Jammu and Kashmir (union territory)
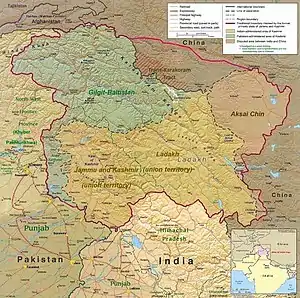
Jammu and Kashmir[lower-alpha 2] is a region administered by India as a union territory[1] and consists of the southern portion of the larger Kashmir region, which has been the subject of a dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947, and between India and China since 1962.[3][18] The Line of Control separates Jammu and Kashmir from the Pakistani-administered territories of Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan in the west and north. It lies to the north of the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab and to the west of Ladakh, which is also subject to the dispute as a part of Kashmir, and administered by India as a union territory.[2]
Jammu and Kashmir | |
|---|---|
  From top to bottom: Lidder Valley, Akhnoor Fort | |
 Emblem | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 33.5°N 75.0°E | |
| Administering country | India |
| Union territory | 31 October 2019 |
| Capital | Srinagar (May–October) Jammu (Nov-April)[4] |
| Districts | 20 |
| Government | |
| • Body | Government of Jammu and Kashmir |
| • Lieutenant Governor | Manoj Sinha |
| • Chief Minister | Vacant |
| • Legislature | Unicameral (114 seats)[5] |
| • Parliamentary constituency | Rajya Sabha (4) Lok Sabha (5) |
| • High Court | High Court of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh |
| Area | |
| • Total | 42,241 km2 (16,309 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation [6] (Nun Peak) | 7,135 m (23,409 ft) |
| Lowest elevation (Chenab River) | 247 m (810 ft) |
| Population (2011)[7] | |
| • Total | 12,267,013 |
| • Density | 290/km2 (750/sq mi) |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Urdu, Kashmiri, Dogri, Hindi, English[8][9] |
| • Spoken | Gojri, Pahari,[10] Punjabi, Bhadarwahi,[11] Bateri,[12] Khowar,[13] Shina,[14][15] Burushaski,[16] |
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (IST) |
| ISO 3166 code | IN-JK |
| Vehicle registration | JK |
| HDI (2018) | |
| Website | www |
Provisions for the formation of the union territory of Jammu and Kashmir were contained within the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019, which was passed by both houses of the Parliament of India in August 2019. The act re-constituted the former state of Jammu and Kashmir into two union territories, one being Jammu and Kashmir and the other being Ladakh, with effect from 31 October 2019.[19]
Terminology
Jammu and Kashmir is named after the two regions it encompasses – the Jammu region and the Kashmir Valley.
The Government of Pakistan and Pakistani sources refer to Jammu and Kashmir as a part of "Indian-occupied Kashmir" ("IOK") or "Indian-held Kashmir" (IHK).[20][21] The Government of India and Indian sources in turn, call the territory under Pakistan control "Pakistan-occupied Kashmir" ("POK") or "Pakistan-held Kashmir" ("PHK").[22][23] "Indian-administered Kashmir" and "Indian-controlled Kashmir" are often used by neutral sources.[24]
History
The state of Jammu and Kashmir was accorded special status by Article 370 of the Constitution of India. In contrast to other states of India, Jammu and Kashmir had its own constitution, flag, and administrative autonomy.[25] Indian citizens from other states were not allowed to purchase land or property in Jammu and Kashmir.[26]
Jammu and Kashmir had three distinct areas: Hindu-majority Jammu region, Muslim-majority Kashmir Valley, and Buddhist-dominated Ladakh.[27] Unrest and violence persisted in the Kashmiri Valley and, following a disputed state election in 1987, an insurgency persisted in protest over autonomy and rights.[27][28]
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) came to power in the 2014 Indian general election and five years later included in their 2019 election manifesto the revocation of Article 370 of the Constitution of India, in order to bring Jammu and Kashmir to equal status with other states.[27]
A resolution to repeal Article 370 was passed by both the houses of the Parliament of India in August 2019. At the same time, a reorganisation act was also passed, which would reconstitute the state into two union territories, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh.[29] The reorganisation took effect from 31 October 2019.[19]
In September 2019, nearly 4,000 people, including two former Chief Ministers and hundreds of other politicians, were arrested by the Indian authorities in Kashmir;[30] the state was put under a lockdown and communication and internet services were suspended.[31]
Geography
Topography


Jammu and Kashmir is home to several valleys such as the Kashmir Valley, Tawi Valley, Chenab Valley, Poonch Valley, Sind Valley, and Lidder Valley.[32] The Kashmir valley is 100 km (62 mi) wide and 15,520.3 km2 (5,992.4 sq mi) in area.[33] The Himalayas divide the Kashmir valley from the Tibetan plateau while the Pir Panjal range, which encloses the valley from the west and the south, separates it from the Punjab Plain of the Indo-Gangetic Plain.[34] Along the northeastern flank of the Valley runs the main range of the Himalayas.[35] This valley has an average height of 1,850 metres (6,070 ft) above sea-level,[33] but the surrounding Pir Panjal range has an average elevation of 10,000 feet (3,000 m).[36] The Jhelum River is the major Himalayan river which flows through the Kashmir valley.[37] The southern Jammu region is mostly mountainous, with the Shivaliks, the middle and the great Himalayas running parallel to each other in a southeast-northwest direction. A narrow southwestern strip constitutes fertile plains. The Chenab, Tawi and Ravi are important rivers flowing through the Jammu region.[38]
Climate
The climate of Jammu and Kashmir varies with altitude and across regions. Southern and southwestern areas have a sub tropical climate, with hot summers and cool winters. This region receives most of its rainfall during the monsoon season. In the east and north, summers are usually pleasant. The effect of the monsoon diminishes in areas lying to the leeward side of the Pir Panjal, such as the Kashmir valley, and much of the rainfall happens in the spring season due to western disturbances. Winters are cold, with temperatures reaching sub-zero levels. Snowfall is common in the valley and the mountain areas.
