Demography of the Roman Empire
Demographically, as in other more recent and thus better documented pre-modern societies, papyrus evidence from Roman Egypt[1] suggests the demographic profile of the Roman Empire had high infant mortality, a low marriage age, and high fertility within marriage. Perhaps half of the Roman subjects died by the age of 5. Of those still alive at age 10, half would die by the age of 50.
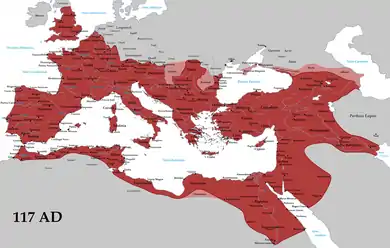
During the 1st and 2nd centuries, the Roman Empire had a population estimated in the range of 59 to 76 million.[2] The population likely peaked just before the Antonine Plague. Harper[3] provides an estimate of a population of 75 million and a population density of about 20 people per square kilometre during its peak. In contrast to other ancient and medieval societies, the Roman Empire appears to have had unusually high urbanization rates. During the 1st and 2nd centuries CE, the population of the city of Rome is conventionally estimated at one million inhabitants. Ian Morris[4] estimated that no other city in Western Eurasia would have as many again until the 19th century.
Background
For the lands around the Mediterranean Sea, and their hinterlands, the period from the second millennium BCE to the early first millennium CE was one of substantial population growth. What would become the territory of the Roman Empire saw an average annual population growth of about 0.1 percent from the 12th century BCE to the 3rd century CE, resulting in a quadrupling of the region's total population. Growth was slower around the eastern Mediterranean, which was already more developed at the beginning of the period, on the order of about 0.07 percent per year.[5] This was stronger growth than that seen in the succeeding period; from about 200 CE to 1800 CE, the European half of the empire only saw about 0.06 to 0.07 percent annual growth (Europe as a whole saw 0.1 percent annual growth rates), and the north African and west Asian parts of the empire saw almost no growth at all.[6]
By comparison, what is now the territory of China experienced 0.1 percent annual growth from 1 CE to 1800 CE. After a population decline following the disintegration of the western half of the Roman state in the fifth and sixth centuries, Europe probably re-attained Roman-era population totals in the twelfth and thirteenth centuries and, following another decline associated with the Black Death, consistently exceeded them after the mid-15th century.[6]
There are no reliable surviving records for the general demography of the Roman Empire. There are no detailed local records, such as underlie the demographic study of early modern Europe, either. Large numbers of impressionistic, moralizing and anecdotal observations on demography survive from literary sources. They are of little use in the study of Roman demography, which tends to rely instead on conjecture and comparison, rather than records and observations.[7]
Mortality
When the high infant mortality rate is factored in (life expectancy at birth) inhabitants of the Roman Empire had a life expectancy at birth of about 22–33 years.[8][9][10] When infant mortality is factored out (i.e., counting only those who survived the first year, 67[8]-75% of the population), life expectancy is around 34-41 more years (i.e., expected to live to age 35–42). When child mortality is factored out (i.e., counting only those who survived to age 5, 55–65% of the population), life expectancy is around 40–45.[9] The ~50% that reached age 10 could also expect to reach ~45-50.[8] The 46-49% that survived to their mid-teens could, on average, expect to reach around 48–54,[9] although of course many lived much longer or shorter lives for varied reasons, including wars for males and childbirth for females. Although these figures rely more on conjecture than ancient evidence, which is sparse and of dubious quality, it is a point of general consensus among historians of the period. It originates in cross-country comparison: given the known social and economic conditions of the Roman Empire, we should expect a life expectancy near the lower bound of known pre-modern populations. Roman demography bears comparison to available data for India and rural China in the early 20th century, where life expectancies at birth were also in the low 20s.[11]
