Eid al-Adha
Eid al-Adha (Arabic: عيد الأضحى, romanized: ʿĪd al-ʾAḍḥā, lit. 'Feast of the Sacrifice') is the second and the larger of the two main holidays celebrated in Islam (the other being Eid al-Fitr). It honours the willingness of Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son Ismail (Ishmael) as an act of obedience to Allah's command. Before Ibrahim could sacrifice his son, however, Allah provided him with a lamb which he was supposed to kill in his son's place because of his willingness to sacrifice his own son in the name of God. In commemoration of this intervention, animals are ritually sacrificed. Part of their meat is consumed by the family which offers the animal, while the rest of the meat is distributed to the poor and the needy. Sweets and gifts are given, and extended family members are typically visited and welcomed.[3] The day is also sometimes called the Greater Eid.[4]
| Eid ul-Adha | |
|---|---|
 Calligraphic fragment dated to 1729–30 displaying blessings for Eid ul-Adha in Arabic | |
| Official name | Eid ul-Adha |
| Observed by | Muslims |
| Type | Islamic |
| Significance | Commemoration of Abraham (Ibrahim)'s willingness to sacrifice his son in obedience of a command from God
|
| Observances | Eid prayers, animal slaughter, charity, social gatherings, festive meals, gift-giving |
| Begins | 10 Dhu al-Hijjah |
| Ends | 13 Dhu al-Hijjah |
| Date | 10 Dhu al-Hijjah |
| 2023 date | 28 June to 2 July[1] |
| 2024 date | 16 June to 20 June[2] |
| Related to | Hajj; Eid al-Fitr |
| Part of a series on |
| Islamic culture |
|---|
| Architecture |
| Art |
|
| Clothing |
| Holidays |
| Literature |
| Music |
|
| Theatre |
|
In the Islamic lunar calendar, Eid al-Adha falls on the tenth day of Dhu al-Hijjah and lasts for four days. In the international (Gregorian) calendar, the dates vary from year to year, shifting approximately 11 days earlier each year.
Pronunciation
Eid al-Adha is also pronounced Eid al-Azha and Eidul Azha, primarily in Iran and regions influenced by the Persian language like the Indian subcontinent; /ˌiːd əl ˈɑːdə, - ˈɑːdhɑː/ EED əl AH-də, - AHD-hah; Arabic: عيد الأضحى, romanized: ʿĪd al-ʾAḍḥā, IPA: [ʕiːd al ˈʔadˤħaː].[5]
Etymology
The Arabic word عيد (ʿīd) means 'festival', 'celebration', 'feast day', or 'holiday'. It itself is a triliteral root عيد with associated root meanings of "to go back, to rescind, to accrue, to be accustomed, habits, to repeat, to be experienced; appointed time or place, anniversary, feast day".[6][7] Arthur Jeffery contests this etymology, and believes the term to have been borrowed into Arabic from Syriac, or less likely Targumic Aramaic.[8]
The holiday is called عيد الأضحى (Eid-ul-Adha) or العيد الكبير (Eid-ul-Kabir) in Arabic.[9] The words أضحى (aḍḥā) and قربان (qurbān) are synonymous in meaning 'sacrifice' (animal sacrifice), 'offering' or 'oblation'. The first word comes from the triliteral root ضحى (ḍaḥḥā) with associated meanings of "immolate ; offer up ; sacrifice ; victimize".[10] No occurrence of this root with a meaning related to sacrifice occurs in the Qur'an[6] but in the Hadith literature. Arab Christians use the term to mean the Eucharistic host. The second word derives from the triliteral root قرب (qaraba) with associated meanings of "closeness, proximity... to moderate; kinship...; to hurry; ...to seek, to seek water sources...; scabbard, sheath; small boat; sacrifice".[7] Arthur Jeffery recognizes the same Semitic root, but believes the sense of the term to have entered Arabic through Aramaic.[8] The word is still used by Aramaic Christians for the Communion service, see Eucharist above. Compare Hebrew korban קָרבן (qorbān).