Administrative divisions

The union territory of Jammu and Kashmir consists of two divisions: Jammu Division and Kashmir Division, and is further divided into 20 districts.[39]
| Division | Name | Headquarters | Area (km2) |
Area (sq miles) |
Rural Area (km2) |
Urban Area (km2) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jammu | Kathua district | Kathua | 2,502 | 966 | 2,458.84 | 43.16 | [40] |
| Jammu district | Jammu | 2,342 | 904 | 2,089.87 | 252.13 | [41] | |
| Samba district | Samba | 904 | 349 | 865.24 | 38.76 | [42] | |
| Udhampur district | Udhampur | 2,637 | 1,018 | 2,593.28 | 43.72 | [43] | |
| Reasi district | Reasi | 1,719 | 664 | 1,679.99 | 39.01 | [44] | |
| Rajouri district | Rajouri | 2,630 | 1,015 | 2,608.11 | 21.89 | [45] | |
| Poonch district | Poonch | 1,674 | 646 | 1,649.92 | 24.08 | [46] | |
| Doda district | Doda | 8,912 | 3,441 | 8,892.25 | 19.75 | [47] | |
| Ramban district | Ramban | 1,329 | 513 | 1,313.92 | 15.08 | [48] | |
| Kishtwar district | Kishtwar | 1,644 | 635 | 1,643.37 | 0.63 | [49] | |
| Total for division | 26,293 | 10,151 | 25,794.95 | 498.05 | |||
| Kashmir | Anantnag district | Anantnag | 3,574 | 1,380 | 3,475.76 | 98.24 | [50] |
| Kulgam district | Kulgam | 410 | 158 | 360.20 | 49.80 | [51] | |
| Pulwama district | Pulwama | 1,086 | 419 | 1,047.45 | 38.55 | [52] | |
| Shopian district | Shopian | 312 | 120 | 306.56 | 5.44 | [53] | |
| Budgam district | Budgam | 1,361 | 525 | 1,311.95 | 49.05 | [54] | |
| Srinagar district | Srinagar | 1,979 | 764 | 1,684.42 | 294.53 | [55] | |
| Ganderbal district | Ganderbal | 259 | 100 | 233.60 | 25.40 | [56] | |
| Bandipora district | Bandipora | 345 | 133 | 295.37 | 49.63 | [57] | |
| Baramulla district | Baramulla | 4,243 | 1,638 | 4,179.44 | 63.56 | [58] | |
| Kupwara district | Kupwara | 2,379 | 919 | 2,331.66 | 47.34 | [59] | |
| Total for division | 15,948 | 6,156 | 15,226.41 | 721.54 | |||
Transport
Air
Jammu and Kashmir has two major airports at the two capitals of the territory: Jammu Airport at Jammu and Sheikh ul Alam Airport at Srinagar, which is also the only international airport in the territory. These airports have regular flights to Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, Chandigarh and other major cities of the country.
Railway

The under-construction Jammu-Baramulla line of the Northern Railways is the only railway line in the territory. Once complete, the line will connect the two regions of Jammu and Kashmir and will also provide a rail link to the Kashmir valley from other parts of the country.
Road

The Jammu-Srinagar National Highway, a segment of the NH44, is the main highway in the territory connecting the two capitals by road. National Highways 1, 144, 144A, 444, 501, 701 and 701A are the other NHs in the territory.
Demographics
As per the 2011 census, Jammu and Kashmir has a total population of 12,267,013. The sex ratio is 889 females per 1000 males. Around 924,485 (7.54%) of the population is scheduled caste and 1,275,106 (10.39%) belong to the scheduled tribes, mainly Gujjar, Bakerwal, and Gaddi. The SCs are mostly concentrated in the Jammu region.