About 300 census returns filed in Egypt in the first three centuries CE survive. R. Bagnall and B. Frier have used them to build female and male age distributions, which show life expectancies at birth of between 22 and 25 years, results broadly consistent with model life tables.[12] Other sources used for population reconstructions include cemetery skeletons, Roman tombstones in North Africa, and an annuities table known as "Ulpian's life table". The basis and interpretation of these sources is disputed: the skeletons cannot be firmly dated, the tombstones show non-representative sample populations, and the sources of "Ulpian's life table" are unknown. Nonetheless, because they converge with low Roman elite survival rates shown in the literary sources, and because their evidence is consistent with data from populations with comparably high mortality rates, such as in 18th century France, and early 20th century China, India, and Egypt, they reinforce the basic assumption of Roman demography: that life expectancies at birth were in the low 20s.[13]
As no population for which accurate observations survive has such a low life expectancy, model life tables must be used to understand this population's age demography. These models, based on historical data, describe 'typical' populations at different levels of mortality. For his demographic synopsis of the Roman Empire, Bruce Frier used the Model West framework, as it is "the most generalized and widely applicable".[14] Because it is based on only one empirical input, the model life table can provide only a very approximate picture of Roman demography. On two important points, the table may seriously misrepresent the Roman situation: the structural relationship between juvenile and adult mortality, and the relative mortality rates across the sexes.[15] In any case, Roman mortality should be expected to have varied greatly across times, places, and perhaps classes.[16][notes 1] A variation of ten years would not have been unusual. A life expectancy range of between 20 and 30 years is therefore plausible,[18] though it may have been exceeded in either direction in marginal regions (e.g., malarious urban districts on one end; high-altitude, low-density settlements on the other).[13]
| Model West, level 3: a possible life table for the Roman Empire | ||||||
| Females | Males | |||||
| Age | Mortality | Cohort | Life expectancy | Mortality | Cohort | Life expectancy |
| 0 | 0.3056 | 100,000 | 25.0 | 0.3517 | 100,000 | 22.8 |
| 1 | 0.2158 | 69,444 | 34.9 | 0.2147 | 64,826 | 34.1 |
| 5 | 0.0606 | 54,456 | 40.1 | 0.0563 | 50,906 | 39.0 |
| 10 | 0.0474 | 51,156 | 37.5 | 0.0404 | 48,041 | 36.2 |
| 15 | 0.0615 | 48,732 | 34.2 | 0.0547 | 46,099 | 32.6 |
| 20 | 0.0766 | 45,734 | 31.3 | 0.0775 | 43,579 | 29.4 |
| 25 | 0.0857 | 42,231 | 28.7 | 0.0868 | 40,201 | 26.6 |
| 30 | 0.0965 | 38,614 | 26.1 | 0.1002 | 36,713 | 23.9 |
| 35 | 0.1054 | 34,886 | 23.7 | 0.1168 | 33,035 | 21.3 |
| 40 | 0.1123 | 31,208 | 21.1 | 0.1397 | 29,177 | 18.7 |
| 45 | 0.1197 | 27,705 | 18.5 | 0.1597 | 25,101 | 16.4 |
| 50 | 0.1529 | 24,389 | 15.6 | 0.1981 | 21,092 | 14.0 |
| 55 | 0.1912 | 20,661 | 13.0 | 0.2354 | 16,915 | 11.8 |
| 60 | 0.2715 | 16,712 | 10.4 | 0.3091 | 12,932 | 9.6 |
| 65 | 0.3484 | 12,175 | 8.4 | 0.3921 | 8,936 | 7.7 |
| 70 | 0.4713 | 7,934 | 6.5 | 0.5040 | 5,432 | 6.1 |
| 75 | 0.6081 | 4,194 | 4.9 | 0.6495 | 2,694 | 4.6 |
| 80 | 0.7349 | 1,644 | 3.6 | 0.7623 | 944 | 3.4 |
| 85 | 0.8650 | 436 | 2.5 | 0.8814 | 225 | 2.4 |
| 90 | 0.9513 | 59 | 1.8 | 0.9578 | 27 | 1.7 |
| 95 | 1.0000 | 3 | 1.2 | 1.0000 | 1 | 1.2 |
| After Frier, "Demography", 789, table 1.[notes 2] | ||||||
The specifics of any ancient age distribution, moreover, would have seen heavy variation under the impact of local conditions.[13] In pre-modern societies, the major cause of death was not the chronic, end-of-life conditions that characterize mortality in industrialized societies, nor primary malnutrition, but acute infectious disease, which has varied effects on age distributions in populations. Pulmonary tuberculosis, for example, characterized much of the Roman region in antiquity; its deaths tend to be concentrated in the early twenties, where model life tables show a mortality trough.[19] Similarly, in pre-modern societies for which evidence is available, such as early modern England and early eighteenth-century China, infant mortality varies independently of adult mortality, to the extent that equal life expectancies at age twenty can be obtained in societies with infant mortality rates of 15% to 35% (life table models omit this; they depend on the assumption that age-specific mortality ratios co-vary in uniform, predictable ratios).[20] No ancient evidence can gauge this effect (the sources have a strong tendency to overlook infant death), and the model life tables might overstate it, but comparative evidence suggests that it is very high: mortality was strongly concentrated in the first years of life.[21]
Mortality on this scale:
- discourages investment in human capital, hindering productivity growth (adolescent mortality rates in Rome were two-thirds higher than in early modern Britain);
- creates large numbers of dependent widows and orphans; and
- hinders long-term economic planning.