Origin
One of the main trials of Ibrahim's life was to face the command of Allah by killing his beloved son. According to the new narrative, Ibrahim kept having nightmares that he was sacrificing his son Ismail son of Hajar. Ibrahim knew that this was a command from Allah and he told his son, as stated in the Quran, "Oh son, I keep dreaming that I am slaughtering you". Ismail replied, "Father, do what you are ordered to do." Ibrahim prepared to submit to the will of Allah and to slaughter his son as an act of faith and obedience to Allah.[11] During the preparation, Shaytaan tempted Ibrahim and his family by trying to dissuade them from carrying out Allah's commandment, and Ibrahim drove Satan away by throwing pebbles at him. In commemoration of their rejection of Satan, stones are thrown during Hajj rites.at symbolic pillars, symbolising the place at which Satan tried to dissuade Ibrahim[12]
Acknowledging that Ibrahim was willing to sacrifice what is dear to him, Allah the Almighty honoured both Ibrahim and Ismail. Angel Jibreel called Ibrahim "O' Ibrahim, you have fulfilled the revelations." and a lamb from heaven was offered by Angel Jibreel to prophet Ibrahim to slaughter instead of Ismail. Muslims worldwide celebrate Eid al Adha to commemorate both the devotion of Ibrahim and the survival of Ismail.[13][14][15]
This story is known as the Akedah in Judaism (Binding of Isaac) and originates in the Torah,[16] the first book of Moses (Genesis, Ch. 22). The Quran refers to the Akedah as follows:[17]
100 My Lord! Bless me with righteous offspring.”
101 So We gave him good news of a forbearing son.
102 Then when the boy reached the age to work with him, Abraham said, “O my dear son! I have seen in a dream that I ˹must˺ sacrifice you. So tell me what you think.” He replied, “O my dear father! Do as you are commanded. Allah willing, you will find me steadfast.”
103 Then when they submitted ˹to Allah’s Will˺, and Abraham laid him on the side of his forehead ˹for sacrifice˺,
104 We called out to him, “O Abraham!
105 You have already fulfilled the vision.” Indeed, this is how We reward the good-doers.
106 That was truly a revealing test.
107 And We ransomed his son with a great sacrifice,
108 and blessed Abraham ˹with honourable mention˺ among later generations:
109 “Peace be upon Abraham.”
110 This is how We reward the good-doers.
111 He was truly one of Our faithful servants.
112 We ˹later˺ gave him good news of Isaac—a prophet, and one of the righteous.— Surah As-Saaffat 37:100–112
The word "Eid" appears once in Al-Ma'ida, the fifth surah of the Quran, with the meaning "a festival or a feast".[18]
Slaughter on Eid al-Adha
The tradition for Eid al-Adha involves slaughtering an animal and sharing the meat in three equal parts – for family, for relatives and friends, and for poor people. The goal is to make sure every Muslim gets to eat meat.[19][20]
Eid prayers

Devotees offer the Eid al-Adha prayers at the mosque. The Eid al-Adha prayer is performed any time after the sun completely rises up to just before the entering of Zuhr time, on the tenth of Dhu al-Hijjah. In the event of a force majeure (e.g. natural disaster), the prayer may be delayed to the 11th of Dhu al-Hijjah and then to the 12th of Dhu al-Hijjah.[21]
Eid prayers must be offered in congregation. Participation of women in the prayer congregation varies from community to community.[22] It consists of two rakats (units) with seven takbirs in the first Raka'ah and five Takbirs in the second Raka'ah. For Shia Muslims, Salat al-Eid differs from the five daily canonical prayers in that no adhan (call to prayer) or iqama (call) is pronounced for the two Eid prayers.[23][24] The salat (prayer) is then followed by the khutbah, or sermon, by the Imam.[25]
