Population growth
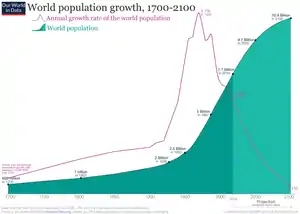
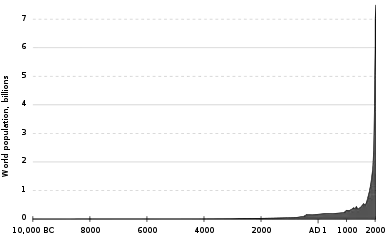
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year.[2] The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 7.9 billion in 2020.[3] The UN projected population to keep growing, and estimates have put the total population at 8.6 billion by mid-2030, 9.8 billion by mid-2050 and 11.2 billion by 2100.[4] However, some academics outside the UN have increasingly developed human population models that account for additional downward pressures on population growth; in such a scenario population would peak before 2100.[5]
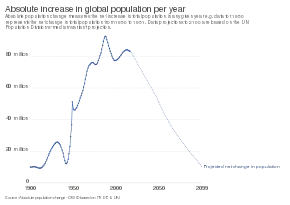
World human population has been growing since the end of the Black Death, around the year 1350.[6] A mix of technological advancement that improved agricultural productivity and sanitation and medical advancement that reduced mortality increased population growth. In some geographies, this has slowed through the process called the demographic transition, where many nations with high standards of living have seen a significant slowing of population growth. This is in direct contrast with less developed contexts, where population growth is still happening.[7] Globally, the rate of population growth has declined from a peak of 2.2% per year in 1963.[8] The global human population is projected to peak during the mid-21st century and decline by 2100.[9]
Population growth alongside increased consumption is a driver of environmental concerns, such as biodiversity loss and climate change,[10][11] due to resources utilised in human development.[12] International policy focused on mitigating the impact of human population growth is concentrated in the Sustainable Development Goals which seek to improve the standard of living globally while reducing the impact of society on the environment.
| Years passed |
Year | Pop. (billions) |
|---|---|---|
| – | 1800 | 1 |
| 127 | 1927 | 2 |
| 33 | 1960 | 3 |
| 14 | 1974 | 4 |
| 13 | 1987 | 5 |
| 12 | 1999 | 6 |
| 12 | 2011 | 7 |
| 12 | 2023* | 8 |
| 14 | 2037* | 9 |
| 18 | 2055* | 10 |
| 33 | 2088* | 11 |
| *World Population Prospects 2017 (United Nations Population Division) | ||
History
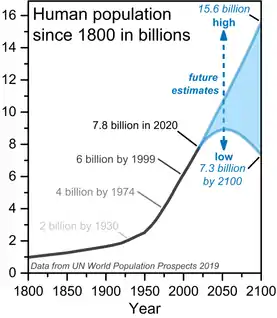
World population has been rising continuously since the end of the Black Death, around the year 1350.[6] Population began growing rapidly in the Western world during the industrial revolution. The most significant increase in the world's population has been since the 1950s, mainly due to medical advancements[14] and increases in agricultural productivity.[15]
Haber process
Due to its dramatic impact on the human ability to grow food, the Haber process, named after one of its inventors, the German chemist Fritz Haber, served as the "detonator of the population explosion", enabling the global population to increase from 1.6 billion in 1900 to 7.7 billion by November 2019.[16]
Thomas McKeown hypotheses
Some of the reasons for the "Modern Rise of Population"[17] were particularly investigated by the British health scientist Thomas McKeown (1912-1988). In his publications, McKeown challenged four theories about the population growth:
- McKeown stated that the growth in Western population, particularly surging in the 19th century, was not so much caused by an increase in fertility, but largely by a decline of mortality particularly of childhood mortality followed by infant mortality,[18][19]
- The decline of mortality could largely be attributed to rising standards of living, whereby McKeown put most emphasis on improved nutritional status,
- His most controversial idea, or at least his most disputed idea, was that he questioned the effectiveness of public health measures, including sanitary reforms, vaccination and quarantine,[20]
- The sometimes fierce disputes that his publication provoked around the "McKeown thesis" have overshadowed his more important and largely unchallenged argument that curative medicine measures played little role in mortality decline, not only prior to the mid-20th century[18] but also until well into the 20th century.[21]
Although the McKeown thesis has been heavily disputed, recent studies have confirmed the value of his ideas.[22] His work is pivotal for present day thinking about population growth, birth control, public health and medical care. McKeown had a major influence on many population researchers, such as health economists and Nobel prize winners Robert W. Fogel (1993) and Angus Deaton (2015). The latter considered McKeown as "the founder of social medicine".[23]
Growth rate models
The "population growth rate" is the rate at which the number of individuals in a population increases in a given time period, expressed as a fraction of the initial population. Specifically, population growth rate refers to the change in population over a unit time period, often expressed as a percentage of the number of individuals in the population at the beginning of that period. This can be written as the formula, valid for a sufficiently small time interval:
A positive growth rate indicates that the population is increasing, while a negative growth rate indicates that the population is decreasing. A growth ratio of zero indicates that there were the same number of individuals at the beginning and end of the period—a growth rate may be zero even when there are significant changes in the birth rates, death rates, immigration rates, and age distribution between the two times.[24]
A related measure is the net reproduction rate. In the absence of migration, a net reproduction rate of more than 1 indicates that the population of females is increasing, while a net reproduction rate less than one (sub-replacement fertility) indicates that the population of females is decreasing.