Religion
Muslims constitute the majority of the population of Jammu and Kashmir with a large Hindu minority.[60]
The Kashmir Division is predominantly Muslim (96.41%) with a small Hindu (2.45%) and Sikh (0.81%) population. Only 808 Kashmiri Hindu Pandit families remain in the valley after their forced displacement by Islamic militants.[61] Shias are mostly concentrated in the Budgam district, where they form about 30-40% of the population.[62][63]
The Jammu Division is predominantly Hindu (66%) with a significant Muslim population (30%). The Muslims form a majority in the Rajouri (63%), Poonch (90%), Doda (54%), Kishtwar (58%) and Ramban (71%) districts of Jammu, while the Hindus form a majority in Kathua (88%), Samba (86%), Jammu (84%) and Udhampur (88%) districts. Reasi district has an almost equal number of Hindus and Muslims.[64]
Language
Jammu & Kashmir: mother-tongue of population, according to the 2011 Census of India.[65]
Kashmiri is the most-spoken language, is mainly spoken in the Kashmir Valley and in the upper reaches of the Chenab Valley, with a sizeable number of speakers in Jammu City. Dogri, related to Punjabi and Pahari, is spoken throughout the plains areas of Jammu division, as well as in parts of the hills. The hill people speak several languages. In the Pir Panjal Range, bordering Pakistan-administered Kashmir, the main language is Pahari-Pothwari, a western variety of Punjabi, as well as Gojri, the language of the Gujjar tribe. In the eastern hills of Jammu division are spoken various Western Pahari languages such as Siraji and Bhaderwahi, which merge with the dialects of western Himachal Pradesh.[65] Urdu is also widely understood and spoken, particularly in the Kashmir region where it acts as the lingua franca alongside Kashmiri and also serves as a medium of instruction along with English, while Hindi is taught and understood in the southern areas of Jammu.
Education

According to the 2011 census, the literacy rate in Jammu and Kashmir was 67.17%, male literacy was 75%, while female literacy was at 56.43%.
Kashmir University located in Srinagar is the main university in the territory. Other universities include Jammu University, Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology of Kashmir, Shri Mata Vaishno Devi University, Islamic University of Science & Technology, etc. Major institutions of higher education are NIT Srinagar, IIT Jammu, IIM Jammu, NIFT Srinagar and IHM Srinagar. Medical colleges include SKIMS, and the Government Medical College in Srinagar and AIIMS Vijaypur.
Government and politics
The union territory of Jammu and Kashmir is administered under the provisions of Article 239 of the Constitution of India. Article 239A, originally formulated for the union territory of Puduchery, will also be applicable to Jammu and Kashmir.[66]
Executive branch
The President of India appoints a Lieutenant Governor for the union territory.[66]
A Council of Ministers led by a Chief Minister is appointed by the Lieutenant Governor from the membership of the legislative assembly. Their role is to advise the Lieutenant Governor in the exercise of functions in matters under the jurisdiction of the legislative assembly. In other matters, the Lieutenant Governor is empowered to act in his own capacity.[66]
Legislative branch
The legislative branch of government is a unicameral legislative assembly, whose tenure is five years. The legislative assembly may make laws for any of the matters in the State List of the Constitution of India except "public order" and "police", which will remain the preserve of the central Government of India. The Lieutenant Governor also has the power to promulgate ordinances which have the same force as the acts of the legislative assembly.[66]
Elections for the Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly are to be held following the implementation of new constituency boundaries which is expected to be completed in 2021.[67]
Judicial branch

The union territory is under the jurisdiction of the Jammu and Kashmir High Court, which also serves as the high court for Ladakh.[66] Police services are provided by the Jammu and Kashmir Police.[68]
Parties
The main political parties active in the region are the Bharatiya Janata Party (State President: Ravinder Raina), the Indian National Congress (State President: Ghulam Ahmad Mir), the Jammu & Kashmir National Conference (President: Farooq Abdullah) and the Jammu and Kashmir People's Democratic Party (President: Mehbooba Mufti). Other parties with a presence in the region include the Communist Party of India (Marxist), the Jammu and Kashmir National Panthers Party, the Jammu and Kashmir People's Conference, the Jammu and Kashmir Apni Party (President: Altaf Bukhari), the Jammu and Kashmir Workers Party (President: Mir Junaid) and Ikkjutt Jammu (President: Ankur Sharma).
Jammu and Kashmir in the Parliament of India
Jammu and Kashmir sends five members (MPs) to the lower house of the Indian parliament (the Lok Sabha) and four members to the upper house (the Rajya Sabha).