At the conclusion of the prayers and sermon, Muslims embrace and exchange greetings with one another (Eid Mubarak), give gifts and visit one another. Many Muslims also take this opportunity to invite their friends, neighbours, co-workers and classmates to their Eid festivities to better acquaint them about Islam and Muslim culture.[26]

Traditions and practices

During Eid ul-Adha, distributing meat amongst the people, chanting the takbir out loud before the Eid prayers on the first day and after prayers throughout the four days of Eid, are considered essential parts of this important Islamic festival.[27]
The takbir consists of:[28]
الله أكبر الله أكبر الله أكبر |
Allāhu akbar, allāhu akbar, allāhu akbar |
Men, women, and children are expected to dress in their finest clothing to perform Eid prayer in a large congregation in an open waqf ("stopping") field called Eidgah or mosque. Affluent Muslims who can afford it sacrifice their best halal domestic animals (usually a camel, goat, sheep, or ram depending on the region) as a symbol of Abraham's willingness to sacrifice his only son.[29] The sacrificed animals, called aḍḥiya (Arabic: أضحية), known also by the Perso-Arabic term qurbāni, have to meet certain age and quality standards or else the animal is considered an unacceptable sacrifice.[30] In Pakistan alone nearly ten million animals are sacrificed on Eid days, costing over $2 billion.[31]
The meat from the sacrificed animal is preferred to be divided into three parts. The family retains one-third of the share; another third is given to relatives, friends, and neighbors; and the remaining third is given to the poor and needy.[29]
Muslims wear their new or best clothes. People cook special sweets, including ma'amoul (filled shortbread cookies) and samosas. They gather with family and friends.[21]
Eid al-Adha in the Gregorian calendar

While Eid al-Adha is always on the same day of the Islamic calendar, the date on the Gregorian calendar varies from year to year since the Islamic calendar is a lunar calendar and the Gregorian calendar is a solar calendar. The lunar calendar is approximately eleven days shorter than the solar calendar.[32] Each year, Eid al-Adha (like other Islamic holidays) falls on one of about two to four Gregorian dates in parts of the world, because the boundary of crescent visibility is different from the International Date Line.[33]
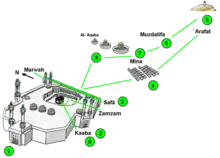
The following list shows the official dates of Eid al-Adha for Saudi Arabia as announced by the Supreme Judicial Council. Future dates are estimated according to the Umm al-Qura calendar of Saudi Arabia.[34] The Umm al-Qura calendar is just a guide for planning purposes and not the absolute determinant or fixer of dates. Confirmations of actual dates by moon sighting are applied on the 29th day of the lunar month prior to Dhu al-Hijjah[35] to announce the specific dates for both Hajj rituals and the subsequent Eid festival. The three days after the listed date are also part of the festival. The time before the listed date the pilgrims visit Mount Arafat and descend from it after sunrise of the listed day.[36]
In many countries, the start of any lunar Hijri month varies based on the observation of new moon by local religious authorities, so the exact day of celebration varies by locality.