Most populations do not grow exponentially, rather they follow a logistic model. Once the population has reached its carrying capacity, it will stabilize and the exponential curve will level off towards the carrying capacity, which is usually when a population has depleted most its natural resources.[25] In the world human population, growth has been following a linear trend throughout the last few decades.[8]
.JPG.webp)
Logistic equation
The growth of a population can often be modelled by the logistic equation[26]
where
- = the population after time t;
- = time a population grows;
- = the relative growth rate coefficient;
- = the carrying capacity of the population; defined by ecologists as the maximum population size that a particular environment can sustain.[25]
As it is a separable differential equation, the population may be solved explicitly, producing a logistic function:
- ,
where and is the initial population at time 0.
Population growth rate
|
7–8 children
6–7 children |
5–6 children
4–5 children |
3–4 children
2–3 children |
1–2 children
0–1 children
|
.svg.png.webp)
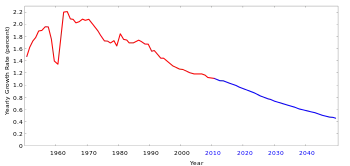
The world population growth rate peaked in 1963 at 2.2% per year and subsequently declined.[8] In 2017, the estimated annual growth rate was 1.1%.[27] The CIA World Factbook gives the world annual birthrate, mortality rate, and growth rate as 1.86%, 0.78%, and 1.08% respectively.[28] The last 100 years have seen a massive fourfold increase in the population, due to medical advances, lower mortality rates, and an increase in agricultural productivity made possible by the Green Revolution.[29]
The annual increase in the number of living humans peaked at 88.0 million in 1989, then slowly declined to 73.9 million in 2003, after which it rose again to 75.2 million in 2006. In 2017, the human population increased by 83 million.[27] Generally, developed nations have seen a decline in their growth rates in recent decades, though annual growth rates remain above 2% in some countries of the Middle East and Sub-Saharan Africa, and also in South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Latin America.[30]
In some countries the population is declining, especially in Eastern Europe, mainly due to low fertility rates, high death rates and emigration. In Southern Africa, growth is slowing due to the high number of AIDS-related deaths. Some Western Europe countries might also experience population decline.[31] Japan's population began decreasing in 2005.[32]
The United Nations Population Division projects world population to reach 11.2 billion by the end of the 21st century. The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation projects that the global population will peak in 2064 at 9.73 billion and decline to 8.89 billion in 2100. [9] A 2014 study in Science concludes that the global population will reach 11 billion by 2100, with a 70% chance of continued growth into the 22nd century.[33][34] The German Foundation for World Population reported in December 2019 that the global human population grows by 2.6 people every second, and could reach 8 billion by 2023.[35][36]
Growth by country
According to United Nations population statistics, the world population grew by 30%, or 1.6 billion humans, between 1990 and 2010.[37] In number of people the increase was highest in India (350 million) and China (196 million). Population growth rate was among highest in the United Arab Emirates (315%) and Qatar (271%).[37]
| Rank | Country | Population | Annual Growth (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 2010 | 2020 (est.)[38] | 1990–2010 | 2010–2020 | ||
| World | 5,306,425,000 | 6,895,889,000 | 7,503,828,180 | 1.3% | 0.8% | |
| 1 | 1,139,060,000 | 1,341,335,000 | 1,384,688,986 | 0.8% | 0.3% | |
| 2 | 873,785,000 | 1,224,614,000 | 1,296,834,042 | 1.7% | 0.6% | |
| 3 | 253,339,000 | 310,384,000 | 329,256,465 | 1.0% | 0.6% | |
| 4 | 184,346,000 | 239,871,000 | 262,787,403 | 1.3% | 0.9% | |
| 5 | 149,650,000 | 194,946,000 | 208,846,892 | 1.3% | 0.7% | |
| 6 | 111,845,000 | 173,593,000 | 207,862,518 | 2.2% | 1.8% | |
| 7 | 97,552,000 | 158,423,000 | 203,452,505 | 2.5% | 2.5% | |
| 8 | 105,256,000 | 148,692,000 | 159,453,001 | 1.7% | 0.7% | |
| 9 | 148,244,000 | 142,958,000 | 142,122,776 | -0.2% | −0.1% | |
| 10 | 122,251,000 | 128,057,000 | 126,168,156 | 0.2% | −0.1% | |
Many of the world's countries, including many in Sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, South Asia and South East Asia, have seen a sharp rise in population since the end of the Cold War. The fear is that high population numbers are putting further strain on natural resources, food supplies, fuel supplies, employment, housing, etc. in some of the less fortunate countries. For example, the population of Chad has ultimately grown from 6,279,921 in 1993 to 10,329,208 in 2009,[39] further straining its resources. Vietnam, Mexico, Nigeria, Egypt, Ethiopia, and the DRC are witnessing a similar growth in population.