- Lok Sabha constituencies in Jammu and Kashmir
| Constituency No. | Constituency | Reserved for (SC/ST/None) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Baramulla | None |
| 2 | Srinagar | None |
| 3 | Anantnag | None |
| 4 | Udhampur | None |
| 5 | Jammu | None |
Economy


Jammu and Kashmir's economy is primarily services-based and agriculture-oriented.[69] The gross domestic product of Jammu and Kashmir was estimated at ₹1.76 lakh crore (US$22 billion) in 2020–21.[70] Along with horticulture and agriculture, tourism is an important industry for Jammu and Kashmir, accounting for about 7% to its economy.[71]
The Kashmir Valley is known for its sericulture and cold-water fisheries.[72] Wood from Kashmir is used to make high-quality cricket bats, popularly known as Kashmir Willow.[73] Major agricultural exports from Jammu and Kashmir include apples, pears, cherries, plums, saffron and walnuts.[74] The traditional Kashmiri handicrafts industry employs a large workforce of around 340 thousand artisans and has potential for producing export goods.[69] Small-scale cottage industries include carpet weaving, silks, shawls, basketry, pottery, copper and silverware, papier-mâché and walnut wood.[69] The horticulture sector is the next biggest source of income in the economy. The temperature of Jammu and Kashmir is also suited to floriculture and can support various species of flora.[69]
Over 500 mineral blocks are present in Jammu and Kashmir, 261 of which are in the Kashmir Division alone.[75] Kishtwar is known as the 'land of sapphire and saffron'.[76] Resources such as timber, herbs and medicinal shrubs, edibles such as mushroom, chilgoza, black zeera, and saffron are available in the forests.[77] The sapphire reserve mines of Machail, Paddar are a source of mineral wealth.[77] Jammu and Kashmir is the only administrative unit in India with a large amount of borax and sapphire resources.[75] It possesses 36 percent of the graphite, 21 percent marble and 14 percent of gypsum present in India.[75] Coal, limestone and magnesite are found scattered among the different districts of the union territory.[75]
Other minerals of significance that occur are bauxite, ball clay and china clay in Udhampur; bentonite in Jammu; diaspore in Rajouri and Udhampur; graphite in Baramulla; lignite and marble in Kupwara; quartz and silica sand in Anantnag, Doda and Udhampur; and quartzite in Anantnag district.[75] In addition, the Department of Geology and Mining has determined the presence of minerals such as magnetite, dolomite, fuel mineral, decorative building stones, slate, and gemstones. All are materials with commercial and industrial uses in many products and factories.[75]
In the fiscal year 2019–20, total exports from Jammu and Kashmir amounted to ₹188.18 million (US$2.4 million).[69] The Jammu & Kashmir Bank, which is listed as a NIFTY 500 conglomerate, is based in the union territory.[78] Jammu and Kashmir is one of the largest recipients of grants from the central government annually.[79] According to the Sustainable Development Goals Index 2021, 10.35 percent of the population of Jammu and Kashmir live below the national poverty line, the third-highest among union territories in the country.[80]
Media
The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) regulates all major aspects pertaining to media and telecommunications in Jammu and Kashmir.[81] In addition, the Jammu and Kashmir administration released their media policy in 2020 which enabled government officers to sanction journalists and media organisations for disseminating "fake news," and is valid for the next five years.[82] The policy attracted criticism for allegedly reducing people to "passive recipients of the information the government intends to disseminate."[83] The Press Council of India (PCI) expressed concern over the provisions of fake news in the policy, as it "interferes with the free functioning of the press."[84]
Major periodicals in Jammu and Kashmir include Greater Kashmir, Rising Kashmir, Kashmir Times, Daily Excelsior, Elite Kashmir and Kashmir Monitor.[85] DD Kashir is the state-owned television broadcaster.[86] Popular private television channels are ETV Urdu and Gulistan News.[87] In association with All India Radio, DD Kashir has established high power transmitters along the India–Pakistan border.[88] Radio Sharda, a worldwide community radio service for Kashmiri Pandits, was started by Ramesh Hangloo.[89] FM Tadka 95.0, BIG FM 92.7, Radio Mirchi and Red FM 93.5 are private FM radio stations.[90]
Internet shutdowns are frequent in Jammu and Kashmir. As of February 2021, the region had 300 internet shutdowns since 2012. In 2020 alone, this number was 115, the highest of any year.[91]
Sports

Sports tournaments in Jammu and Kashmir are organised by both the Indian army and police, as well as mainstream political parties and the All Parties Hurriyat Conference.[92] Sportspersons who represent India in tournaments face stigmatisation from separatists.[92]
Jammu and Kashmir has 18 stadiums, 23 training centres, three indoor sports complexes and 42 government-maintained playing fields.[93] Srinagar is home to the Sher-i-Kashmir Stadium, a stadium where international cricket matches have been played.[94] The Maulana Azad Stadium in Jammu is one of the home venues for the Jammu and Kashmir cricket team.[95] The Bakshi Stadium in Srinagar, named after Bakshi Ghulam Mohammad, hosts football matches.[96]
Institutions such as the Jawahar Institute of Mountaineering and Winter Sports provides mountaineering, skiing and adventure courses.[97] The Royal Springs Golf Course, Srinagar, located on the banks of Dal lake, is considered one of the best golf courses in India.[98] Jammu and Kashmir was also host to the first Khelo India Winter Games, held in 2020 in Gulmarg.[99] Jammu and Kashmir came first with the most gold medals at 26, followed by the Indian Army team with 8 gold medals.[100] The second edition of the winter games were also held in Gulmarg in 2021, with Jammu and Kashmir coming first again.[101]
Tourism
Some major tourist attractions in Jammu and Kashmir are Srinagar, the Mughal Gardens, Gulmarg, Pahalgam, Patnitop and Jammu. Every year, thousands of Hindu pilgrims visit holy shrines of Vaishno Devi and Amarnath which has had significant impact on the state's economy.[102]
The Kashmir valley is one of the top tourist destinations in India.[103] Gulmarg, one of the most popular ski resort destinations in India, is also home to the world's highest green golf course.[104] The decrease in violence in the state has boosted the state's economy, specifically tourism.[105]
Jammu and Kashmir is also famous for its scenic beauty, flower gardens, apple farms and more. It attracts tourists for its unique handicrafts and the world-famous Kashmiri Shawls.