| Islamic year | Gregorian date |
|---|---|
| 1421 | 5 March 2001 |
| 1422 | 22 February 2002 |
| 1423 | 11 February 2003 |
| 1424 | 1 February 2004 |
| 1425 | 20 January 2005 |
| 1426 | 30 December 2006 |
| 1427 | 20 December 2007 |
| 1428 | 8 December 2008 |
| 1429 | 27 November 2009 |
| 1430 | 16 November 2010 |
| 1431 | 6 November 2011 |
| 1432 | 26 October 2012 |
| 1433 | 14 October 2013 |
| 1434 | 5 October 2014 |
| 1435 | 24 September 2015 |
| 1436 | 12 September 2016 |
| 1437 | 2 September 2017 |
| 1438 | 20 August 2018 |
| 1439 | 11 August 2019 |
| 1440 | 31 July 2020 |
| 1441 | 20 July 2021 |
| 1442 | 9 July 2022 |
| 1443 | 28 June 2023 (calculated) |
| 1444 | 16 June 2024 (calculated) |
| 1445 | 6 June 2025 (calculated) |
| 1446 | 26 May 2026 (calculated) |
| 1447 | 16 May 2027 (calculated) |
| 1448 | 4 May 2028 (calculated) |
| 1449 | 23 April 2029 (calculated) |
| 1450 | 13 April 2030 (calculated) |
| 1451 | 2 April 2031 (calculated) |
| 1452 | 21 March 2032 (calculated) |
| 1453 | 11 March 2033 (calculated) |
| 1454 | 28 February 2034 (calculated) |
| 1455 | 17 February 2035 (calculated) |
| 1456 | 7 February 2036 (calculated) |
| 1457 | 26 January 2037 (calculated) |
| 1458 | 16 January 2038 (calculated ) |
Explanatory notes
-
Translation: Allah is the greatest, Allah is the greatest, Allah is the greatest
There is no god but Allah
Allah is greatest, Allah is greatest
and to Allah goes all praise.[21]
Because the Hijri year differs by about 11 days from the AD year, Eid al-Adha can occur twice a year, in the year 1029, 1062, 1094, 1127, 1159, 1192, 1224, 1257, 1290, 1322, 1355, 1387, 1420, 1452, 1485, 1518, 1550, 1583, 1615, 1648, 1681, 1713, 1746, 1778, 1811, 1844, 1876, 1909, 1941, 1974, 2006, 2039, 2072, 2104, 2137, 2169, 2202, 2235, 2267 and 2300. (will continue to occur every 32 or 33 years).
References
- "Islamic Holidays, 2010–2030 (A.H. 1431–1452)". InfoPlease. Archived from the original on 18 December 2019. Retrieved 8 September 2020.
- Hughes, David (18 July 2021). "When Eid al-Adha 2021 falls – and how long the festival lasts". inews.co.uk. Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- "Id al-Adha". Oxford Islamic Studies Online. Retrieved 11 July 2020.
- Haigh, Phil (31 July 2020). "What is the story of Eid al-Adha and why is it referred to as Big Eid?". Metro. Retrieved 25 April 2021.
Simply, Eid al-Adha is considered the holier of the two religious holidays and so it is referred to as 'Big Eid' whilst Eid al Fitr can be known as 'Lesser Eid'. Eid al-Kabir means 'Greater Eid' and is used in Yemen, Syria, and North Africa, whilst other translations of 'Large Eid' are used in Pashto, Kashmiri, Urdu and Hindi. This distinction is also known in the Arab world, but by calling 'Bari Eid' bari, this Eid is already disadvantaged. It is the 'other Eid'. 'Bari Eid', or Eid-ul-Azha, has the advantage of having two major rituals, as both have the prayer, but it alone has a sacrifice. 'Bari Eid' brings all Muslims together in celebrating Hajj, which is itself a reminder of the Abrahamic sacrifice, while 'Choti Eid' commemorates solely the end of the fasting of Ramazan.
- "Definition of Eid al-Adha | Dictionary.com". www.dictionary.com. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- Oxford Arabic Dictionary. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 2014. ISBN 978-0-19-958033-0.
- Badawi, Elsaid M.; Abdel Haleem, Muhammad (2008). Arabic–English Dictionary of Qur'anic Usage. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-14948-9.
- Jeffery, Arthur (2007). The Foreign Vocabulary of the Qur'ān. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-15352-3.
- Noakes, Greg (April–May 1992). "Issues in Islam, All About Eid". Washington Report on Middle East Affairs. Retrieved 28 December 2011.
- Team, Almaany. "Translation and Meaning of ضحى In English, English Arabic Dictionary of terms Page 1". almaany.com. Archived from the original on 26 August 2019. Retrieved 26 August 2019.
- Bate, John Drew (1884). An Examination of the Claims of Ismail as Viewed by Muḥammadans. BiblioBazaar. p. 2. ISBN 978-1117148366. Archived from the original on 6 February 2015. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
Ishmael sacrifice.