With the prevalence of debilitating diseases, the number of effective working years was even worse: health-adjusted life expectancy (HALE), the number of years lived in good health, varies from life expectancy by no more than 8% in modern societies; in high-mortality societies such as Rome, it could be as much as one-sixth (17%) beneath total life expectancy. A HALE of less than 20 years would have left the empire with very depressed levels of economic productivity.[22]
Fertility
To maintain replacement levels under such a mortality regime—much less to achieve sustained growth—fertility figures needed to be very high. With life expectancies of twenty to thirty, women would have to give birth to between 4.5 and 6.5 children to maintain replacement levels. Given elevated levels of divorce, widowhood, and sterility, however, the birth rate would have needed to be higher than that baseline, at around 6 to 9 children per woman.[23] Fertility could not long have either fallen below or outstripped replacement levels. A population which maintained an annual growth or decline of 0.7% would double or halve itself every century. Such rates are feasible locally or over a short period of time, and deaths could consistently outstrip births during epidemics, but, in the long term, convergence to maintenance levels was the rule.[24]
The surviving census returns from Roman Egypt speak to a population that had not yet undergone the "fertility transition"; artificial fertility controls like contraception and abortion were not widely used to alter natural fecundity in the Roman period. Only family limitation, in which couples ceased procreating after they had attained an acceptable level of children, could have been widespread.[25] There is no indication that even this limitation was widespread, however; the recorded distribution shows no evidence of being governed by parity or maternal age.[26]
| Marital fertility in Roman Egypt | ||||||
| Age | Roman Egypt | Natural fertility | ||||
| Attested rates | Gompertz Model | |||||
| 12–14 | 22 | 23 | 225 | |||
| 15–19 | 232 | 249 | 420 | |||
| 20–24 | 343 | 333 | 460 | |||
| 25–29 | 367 | 325 | 431 | |||
| 30–34 | 293 | 299 | 396 | |||
| 35–39 | 218 | 262 | 321 | |||
| 40–44 | 219 | 166 | 167 | |||
| 45–49 | 134 | 37 | 24 | |||
| After Frier, "Natural fertility", 325, table 1.[notes 3] | ||||||
Imperial Rome largely conforms to what is known as the "Mediterranean" pattern of marital fertility: men married late and women married early.[28] The evidence on marriage age is fairly robust for Roman elites: men in the senatorial class were expected to marry in their early twenties; women were expected to marry in their early teens. According to the most plausible interpretation of the evidence from funerary commemoration, in the lower classes, women married in their late teens or early twenties, and men married in their late twenties or early thirties.[29]
The Roman pattern thus stands in contrast to the "Eastern" (i.e., East Asian) pattern, in which both men and women married young.[28] China, the major example of the "Eastern" pattern, also had lower levels of fertility than Rome. This was apparently achieved by a combination of prolonged breastfeeding, female infanticide, and male celibacy, though the details are controversial.[30] Roman families share some features of the "Eastern" pattern. Roman Egypt, for example, had a custom of extended breastfeeding, which may have lengthened birth spacing. Egyptian fertility levels are comparable to those recorded in the early modern Japanese village Nakahara, where about half the population practiced family limitation. On the historian Walter Scheidel's judgment, this speaks to the incidence of family limitation even in what are supposedly "natural fertility" regimes.[31]
Roman and Greek literary and legal tradition also makes frequent reference to the "Eastern" demographic features infanticide and child exposure. Although the extent of these practices is unlikely to have been small, it is nonetheless impossible to quantify (nor can reported gender ratios permit judgment on the prevalence of femicide). These "Eastern" features did not prevail in medieval or modern Europe, where there were cultural and structural factors directly discouraging them or diminishing their effects on childhood mortality (religious doctrine, legal enforcement, institutions of foundling care, child labor, wet-nursing, etc.). These constraints were weak or absent in Greek and Roman society.[32]
Migration