 Vaishno Devi Temple in winter
Vaishno Devi Temple in winter Shalimar Gardens
Shalimar Gardens

Notes
- Jammu and Kashmir is a disputed territory between India and Pakistan. Jammu and Kashmir has 42,241 km2 (16,309 sq mi) of area administered by India and 13,297 km2 (5,134 sq mi) of area controlled by Pakistan under Azad Kashmir which is claimed by India as part of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Pronounced variably as /ˈdʒæmuː/ or /ˈdʒʌmuː/, /ˈkæʃmɪər/ or /kæʃˈmɪər/.[17]
See also
- Jammu and Kashmir (princely state), for the entity that existed till 1952
- Kashmiriyat
- Tourism in Jammu and Kashmir
- Kashmiri cinema
- Literature of Kashmir
- Music of Jammu and Kashmir
- Kus Bani Koshur Karorpaet
- DD Kashir
- AIR Srinagar
- University of Kashmir
- University of Jammu
- Central University of Kashmir
- Central University of Jammu
- Jammu and Kashmir cricket team
- Real Kashmir F.C.
- Jammu and Kashmir football team
- Jammu and Kashmir Police
- Jammu and Kashmir Light Infantry
- Jammu and Kashmir Rifles
References
- Akhtar, Rais; Kirk, William (22 March 2021), "Jammu and Kashmir", Encyclopaedia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., retrieved 2 April 2022,
The union territory is part of the larger region of Kashmir, which has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since the partition of the subcontinent in 1947. ... The territory that India administered on its side of the line, which contained both Jammu (the seat of the Dogra dynasty) and the Vale of Kashmir, took on the name Jammu and Kashmir. However, both India and Pakistan have continued to claim the entire Kashmir region
- Briticannica, Eds Encycl. (1 March 2021), "Ladakh", Encyclopaedia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., retrieved 2 April 2022,
Ladakh, large area of the northern and eastern Kashmir region, northwestern Indian subcontinent. Administratively, Ladakh is divided between Pakistan (northwest), as part of Gilgit-Baltistan, and India (southeast), as part of Ladakh union territory (until October 31, 2019, part of Jammu and Kashmir state); in addition, China administers portions of northeastern Ladakh.
- (a) Encyclopaedia Britannia (ed.), "Kashmir, region Indian subcontinent", Encyclopædia Britannica, retrieved 15 August 2019 (subscription required) Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent ... has been the subject of dispute between India and Pakistan since the partition of the Indian subcontinent in 1947. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, the last two being part of a territory called the Northern Areas. Administered by India are the southern and southeastern portions, which constitute the state of Jammu and Kashmir but are slated to be split into two union territories. China became active in the eastern area of Kashmir in the 1950s and has controlled the northeastern part of Ladakh (the easternmost portion of the region) since 1962.";
(b) "Kashmir", Encyclopedia Americana, Scholastic Library Publishing, 2006, p. 328, ISBN 978-0-7172-0139-6 C. E Bosworth, University of Manchester Quote: "KASHMIR, kash'mer, the northernmost region of the Indian subcontinent, administered partlv by India, partly by Pakistan, and partly by China. The region has been the subject of a bitter dispute between India and Pakistan since they became independent in 1947"; - The Hindu Net Desk (8 May 2017). "What is the Darbar Move in J&K all about?". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 10 November 2017. Retrieved 23 February 2019.
- Shaswati Das. "Jammu and Kashmir transitions from a state into 2 federal units". livemint.com. Live Mint. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
Jammu and Kashmir will also have its own legislative assembly, under which, according to the Act, the number of seats will go up to 114 from 87 currently, following a delimitation exercise.
- Singh, Jogindar (1975). "Saser Kangri". The American Alpine Journal (AAJ): 67. Archived from the original on 14 February 2019. Retrieved 14 February 2019. pdf of original pages
- Singh, Vijaita (29 February 2020). "Only J&K will use 2011 Census for delimitation". The Hindu. Retrieved 6 November 2020.
