeSH Browser". meshb.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 9 November 2020.
- Rajendran, Arya; Sivapathasundharam, B. (2014). Shafer's Textbook of Oral Pathology. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 193. ISBN 978-81-312-3800-4.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.