According to the Cavalli–Sforza reconstruction of genetic history, there was little migration in Europe after the Iron Age. Most population growth can therefore be ascribed to the gradual expansion of local populations under conditions of improving fertility, rather than inter-regional transfer. That said, local migration from village to village may have been substantial; for the successful dedication and expansion of new settlements, it would have been necessary. The geography of the Mediterranean made this fairly convenient;[33] at the beginning of the empire, about 750,000 Italians lived in the provinces.[34] Julius Caesar, Mark Anthony and Octavian–Augustus settled many of their veterans in colonies, in Italy, and the provinces. Those established in Italy up to 14 BCE have been studied by Keppie (1983). In his account of the achievements of his long reign (Res Gestae), Augustus stated that he had settled 120,000 soldiers in twenty colonies in Italy in 31 BCE, then 100,000 men in colonies in Spain and southern Gaul in 14 BCE, followed by another 96,000 in 2 BCE.[35] Brian Campbell also states "From 49 to 32 BCE about 420,000 Italians were recruited" – which would thus be the Veteran (citizen) stock that was largely sent to the provinces (colonies) during Augustus; The Lex Calpurnia however also allowed citizenship to be granted for distinguished bravery – as example the 1,000 Socii from Camerinum after Vercellae 101 BCE (Plutarch Mar. XXXVIII) or the auxiliary (later Legio XXII Deiotariana) after Zela. By the time of Augustus the legions consisted mostly of ethnic Latins/Italics and Cisalpine Gauls.[36] Historian Theodore Mommsen estimated that under Hadrian nearly 1/3 of the eastern Numidia population (roughly modern Tunisia) was descended from Roman veterans.[37]
Population
Modern estimates of the population of the Roman Empire started with the fundamental work of 19th-century historian Karl Julius Beloch.[38] His estimates of the area of different components of the empire, based on planimetric estimates by contemporary military cartographers, have not been challenged by any more modern analyst. By providing a check to population densities, these area figures compel a baseline level of plausibility.[39] Beloch's 1886 estimate of the population of the empire in 14 CE has withstood contemporary and more recent criticism, and underlies modern analysis (his 1899 revision of those figures is less esteemed). Only his estimates for Anatolia and Greater Syria required extensive revision; Beloch estimated population figure, 19 million, produced population densities not otherwise achieved in those areas until the 20th century. Bruce Frier, in a recent estimate of the population of the empire, suggested a figure of 12 million as "considerably more plausible".[40] Beloch's figures for Spain and Africa have also been revised downwards.[41] In a more recent publication, Kyle Harper suggests 75 million for the empire as a whole with 16 million for Anatolia and Greater Syria.[42]
This estimate produces a population density of ca. 20 inhabitants per square kilometer a low figure by modern standards (the United Kingdom, for example, has a population density of 254.7/km2). The population density in the Greek East was 24/km2, denser than the Latin West at 17/km2; only the Western provinces of Italy and Sicily had a density higher than the average of the East.[43]
| Estimate of the Population of the Empire | |||
| Region | Area (1000 km2) |
Mid-2nd century CE Population (millions) |
Mid-2nd century CE Density (per km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greek peninsula[notes 4] | 160 | 3 | 19 |
| Anatolia | 670 | 10 | 15 |
| Greater Syria[notes 5] | 140 | 6 | 43 |
| Egypt[notes 6] | 30 | 5 | 167 |
| Greek East | 1,000 | 24 | 24.0 |
| Britain | 160 | 2 | 13 |
| Italy (w/ islands) | 310 | 14 | 45 |
| North Africa | 420 | 8 | 19 |
| Iberia | 590 | 9 | 15 |
| Gaul and Germany | 680 | 12 | 18 |
| Danube Region[notes 7] | 670 | 6 | 9 |
| Latin West | 2,830 | 49 | 17.3 |
| Roman Empire | 3,830 | 75 | 19.6 |
| "Area" includes the client kingdoms taken over soon after 14 CE. After Harper (2017), page 30, table 2.1. | |||
Harper [46] estimates the population at the time of Augustus at 60 million, a discrepancy of 10% from Beloch's 1886 estimate, and suggests a population growth rate of 0.1% per year, reaching 75 million after nearly two centuries of growth. Current estimates suggest that slaves constituted about 15 percent of the Empire's total population; the proportionate figure would be much higher in Italy and much lower in Africa and Egypt.[47]
Bruce Frier's estimate produces a population density of 13.6 inhabitants per square kilometer. The population density in the Greek East was 20.9/km2, twice as dense as the Latin West at 10.6/km2; only the Western provinces of Italy and Sicily had a density comparable to the East.[48]
| Estimate of the Population of the Empire | ||||||
| Region | Area (1000 km2) |
14 CE Population (millions) |
14 CE Density (per km2) |
164 CE Population (millions) |
164 CE Density (per km2) |
Population increase (per cent) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greek peninsula[notes 8] | 267 | 2.8 | 10.5 | 3.0 | 11.2 | 7.1 |