- "The Jammu and Kashmir Official Languages Act, 2020" (PDF). The Gazette of India. 27 September 2020. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 October 2020. Retrieved 27 September 2020.
- "Parliament passes JK Official Languages Bill, 2020". Rising Kashmir. 23 September 2020. Archived from the original on 24 September 2020. Retrieved 23 September 2020.
- Khan, N. (6 August 2012). The Parchment of Kashmir: History, Society, and Polity. Springer. p. 184. ISBN 9781137029584. Archived from the original on 23 February 2019. Retrieved 23 February 2019.
- "Bhadrawahi". Ethnologue.com. Retrieved 6 August 2019.
- Bateri.
- Simons, Gary F.; Fennig, Charles D. (2017). Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Twentieth Edition. Dallas: SIL International.
- Crane, Robert I. (1956). Area Handbook on Jammu and Kashmir State. University of Chicago for the Human Relations Area Files. p. 179.
Shina is the most eastern of these languages and in some of its dialects such as the Brokpa of Dah and Hanu and the dialect of Dras, it impinges upon the area of the Sino-Tibetan language family and has been affected by Tibetan with an overlay of words and idioms.
- Aggarwal, J. C.; Agrawal, S. P. (1995). Modern History of Jammu and Kashmir: Ancient times to Shimla Agreement. Concept Publishing Company. ISBN 9788170225577. Archived from the original on 24 February 2019. Retrieved 23 February 2019.
- "Pakistan's "Burushaski" Language Finds New Relatives". Npr.org. Retrieved 6 August 2019.
- Jones, Daniel (2003) [1917], Peter Roach; James Hartmann; Jane Setter (eds.), English Pronouncing Dictionary, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-3-12-539683-8
- Osmańczyk, Edmund Jan (2003), Encyclopedia of the United Nations and International Agreements: G to M, Taylor & Francis, pp. 1191–, ISBN 978-0-415-93922-5 Quote: "Jammu and Kashmir: Territory in northwestern India, subject to a dispute between India and Pakistan. It has borders with Pakistan and China."
- Ministry of Home Affairs (9 August 2019), "In exercise of the powers conferred by clause a of section 2 of the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act." (PDF), The Gazette of India, retrieved 9 August 2019
- Zain, Ali (13 September 2015). "Pakistani flag hoisted, pro-freedom slogans chanted in Indian Occupied Kashmir – Daily Pakistan Global". En.dailypakistan.com.pk. Archived from the original on 18 November 2015. Retrieved 17 November 2015.
- "Pakistani flag hoisted once again in Indian Occupied Kashmir". Dunya News. 11 September 2015. Retrieved 17 November 2015.
- Snedden, Christopher (2013). Kashmir: The Unwritten History. HarperCollins India. pp. 2–3. ISBN 978-9350298985.
- "The enigma of terminology". The Hindu. 27 January 2014. Archived from the original on 16 October 2015.
- South Asia: fourth report of session 2006–07 by Great Britain: Parliament: House of Commons: Foreign Affairs Committee page 37
- K. Venkataramanan (5 August 2019), "How the status of Jammu and Kashmir is being changed", The Hindu
- "Article 370 and 35(A) revoked: How it would change the face of Kashmir". The Economic Times. 5 August 2019.
- Article 370: What happened with Kashmir and why it matters. BBC (6 August 2019). Retrieved 7 August 2019.
- Jeelani, Mushtaq A. (25 June 2001). "Kashmir: A History Littered With Rigged Elections". Media Monitors Network. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 24 February 2017.
- "Parliament Live | Lok Sabha passes Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Bill, Ayes: 370, Noes 70". The Hindu. 6 August 2019. Retrieved 6 August 2019.
- Ghoshal, Devjyot; Pal, Alasdair (12 September 2019). "Thousands detained in Indian Kashmir crackdown, official data reveals". Reuters.
- "Kashmir in lockdown after autonomy scrapped". BBC News. 6 August 2019. Retrieved 6 June 2021.
- Vij, Shivam (5 May 2017). "Kashmir Is A Prison With Three Walls". HuffPost. Archived from the original on 5 May 2017. Retrieved 9 August 2019. Alt URL
- Guruswamy, Mohan (28 September 2016). "Indus: The water flow can't be stopped". The Asian Age. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
- Khan, Asma (26 April 2018). "A Tryst of the Heart and History along the Karakoram Highway". Greater Kashmir. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
- Andrei, Mihai (11 March 2019). "Why India and Pakistan keep fighting over Kashmir – the history of the Kashmir conflict". GME Science. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
- Vrinda; J. Ramanan (21 December 2017). "Doorway of the gods: Himalaya crosses five countries". The Hindu. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
- "Jhelum River". Encyclopædia Britannica. 15 December 2015. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
- Agencies (29 July 2019). "Flooding alert issued as India releases water". The Nation. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
- "Ministry of Home Affairs:: Department of Jammu & Kashmir Affairs". Archived from the original on 8 December 2008. Retrieved 28 August 2008.