The following table gives some example countries or territories:
| Country/territory | Life expectancy in years (2008) |
Total population growth from 1960s to 2007-2011 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1967 | 1990 | 1994 | 2002 | 2008 | |||
| N/A* | N/A* | 3,437,000[40] | 4,298,269 | 5,673,520[41] | 61[42] | 2,236,520 | |
| 23,457,000*[43] | 50,974,000* [44] | 54,939,000[40] | 67,673,031(2003) | 79,221,000[45] | 55[42] | 55,764,000 | |
| 14,355,000†[43] | 25,204,000† [44] | 27,361,000†[40] | 38,114,160 (2003)† | 42,272,000†[41] | 50†[42] | 27,917,000 | |
| 3,410,000[43] | 5,679,000[44] | 6,183,000[40] | 9,253,493(2003) | 10,329,208 (2009)[39] | 47[42] | 6,919,205 | |
| 3,546,000[43] | 7,732,000[44] | 8,846,000[40] | 10,790,352 (2001) | 15,306,252 (2009)[46] | 44[42] | 11,760,252 | |
| 61,450,000[43] | 88,500,000[44] | 108,467,000[40] | 129,934,911 | 158,259,000[41] | 47[42] | 96,809,000 | |
| 4,745,000[43] | 8,156,000[44] | 10,462,000[40] | 11,340,480 | 14,517,176(2010)[47] | 50[42] | 9,772,176 | |
| 1,050,000[43] | 2,025,000 [44] | 2,211,000[40] | 2,667,859 (2003) | 3,291,000 (2009)[39] | 54[42] | 2,241,000 | |
| 3,607,000[43] | 7,327,000[44] | 8,102,000[40] | 9,967,215 | 13,711,597 (2009)[48] | 57[42] | 10,104,597 | |
| 343,000[43] | 861,000[44] | 1,081,000[40] | 1,367,124 (2000) | 1,705,000[41] | 55[42] | 1,362,000 | |
| 11,833,126 (1966)[43] | 25,012,000[44] | 27,325,000 [40] | 32,818,500 (2003) | 34,895,000[45][49] | 74[42] | 23,061,874 | |
| 16,353,000[43] | 35,562,000[44] | 42,552,000[40] | 55,225,478 (2003) | 70,916,439 [45][50] | 54[42] | 54,563,439 | |
| 30,083,419 (1966)[43] | 53,153,000[44] | 58,326,000[40] | 70,712,345 (2003) | 79,089,650 [45][51] | 72[42] | 49,006,231 | |
(overseas region of France) | 418,000[43] | N/A[44] | N/A[40] | 720,934 (2003) | 827,000 (2009) [41] | N/A[42] | 409,000 |
(British Overseas Territory) | 2,500[43] | N/A[44] | N/A[40] | 2,967 (2003) | 3,140(2010)[52] | N/A[42] | 640 |
| 8,935,500[43] | 13,173,000[44] | 13,994,000[40] | 15,116,435 | 17,224,200 (2011) | 77[42] | 8,288,700 | |
| 19,191,000[43] | 32,987,000[44] | 34,520,000[40] | 41,088,227 | 45,925,397 (2010)[53] | 73[42] | 26,734,397 | |
| 85,655,000[43] | 150,368,000[44] | 153,725,000[40] | 174,468,575 (2000) | 190,732,694 (2010) [54] | 72[42] | 105,077,694 | |
| 45,671,000[43] | 86,154,000[44] | 93,008,000[40] | 103,400,165 (2000) | 112,322,757 (2010)[55] | 76[42] | 66,651,757 | |
| 476,727 (1966)[43] | 765,000[44] | 771,000[40] | 844,330 (2001) | 849,000[49] (2010) | 70[42] | 372,273 | |
| 6,050 (1966)[43] | 10,000[44] | N/A[40] | 12,329 | 9,322 (2011)[56] | N/A[42] | 3,272 | |