| Anatolia | 547 | 8.2 | 15.0 | 9.2 | 16.8 | 12.2 |
| Greater Syria[notes 9] | 109 | 4.3 | 39.4 | 4.8 | 44.0 | 11.6 |
| Cyprus | 9.5 | 0.2 | 21.2 | 0.2 | 21.1 | – |
| Egypt[notes 10] | 28 | 4.5 | 160.7 | 5.0 | 178.6 | 11.1 |
| Libya[notes 11] | 15 | 0.4 | 26.7 | 0.6 | 40.0 | 50.0 |
| Greek East | 975.5 | 20.4 | 20.9 | 22.9 | 23.5 | 12.3 |
| Annexations | 0.2 | |||||
| Greek East (with annexations) | 23.1 | |||||
| Italy | 250 | 7.0 | 28.0 | 7.6 | 30.4 | 8.6 |
| Sicily | 26 | 0.6 | 23.1 | 0.6 | 23.1 | – |
| Sardinia and Corsica | 33 | 0.5 | 15.2 | 0.5 | 15.2 | – |
| Maghreb[notes 12] | 400 | 3.5 | 8.8 | 6.5 | 16.3 | 85.7 |
| Iberia | 590 | 5.0 | 8.5 | 7.5 | 12.7 | 50.0 |
| Gaul and Germany | 635 | 5.8 | 9.1 | 9.0 | 14.2 | 55.2 |
| Danube Region[notes 13] | 430 | 2.7 | 6.3 | 4.0 | 9.3 | 48.1 |
| Latin West | 2,364 | 25.1 | 10.6 | 35.7 | 15.1 | 42.2 |
| Annexations | 2.5 | |||||
| Latin West (with annexations) | 38.2 | |||||
| Roman Empire | 3,339.5 | 45.5 | 13.6 | 61.4 | 15.9 | 34.9 |
| "Area" includes the client kingdoms taken over soon after 14 CE. After Frier, "Demography", 812, table 5, 814, table 6. | ||||||
| Estimated Distribution of Citizenship in the Roman Empire[49] | ||||||
| Region | Citizens (per cent) |
Noncitizen residents (per cent) |
Slaves (per cent) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rome | 55 | 15 | 30 | |||
| Italy | 70 | 5 | 25 | |||
| Spain and Gaul | 10 | 70 | 20 | |||
| Other Western Provinces | 3 | 80 | 17 | |||
| Greece and Asia Minor | 3 | 70 | 27 | |||
| North African Provinces | 2 | 70 | 28 | |||
| Other Eastern Provinces | 1 | 80 | 19 | |||
There are few recorded population numbers for the whole of antiquity, and those that exist are often rhetorical or symbolic. Unlike the contemporaneous Han dynasty, no general census survives for the Roman Empire. The late period of the Roman Republic provides a small exception to this general rule: serial statistics for Roman citizen numbers, taken from census returns, survive for the early Republic through the 1st century CE.[50] Only the figures for periods after the mid-3rd century BCE are reliable, however. Fourteen figures are available for the 2nd century BCE (from 258,318 to 394,736). Only four figures are available for the 1st century BCE, and are feature a large break between 70/69 BCE (910,000) and 28 BCE (4,063,000). The interpretation of the later figures—the Augustan censuses of 28 BCE, 8 BCE, and 14 CE—is therefore controversial.[51] Alternate interpretations of the Augustan censuses (such as those of E. Lo Cascio[52]) produce divergent population histories across the whole imperial period.[53]
| Population of Italy and the islands in 165 CE | ||||||
| Population (millions) |
Area (1000 km2) |
Density (per km2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard interpretation of the Augustan censuses | 8–9 | 310 | 26–29 | |||
| Revised interpretation of the Augustan censuses | 12–13 | 310 | 39–42 | |||
| After Scheidel, "Demography", 47 n. 42, 47. | ||||||
The enfranchisement of the Cisalpine provinces and the Italian Allies after the Social War would account for some of the population growth of the 1st century BCE.[54] Alternate readings of the Augustan census both accept the basic accuracy of the figures, but assume different methods on the part of the census-takers. The standard interpretation assumes that the census-takers included all citizens—men, women, and children—in the Augustan censuses; the revised interpretation assumes that the census-takers only counted adult men, as they had during the Republican period. The standard interpretation is not supported by any evidence internal to the text, but reduces the implied population totals for 28 BCE Italy from 10 million to a more plausible 4 million.[55] The high total earns support from recorded conflict over land in the late Republic and other indications of population pressure, but does not accord well with comparative evidence from other periods and other parts of the empire.[56]
Earlier Estimates
Beloch's 1886 estimate for the population of the empire during the reign of Augustus:[57][58]
| Region | Population (in millions) |
|---|---|
| Total Empire | 54 |
| European part | 23 |
| Asian part | 19.5 |
| North African part | 11.5 |
Russell's 1958 estimate for the population of the empire in 350 CE:[58]
| Region | Population (in millions) |
|---|---|
| Total Empire | 39.3 |
| European part | 18.3 |
| Asian part | 16 |
| North African part | 5 |
Recent demographic studies have argued for a population peak ranging from 70 million (comparable to the contemporaneous and similarly sized Han empire in China), with one-tenth of them located in Italy itself, to more than 100 million.[59]

Urbanization

By the standards of pre-modern economies, the Roman Empire was highly urbanized.