- District Census Handbook Kathua (PDF). Census of India 2011, Part A (Report). 18 June 2014. p. 8. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- District Census Handbook Jammu, Part A (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 18 June 2014. pp. 13, 51, 116. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
District Census Handbook Jammu, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. pp. 13, 24. Retrieved 21 November 2020. - District Census Handbook Samba, Part A (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 18 June 2014. pp. 9, 34, 36, 100. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
District Census Handbook Samba, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. pp. 10, 12, 22. Retrieved 21 November 2020. - District Census Handbook Udhampur (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. pp. 12, 22. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- District Census Handbook Reasi, Part A (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 18 June 2014. pp. 9, 37, 88. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
District Census Handbook Reasi, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. pp. 9, 13, 24. Retrieved 21 November 2020. - District Census Handbook Rajouri, Part A (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 18 June 2014. pp. 11, 107. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
District Census Handbook Rajouri, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. pp. 9, 10, 12, 22. Retrieved 21 November 2020. - District Census Handbook Punch, Part A (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 18 June 2014. pp. 9, 99. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
District Census Handbook Punch, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. pp. 11, 13, 24. Retrieved 21 November 2020. - District Census Handbook Doda, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 18 June 2014. pp. 9, 12, 99. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- District Census Handbook Ramban, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 18 June 2014. pp. 10, 12. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- District Census Handbook Kishtwar, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 18 June 2014. pp. 9, 10, 22. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
Part B page 9 says the rural area is 1,643.65 km2 (634.62 sq mi), whilst pages 10 and 22 says 1,643.37 km2 (634.51 sq mi). - District Census Handbook Anantnag, Part A (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). July 2016. p. 9. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
District Census Handbook Anantnag, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). July 2016. pp. 12, 22. Retrieved 21 November 2020. - District Census Handbook Kulgam, Part A (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). July 2016. p. 10. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
District Census Handbook Kulgam, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. pp. 12, 22. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
Part B page 12 says the area of the district is 404 km2 (156 sq mi), but page 22 says 410 km2 (160 sq mi). - District Census Handbook Pulwama, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. pp. 12, 22. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- District Census Handbook Shupiyan, Part A (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. p. 10. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
District Census Handbook Shupiyan, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. pp. 12, 22. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
Part B pages 12 and 22 say the district area is 312.00 km2 (120.46 sq mi), but Part A page 10 says 307.42 km2 (118.70 sq mi). - District Census Handbook Badgam, Part A (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). July 2016. pp. 10, 46. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
District Census Handbook Badgam, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. pp. 11, 12, 22. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
Part A says the district area is 1,371 km2 (529 sq mi), Part B says 1,371 km2 (529 sq mi) (page 11) and 1,361 km2 (525 sq mi) (page 12s and 22). - District Census Handbook Srinagar, Part A (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). July 2016. pp. 11, 48. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
Part A page 48 says the district area was 2,228.0 km2 (860.2 sq mi) in 2001 and 1,978.95 km2 (764.08 sq mi) in 2011. - District Census Handbook Ganderbal, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). July 2016. pp. 11, 12 and 22. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
Part B page 11 says the district area is 393.04 km2 (151.75 sq mi), but pages 12 and 22 say 259.00 km2 (100.00 sq mi). - District Census Handbook Bandipora, Part A (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). July 2016. pp. 10, 47. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
District Census Handbook Bandipora, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. pp. 11, 20. Retrieved 21 November 2020. - District Census Handbook Baramulla, Part A (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). July 2016. p. 11. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
District Census Handbook Baramulla, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. p. 22. Retrieved 21 November 2020. - District Census Handbook Kupwara, Part A (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). July 2016. p. 7. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
District Census Handbook Kupwara, Part B (PDF). Census of India 2011 (Report). 16 June 2014. pp. 11, 12. Retrieved 21 November 2020. - "Table C-16 Population by Religion: Jammu and Kashmir". www.censusindia.gov.in. Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India.
- https://theprint.in/features/locked-up-like-animals-pandits-want-to-flee-kashmir-hope-its-their-last-exodus/988337/l
- "Are Kashmiri Shias The Next Pandits?". 14 November 2013. Archived from the original on 21 June 2015. Retrieved 21 May 2014.
- Iyer-Mitra, Abhijit (27 September 2019). "After scrapping of Article 370, Shias in Kashmir are in a state of relief and caution". ThePrint. Retrieved 11 September 2021.
- "Population by religion community – 2011". Census of India, 2011. The Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Archived from the original on 25 August 2015.
- "Table C-16 Population by Mother Tongue: Jammu and Kashmir". www.censusindia.gov.in. Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India.
- Jammu & Kashmir Reorganisation Bill passed by Rajya Sabha: Key takeaways, The Indian Express, 5 August 2019.
