Ventriculomegaly
Ventriculomegaly is a brain condition that mainly occurs in the fetus when the lateral ventricles become dilated. The most common definition uses a width of the atrium of the lateral ventricle of greater than 10 mm.[1] This occurs in around 1% of pregnancies.[2] When this measurement is between 10 and 15 mm, the ventriculomegaly may be described as mild to moderate. When the measurement is greater than 15mm, the ventriculomegaly may be classified as more severe.[3]
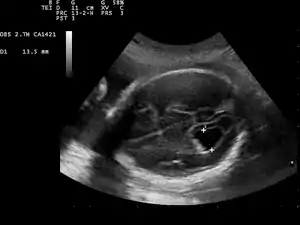
Enlargement of the ventricles may occur for a number of reasons, such as loss of brain volume (perhaps due to infection or infarction), or impaired outflow or absorption of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles, called hydrocephalus or normal pressure hydrocephalus associated with conspicuous brain sulcus. Often, however, there is no identifiable cause. The interventricular foramen may be congenitally malformed, or may have become obstructed by infection, hemorrhage, or rarely tumor, which may impair the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid, and thus accumulation in the ventricles.
This diagnosis is generally found in routine fetal anomaly scans at 18–22 weeks gestation. It is one of the more common abnormal brain findings on prenatal ultrasound, occurring in around 1–2 per 1,000 pregnancies.[4] In many cases of mild ventriculomegaly, however, there is resolution of ventriculomegaly during the pregnancy.
Associations
Ventriculomegaly is also known to be associated with other malformations such as agenesis of the corpus callosum, spina bifida, and heart defects. Fetuses with both isolated ventriculomegaly and with other anomalies have an increased risk of having a chromosomal abnormality, including that of Down syndrome.[3][5]
Many conditions associated with ventriculomegaly can be defined prior to birth, but the possibility remains of other anomalies (either structural, chromosomal or genetic) only being identified later in pregnancy or after birth.[6] Ventriculomegaly associated with abnormal findings and other structural malformations, often has an adverse prognosis, which ranges from disability (often mild) to death. However, in cases of mild isolated ventriculomegaly, there is around a 90% chance of a normal outcome.[5][7]
Increasingly, fetal magnetic resonance imaging is being considered as part of the assessment of pregnancies complicated by fetal ventriculomegaly,[8] and appears to be important in the postnatal assessment of affected children.[9]
Although evaluation of lateral ventricles dimensions is decisive for establishing a diagnosis of ventriculomegaly, the shape of the ventricular system, including that of the frontal horns, is also important.[10]
See also
References
- Cardoza, J D; Goldstein, R B; Filly, R A (December 1988). "Exclusion of fetal ventriculomegaly with a single measurement: the width of the lateral ventricular atrium". Radiology. 169 (3): 711–714. doi:10.1148/radiology.169.3.3055034. PMID 3055034.
- Salomon, L. J.; Bernard, J. P.; Ville, Y. (July 2007). "Reference ranges for fetal ventricular width: a non-normal approach". Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology. 30 (1): 61–66. doi:10.1002/uog.4026. PMID 17506037.
- Breeze, Andrew C. G.; Alexander, Peta M. A.; Murdoch, Edile M.; Missfelder-Lobos, Hannah H.; Hackett, Gerald A.; Lees, Christoph C. (February 2007). "Obstetric and neonatal outcomes in severe fetal ventriculomegaly". Prenatal Diagnosis. 27 (2): 124–129. doi:10.1002/pd.1624. PMID 17152115.
- Achiron, R.; Schimmel, M.; Achiron, A.; Mashiach, S. (1 March 1993). "Fetal mild idiopathic lateral ventriculomegaly: is there a correlation with fetal trisomy?". Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology. 3 (2): 89–92. doi:10.1046/j.1469-0705.1993.03020089.x. PMID 12797298.
- Gaglioti, P.; Danelon, D.; Bontempo, S.; Mombrò, M.; Cardaropoli, S.; Todros, T. (April 2005). "Fetal cerebral ventriculomegaly: outcome in 176 cases". Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology. 25 (4): 372–377. doi:10.1002/uog.1857. PMID 15791694.
- Breeze, Andrew C.G.; Dey, Prakash K.; Lees, Christoph C.; Hackett, Gerald A.; Smith, Gordon C.S.; Murdoch, Edile M. (1 January 2005). "Obstetric and neonatal outcomes in apparently isolated mild fetal ventriculomegaly". Journal of Perinatal Medicine. 33 (3): 236–40. doi:10.1515/JPM.2005.043. PMID 15914347. S2CID 8354468.
- Signorelli, M.; Tiberti, A.; Valseriati, D.; Molin, E.; Cerri, V.; Groli, C.; Bianchi, U. A. (January 2004). "Width of the fetal lateral ventricular atrium between 10 and 12 mm: a simple variation of the norm?". Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology. 23 (1): 14–18. doi:10.1002/uog.941. PMID 14970992.
- Glenn, OA; Barkovich, AJ (September 2006). "Magnetic resonance imaging of the fetal brain and spine: an increasingly important tool in prenatal diagnosis, part 1". American Journal of Neuroradiology. 27 (8): 1604–11. PMID 16971596.
- Falip, Céline; Blanc, Nathalie; Maes, Emmanuelle; Zaccaria, Isabelle; Oury, Jean François; Sebag, Guy; Garel, Catherine (28 August 2007). "Postnatal clinical and imaging follow-up of infants with prenatal isolated mild ventriculomegaly: a series of 101 cases". Pediatric Radiology. 37 (10): 981–989. doi:10.1007/s00247-007-0582-2. PMID 17724586. S2CID 10476912.
- Glonek, M; Kedzia, A; Derkowski, W (July 2003). "Prenatal assessment of ventriculomegaly: an anatomical study". Medical Science Monitor. 9 (7): MT69-77. PMID 12883459.