According to recent work, there are at least 1,388 identified urban sites in the Roman world dated from the Late Republican and Early Imperial period.[60] At its peak, the city of Rome had at least one million inhabitants, a total not equaled again in Europe until the 19th century.[60][61] As the imperial capital, Rome was sustained by transfers in kind from throughout the empire; no other city could be sustained at this level. The other major cities in the empire (Alexandria, Antioch, Carthage, Ephesus, Salona etc.) had populations of over a hundred thousand, with Alexandria having a population estimated at around half a million.[60][61] Most of these 1,388 cities were small, usually possessing around 5,000 inhabitants. Out of the 885 cities whose build-up area has been estimated, slightly less than half, 405 cities, have an area that suggests a population larger than 5,000, and approximately 8% (69 out of 885) of the sites have an area that suggests a population larger than 30,000. Using a population threshold of 5,000 individuals and extrapolating from the sample of 885 cities with estimated build-up area to all 1,388 cities, the cumulative urban population of the empire can be estimated at around 14 million in the ca. 600 cities with over 5,000 inhabitants, given the conventional estimates for the total population of the empire at 50 to 60 million this implies an urbanization rate of 25–30%, a rate of urbanization that is twice as high as that of Europe at the turn of the 19th century.[60][61]
High mortality rates and pre-modern sanitary conditions made urban regions net population sinks, with more local deaths than births. They could only be sustained by constant immigration.[62] The large cities provided a major stimulus to demand, and not only for agricultural products but for manufactured goods and luxury items as well.[63]
Earlier Estimates
Russell (1958) produced estimates for the urban population in Late Antiquity, these estimates are much lower than more recent estimates which refer to the Early Imperial Period, they are as follows.[58]
| City | Population (thousands) |
Region |
|---|---|---|
| Rome | 350 | Italy |
| Alexandria | 216 | Egypt |
| Antioch | 90 | Syria |
| Smyrna | 90 | Asia Minor |
| Cádiz | 65 | Hispania |
| Salona | 60 | Dalmatia |
| Ephesus | 51 | Asia Minor |
| Carthage | 50 | Africa |
| Corinth | 50 | Greece |
| Jerash | 40 | Jordan |
| Apamea | 37 | Syria |
| Capua | 36 | Italy |
| Ancyra | 34 | Asia Minor |
| Nicomedia | 34 | Asia Minor |
| Oxyrhyncus | 34 | Egypt |
| Memphis | 34 | Egypt |
| Damascus | 31 | Syria |
| Bostra | 30 | Syria |
| Athens | 28 | Greece |
| Tarragona | 27 | Hispania |
| Cyzicus | 24 | Asia Minor |
| Hermopolis | 24 | Egypt |
| Pergamum | 24 | Asia Minor |
| Mytilene | 23 | Asia Minor |
| Arsinoe | 20 | Egypt |
| Córdoba | 20 | Hispania |
| Cirta | 20 | Africa |
| Hadrumetum | 20 | Africa |
| Pisa | 20 | Italy |
| Rusicade | 20 | Africa |
| Tyre | 20 | Syria |
| Catania | 18 | Italy |
| Nicaea | 18 | Asia Minor |
| Antiochia | 17 | Asia Minor |
| Antinoe | 16 | Egypt |
| Sicca V. | 16 | Africa |
| Mérida | 15 | Hispania |
| Miletus | 15 | Asia Minor |
| Naples | 15 | Italy |
| Heliopolis | 14 | Egypt |
| Baalbek | 13.5 | Syria |
| Thugga | 13 | Africa |
| Isaura | 12 | Asia Minor |
| Sidon | 12 | Syria |
| Bologna | 10 | Italy |
| Cartagena | 10 | Hispania |
| Hippo Regis | 10 | Africa |
| Jerusalem | 10 | Syria |
| Lambraesis | 10 | Africa |
| Pamplona | 10 | Hispania |
| Thysdrus | 10 | Africa |
| Trebizond | 10 | Asia Minor |
Notes
- Frier elsewhere quotes material to the effect that cross-class variation in life expectancy in high mortality societies is small.[17]
- "Mortality" is a function predicting the likelihood that a person aged exactly (x) will die before the next indicated interval; "cohort" lists the number of survivors to exact age (x).
- The Gompertz figures are obtained using linear regression on the census figures to create a relational fertility model, producing a probable schedule of true fertility rates. The model uses two values, α and β, that determine the model's relationship to a standard of early marriage and natural fertility. For this dataset, α, which indicates variation from median age of marital maternity, is −0.05, and β, which indicates the degree of fertility concentration, is 0.80. As the standard figure for β is 1.0, the dataset for Roman Egypt shows a wider spread of childbearing than is typical of the standard.[27]
- Roughly includes the southern Balkan peninsula; Greece, Albania, North Macedonia, and Serbia. Or approximately the Roman provinces of Achaea, Macedonia, and Epirus.[44]
- Defined to include the modern territories of Lebanon, Israel and Palestine, as well as approximately the western half of Syria (i.e. the coastal Levant).[45]
- Area figure is only the narrow strip of land along the Nile and its delta. Not the vast deserts of Egypt.[45]
- Areas generally south of the river Danube. Includes the Roman provinces of Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia Superior, Pannonia Inferior, Illyricum (or Dalmatia) and Moesia (Superior and Inferior). Parts of modern Switzerland, southern Germany and Austria, western Hungary, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia, Montenegro, central Serbia and northern Bulgaria.[45]
- Roughly includes the southern Balkan peninsula; Greece, Albania, North Macedonia, Serbia, about half of Bulgaria and European Turkey. Or approximately the Roman provinces of Achaea, Macedonia, Epirus and Thracia.[45]
- Defined to include the modern territories of Lebanon, Israel and Palestine, as well as approximately the western half of Syria (i.e. the coastal Levant).[45]
- Area figure is only the narrow strip of land along the Nile and its delta. Not the vast deserts of Egypt.[45]
- Refers only to the coastal area of Cyrenaica.[45]
- Refers to the coastal area of North Africa. i.e. Northern areas of Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and most of coastal Libya (except Cyrenaica).[45]
- Areas generally south of the river Danube. Includes the Roman provinces of Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia Superior, Pannonia Inferior, Illyricum (or Dalmatia) and Moesia (Superior and Inferior). Parts of modern Switzerland, southern Germany and Austria, western Hungary, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia, Montenegro, central Serbia and northern Bulgaria.[45]
References
Citations
- Scheidel, "Demography".