- Firestone, Reuven (1990). Journeys in Holy Lands: The Evolution of the -Ishmael Legends in Islamic Exegesis. SUNY Press. p. 98. ISBN 978-0791403310.
- "The Significance of Hari Raya Aidiladha". muslim.sg. Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 17 October 2019.
- Elias, Jamal J. (1999). Islam. Routledge. p. 75. ISBN 978-0-415-21165-9. Archived from the original on 10 June 2016. Retrieved 24 October 2012.
- Muslim Information Service of Australia. "Eid al – Adha Festival of Sacrifice". Missionislam.com. Archived from the original on 8 December 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2011.
- Stephan Huller, Stephan (2011). The Real Messiah: The Throne of St. Mark and the True Origins of Christianity. Watkins; Reprint edition. ISBN 978-1907486647.
- Fasching, Darrell J.; deChant, Dell (2011). Comparative Religious Ethics: A Narrative Approach to Global Ethics. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1444331332.
- Quran 5:114 -The Clear Quran— Jesus, son of Mary, prayed, “O Allah, our Lord! Send us from heaven a table spread with food as a feast for us—the first and last of us—and as a sign from You. Provide for us! You are indeed the Best Provider.” Quran 5:114 -Sahih International— Said Jesus, the son of Mary, "O Allāh, our Lord, send down to us a table [spread with food] from the heaven to be for us a festival for the first of us and the last of us and a sign from You. And provide for us, and You are the best of providers."
- "Qurbani Meat Distribution Rules". Muslim Aid.
- "Qurbani Meat Distribution Rules". islamicallrounder. 30 March 2022.
- H. X. Lee, Jonathan (2015). Asian American Religious Cultures [2 volumes]. ABC-CLIO. p. 357. ISBN 978-1598843309.
- Asmal, Fatima (6 July 2016). "South African women push for more inclusive Eid prayers". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 5 September 2016. Retrieved 12 September 2016.
- "Sunnah during Eid ul Adha according to Authentic Hadith". 13 November 2010. Archived from the original on 2 May 2013. Retrieved 28 December 2011 – via Scribd.
- حجم الحروف – Islamic Laws : Rules of Namaz » Adhan and Iqamah. Retrieved 10 August 2014
- "Eid ul-Fitr 2020: How to say Eid prayers". Hindustan Times. 23 May 2020. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- "The Significance of Eid". Isna.net. Archived from the original on 26 January 2013. Retrieved 28 December 2011.
- McKernan, Bethan (29 August 2017). "Eid al-Adha 2017: When is it? Everything you need to know about the Muslim holiday". .independent. Archived from the original on 9 August 2019. Retrieved 28 July 2018.
- "Eid Takbeers – Takbir of Id". Islamawareness.net. Archived from the original on 19 February 2012. Retrieved 28 December 2011.
- Buğra Ekinci, Ekrem (24 September 2015). "Qurban Bayram: How do Muslims celebrate a holy feast?". dailysabah. Archived from the original on 28 July 2018.
- Cussen, V.; Garces, L. (2008). Long Distance Transport and Welfare of Farm Animals. CABI. p. 35. ISBN 978-1845934033.
- Ahsan Butt (16 November 2010). "Bakra Eid: The cost of sacrifice". Asian Correspondent. Archived from the original on 28 December 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2011.
- Hewer, Chris (2006). Understanding Islam: The First Ten Steps. SCM Press. p. 111. ISBN 978-0334040323.
he Gregorian calendar.
- Staff, India com (30 July 2020). "Eid al-Adha or Bakrid 2020 Date And Time: History And Significance of The Day". India News, Breaking News, Entertainment News | India.com. Retrieved 31 July 2020.
- "Eid al-Adha 2016 date is expected to be on September 11". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 14 August 2016. Retrieved 14 August 2016.
- "Mount Ararat | Location, Elevation, & Facts". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
External links
 Media related to Eid al-Adha at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Eid al-Adha at Wikimedia Commons- Muttaqi, Shahid ‘Ali. "The Sacrifice of 'Eid al-Adha'".