- "Jammu and Kashmir assembly election in 2021 after delimitation: EC sources". Zee News. 29 August 2019.
- Ratan, Devesh; Johri, Iti (7 August 2019). "Salient Features Of Jammu & Kashmir Reorganization Bill [Read Bill]". LiveLaw.in: All about law. Retrieved 7 August 2019.
- "Jammu And Kashmir Presentation And Economic Growth Report". India Brand Equity Foundation. 29 July 2021.
- "MOSPI State Domestic Product, Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation". Government of India. 15 March 2021. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- "Jammu and Kashmir's tourism flourishes, receives highest footfall since Independence".
- "Time for SKUAST-Jammu to start Horti, Dairy Farming, Agri Engineering deptts: LG". The Kashmir Images. 16 March 2021.
- "Jalandhar bats with Pakistani goods". The New Indian Express. 5 November 2017.
- "J&K special report: Ready reckoner of top agri-product manufacturers and industry bodies from Jammu & Kashmir". Gulf News. 27 December 2020.
- "New Mining Policy in J&K: Interests of locals are paramount, not revenue". The Kashmir Images. 11 September 2020.
- Syed Amjad Shah (11 July 2021). "Kishtwar couple globalising local produce; promoting Kashmiri-Dogra arts and crafts". Greater Kashmir.
- "Kishtwar Ignored Beauty". Daily Excelsior. 15 March 2020.
- "The Jammu & Kashmir Bank Ltd. - Stock Price". The Financial Express. Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- "Demand for Grants of Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir 2021-22" (PDF). Finance Department Jammu and Kashmir. Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- "10.35% Population In J&K Living Below Poverty Line: Survey". Kashmir Observer. 11 June 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2021.
- The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India Act, 1997. Georg Thieme Verlag. p. 112. GGKEY:BJ6HEPE0NRE.
- "Why Journalists Are Worried About the New Media Policy in Jammu and Kashmir". The Wire. 17 July 2020.
- "Kashmir Media Policy: Accentuating the Curbs on the Freedom of Press". Economic and Political Weekly: 7–8. 19 August 2020.
- "Press Council of India seeks J&K govt reply on 'fake news' in its media policy". The New Indian Express. 17 June 2020.
- Mass Media in India - 2004. Compiled Edited by Research, Reference and Training Division National Documentation Centre on Mass Communication. Publications Division, Ministry of Information & Broadcasting. 2016. ISBN 9788123023380.
- "Kashmir gets its own version of KBC from today". The Tribune. 29 April 2019.
- "Amid Shutdown, a Private News Channel Connects Thousands in J&K". The Wire. 24 September 2019.
- "Rediff on the NeT: AIR, DD to counter Pak propaganda along border areas". Rediff.com. 16 December 1999.
- Mohan, Archis (6 February 2016). "The borderline cases of Jammu & Kashmir". Business Standard India. Archived from the original on 8 November 2017.
- "FM radio stations and their audiences bloom in restive Kashmir". Asia Times. 25 September 2018.
- "India: number of internet shutdowns J&K 2021". Statista. Retrieved 29 July 2021.
- Gupta, Amit (16 October 2020). "Sports in Kashmir: How 5 journalists run a magazine that focuses on local sports". Mumbai Mirror.
- "Department of Youth Services & Sports". Department of Youth Services and Sports. Government of Jammu and Kashmir. Archived from the original on 29 November 2019. Retrieved 29 November 2019.
- "Records / Sher-i-Kashmir Stadium, Srinagar / One-Day Internationals". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 13 August 2014.
- "Molana Azad Stadium, Jammu". CricketArchive. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
- "J&K stadium hosts football match after 25-year gap". The Times of India. 16 July 2012. Archived from the original on 11 May 2013. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
- "UT Govt denies pensionary benefits to retired employees of JIM&WS". Daily Excelsior. 5 July 2021.
- "India". Robert Trent Jones – Golf Architects. Archived from the original on 12 December 2013.
- Ashiq, Peerzada (7 March 2020). "Khelo India Winter Games kicked off in J&K". The Hindu. ISSN 0971-751X.
- Iveson, Ali (15 March 2020). "Hosts win 26 gold medals as first-ever Khelo India Winter Games conclude". Inside the Games. Archived from the original on 19 December 2020.
- "Spectacular Closing Ceremony of 2nd Khelo India National Winter Games organized at Gulmarg". Kashmir News Service. 2 March 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - "Amarnath Board to study yatra impact on Kashmir economy". Online edition of The Hindu. Chennai, India. 13 September 2007. Retrieved 6 June 2009.
- "Foreign tourists flock Kashmir". Online edition of The Hindu. Chennai, India. 18 March 2009. Retrieved 18 March 2009.
- Cris Prystay (26 October 2007). "Fairway to Heaven". The Wall Street Journal.
- "Tourists arrival gives boost to J-K economy". Sify. Archived from the original on 16 July 2011.