- Scheidel, "Demography".
- Harper, "Fate of Rome" (2017)
- Morris, "The Measure of Civilization" Date 2013.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 42–43.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 43.
- Frier, "Demography", 787; Scheidel, "Demography", 42.
- Boatwright, Mary T. (2021). Imperial Women of Rome: Power, Gender, Context. Oxford University Press. p. 87. ISBN 978-0-19-045589-7.
- Saller, Richard P. (1997). Patriarchy, Property and Death in the Roman Family. Cambridge [England]: Cambridge University Press. pp. 22–25. ISBN 978-0-521-59978-8.
-
- Ryan, Garrett (1 September 2021). Naked Statues, Fat Gladiators, and War Elephants: Frequently Asked Questions about the Ancient Greeks and Romans. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 44. ISBN 978-1-63388-703-9.
- Scheidel, Walter (2017). Debating Roman Demography. BRILL. p. 29. ISBN 978-90-04-35109-7.
25-30
- Flower, Harriet I. (2014). The Cambridge Companion to the Roman Republic. Cambridge University Press. p. 105. ISBN 978-1-139-99238-1.
- Scheidel, Walter (2006). "Growing up fatherless in antiquity: the demographic background" (PDF): 2.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Carrieri, Maria Patrizia; Serraino, Diego (1 December 2005). "Longevity of popes and artists between the 13th and the 19th century". International Journal of Epidemiology. 34 (6): 1435–1436. doi:10.1093/ije/dyi211.
- Wolf, Arthur P. (2005). Inbreeding, Incest, and the Incest Taboo: The State of Knowledge at the Turn of the Century. Stanford University Press. p. 97. ISBN 978-0-8047-5141-4.
- Kotre, John N.; Hall, Elizabeth (1997). Seasons of Life: The Dramatic Journey from Birth to Death. University of Michigan Press. pp. 47–49. ISBN 978-0-472-08512-5.
- Frier, "Demography", 788.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 38–39.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 39.
- Frier, "Demography", 788. On this model, Frier cites A. J. Coale and P. Demeny Regional Model Life Tables and Stable Populations, 2nd ed. (Princeton, 1983).
- Frier, "Demography", 789. See also the extensive criticism in Scheidel, "Roman age structure", 1–26.
- Frier, "Demography", 789.
- Frier, "Roman life expectancy", 228 n. 36.
- Frier, "Demography", 789; Scheidel, "Demography", 39.
- Scheidel, "Roman age structure", 8.
- Scheidel, "Roman age structure", 6–7.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 40.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 40–41.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 41.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 41–42.
- Frier, "Natural fertility", 318–26; Scheidel, "Demography", 66–67.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 67.
- Frier, "Natural fertility", 325–26.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 68.
- Saller, "Household", 90.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 68–69.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 69.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 69–70.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 49–50.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 49–50, 64, 64 n. 114, citing P. A. Brunt, Italian Manpower 225 B.C.–A.D. 14 (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1987), 263.
- Pat Southern – The Roman Army: A Social and Institutional History (2006/Oxford Uni.)
- B. Campbell The Roman Army, 31 BC–AD 337 p.9
- Abun-Nasr, A History of the Maghrib (1970, 1977) at 35–37.
- Frier, "Demography", 811; Maddison, Contours of the World Economy, 32–33.
- Maddison, Contours of the World Economy, 33.
- Frier, "Demography", 811, 811 n. 95.
- Frier, "Demography", 811 n. 97.
- Harper, "Fate of Rome" (2017)
- Harper, "Fate of Rome" (2017)
- Harper (2017), "The Fate of Rome"
- Frier, "Demography", 812 table 5.
- Harper, "Fate of Rome" (2017)
- Frier, "Demography", 812.
- Frier, "Demography", 811–12.
- Goldhill, Simon (2006). Being Greek Under Rome: Cultural Identity, the Second Sophistic and the Development of Empire. Cambridge University Press.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 42.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 45. Augustan census figures are recorded in the Res Gestae 8.
- Lo Cascio, "Size of the Roman Population", 23–40.
- Maddison, Contours of the World Economy, 33; Scheidel, "Demography", 47 n. 42, 47.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 45 n. 35.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 45.
- Scheidel, "Demography", 47.
- Beloch, Karl Julius (1886). Die Bevölkerung der griechisch-römischen Welt. p. 507.
- Russell, J. C. (1958). "Late ancient and medieval population". Philadelphia, PA: American Philosophical Society.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Scheidel, Walter (April 2006) "Population and demography" in Princeton/Stanford Working Papers in Classics, p. 9
- Hanson, J. W. (2016). An Urban Geography of the Roman World, 100 BC to AD 300. Oxford: Archaeopress. ISBN 9781784914721.
- Hanson, J. W.; Ortman, S. G. (15 November 2017). "A systematic method for estimating the populations of Greek and Roman settlements". Journal of Roman Archaeology. 30: 301–324. doi:10.1017/S1047759400074134. S2CID 165770409.
- Frier, "Demography", 813.
- Kehoe, "The Early Roman Empire: Production", 543.
Ancient sources
- Digest.
- Scott, S. P., trans. The Digest or Pandects in The Civil Law. 17 vols. Cincinnati: Central Trust Company, 1932. Online at the Constitution Society. Accessed 31 August 2009.
- Res Gestae Divi Augusti
- Shipley, F., trans. Compendium of Roman History. Res Gestae Divi Augusti. Loeb Classical Library. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1924. Online at LacusCurtius. Accessed 18 June 2010.
- Tacitus. Annales.
- Jackson, J., trans. Annals. Loeb Classical Library. 4 vols. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1931–37. Online at LacusCurtius. Accessed 18 June 2010.
Modern sources
- Allen, Robert C. "How prosperous were the Romans? Evidence from Diocletian’s Price Edict (301 AD)", University of Oxford, Department of Economics, Discussion Paper Series No. 363 (October 2007), rept. in Alan Bowman and Andrew Wilson, eds., Quantifying the Roman Economy (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2009), 327–45.
- Frier, Bruce W (1982). "Roman Life Expectancy: Ulpian's Evidence". Harvard Studies in Classical Philology. 86: 213–51. doi:10.2307/311195. JSTOR 311195. PMID 16437859.
- Frier, Bruce W (1994). "Natural Fertility and Family Limitation in Roman Marriage". Classical Philology. 89 (4): 318–33. doi:10.1086/367430. PMID 16435460. S2CID 7839595.
- Frier, Bruce W. "Demography", in Alan K. Bowman, Peter Garnsey, and Dominic Rathbone, eds., The Cambridge Ancient History XI: The High Empire, A.D. 70–192, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000), 827–54.
- Hanson, J. W. (2016). An Urban Geography of the Roman World, 100 BC to AD 300. Oxford: Archaeopress. ISBN 9781784914721.
- Hanson, J. W.; Ortman, S. G. (2017). "A systematic method for estimating the populations of Greek and Roman settlements". Journal of Roman Archaeology. 30: 301–324.
- Harper, Kyle. "The Fate of Rome", Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press, 2017.
- Hopkins, Keith (1966). "On the Probable Age Structure of the Roman Population". Population Studies. 20 (2): 245–64. doi:10.2307/2172985. JSTOR 2172985. PMID 22084913.
- Kehoe, Dennis P. "The Early Roman Empire: Production", in W. Scheidel, I. Morris and R. Saller, eds., The Cambridge Economic History of the Greco-Roman World (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007), 543–69.
- Lo Cascio, Elio (1994). "The Size of the Roman Population: Beloch and the Meaning of the Augustan Census Figures". Journal of Roman Studies. 84: 23–40. doi:10.2307/300868. JSTOR 300868. S2CID 161237859.
- Lo Cascio, Elio. "The Early Roman Empire: The State and the Economy", in W. Scheidel, I. Morris and R. Saller, eds., The Cambridge Economic History of the Greco-Roman World (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007), 619–47.
- Maddison, Angus. Contours of the World Economy, 1–2030 AD: Essays in Macro-Economic History. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007.
- Morris, Ian.The Measure of Civilization. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press, 2013.
- Morris, Ian, Richard P. Saller, and Walter Scheidel. "Introduction", in W. Scheidel, I. Morris and R. Saller, eds., The Cambridge Economic History of the Greco-Roman World (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007), 1–12.
- Saller, Richard P. "Household and Gender", in W. Scheidel, I. Morris and R. Saller, eds., The Cambridge Economic History of the Greco-Roman World (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007), 87–112.
- Scheidel, Walter (2001). "Roman Age Structure: Evidence and Models". Journal of Roman Studies. 91: 1–26. doi:10.1017/s0075435800015811.
- Scheidel, Walter. "Demography", in W. Scheidel, I. Morris and R. Saller, eds., The Cambridge Economic History of the Greco-Roman World (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007), 38–86.
- Scheidel, Walter (2010). "Real Wages in Early Economies: Evidence for Living Standards from 1800 BCE to 1300 CE". Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient. 53 (3): 425–62. doi:10.1163/156852010x506038.
- Scheidel, Walter; Friesen, Steven J. (2009). "The Size of the Economy and the Distribution of Income in the Roman Empire". Journal of Roman Studies. 99: 61–91. doi:10.3815/007543509789745223. S2CID 202968244.
- Temin, Peter. "Estimating GDP in the Early Roman Empire", in E. Lo Cascio, ed., Innovazione tecnica e progresso economico nel mondo romano (2006), 31–54.