| 1,876,000[43] | 2,420,000[44] | 2,429,000[40] | 2,695,867 (2003) | 2,847,232[57](2010) | 74[42] | 971,232 | |
| 11,540,764 (1964)[43] | 17,086,000[44] | 17,843,000[40] | 19,546,792 (2003) | 26,342,068[58] (2010) | 82[42] | 10,066,508 | |
| 1,965,500 (1964)[43] | 3,250,000[44] | 3,414,000[40] | 3,510,484 | 2,986,952 (July 2010 est.)[39][59] | 78[42] | 1,021,452 | |
| 31,944,000[43] | 38,180,000[44] | 38,554,000[40] | 38,626,349 (2001) | 38,192,000 (2010)[60] | 75[42] | 6,248,000 | |
| 10,212,000[43] | 10,553,000[44] | 10,261,000[40] | 10,106,017 | 9,979,000 (2010)[61] | 73[42] | -142,000 | |
| 8,226,564 (1965)[43] | 8,980,000[44] | 8,443,000[40] | 7,707,495(2000) | 7,351,234 (2011)[62] | 73[42] | -875,330 | |
| 55,068,000 (1966)[43] | 57,411,000[44] | 58,091,000[40] | 58,789,194 | 62,008,048 (2010)[63] | 79[42] | 7,020,048 | |
| 2,884,002 (1966)[43] | 3,503,000[44] | 3,571,000[40] | 3,840,838 (2000) | 4,470,700[64] (2010) | 78[42] | 1,586,698 | |
| 720,000,000[43] | 1,139,060,000[44] | 1,208,841,000[40] | 1,286,975,468 (2004) | 1,339,724,852 (2010)[65] | 73[42] | 619,724,852 | |
| 98,274,961 (1965)[43] | 123,537,000[44] | 124,961,000[40] | 127,333,002 | 127,420,000 (2010)[66] | 82[42] | 28,123,865 | |
| 511,115,000[43] | 843,931,000[44] | 918,570,000[40] | 1,028,610,328 (2001) | 1,210,193,422 (2011)[67] | 69[42] | 699,078,422 | |
| 1,956,000 (1967)[43] | 3,003,000 (1990) [44] | 2,930,000 (1994)[40] | 4,452,732 (2002) | 5,076,700 (2010)[68] | 82 (2008)[42] | 3,120,700 | |
| 24,000 (1967)[43] | 29,000 (1990) [44] | N/A (1994)[40] | 31,842 (2000) | 35,586[69] (2010) | (2008)[42] | 11,586 | |
| 8,716,000 (1967)[43] | 10,123,000 (1990) [44] | 10,426,000 (1994)[40] | 10,964,020 (2001)[70] | 11,305,118 (2011)[71] | N/A (2008)[42] | 2,589,118 | |
(Danish dependency) | 38,000 (1967)[43] | N/A (1990) [44] | N/A (1994)[40] | 46,345 (2000) | 48,917 (2010) [72] | N/A (2008)[42] | 18,917 |
| 20,000 (1967)[43] | 29,000 (1990) [44] | N/A (1994)[40] | 33,307 (2000) | 35,789 (2009)[73] | (2008)[42] | 15,789 | |
| 29,207,856 (1966)[43] | 42,793,000 (1990) [44] | 44,453,000 (1994)[40] | 48,324,000 (2003) | 48,875,000 (2010) [74] | (2008)[42] | 19,667,144 | |
| 12,700,000 (1967)[43] | 21,773,000 (1990) [44] | 23,483,000 (1994)[40] | 22,224,195 (2002) | 24,051,218 (2010)[75] | (2008)[42] | 11,351,218 | |
| 107,200 (1967)[43] | 266,000 (1990) [44] | 280,000 (1994)[40] | 332,844 (2001) | 401,890 (2011)[76] | 76 (2008)[42] | 306,609 | |
| 10,671,000 (1967)[43] | 17,861,000 (1990) [44] | 19,489,000 (1994)[40] | 21,793,293 (2002) | 27,565,821 (2010)[77] | (2008)[42] | 16,894,821 | |
| 32,680,000 (1967)[43] | 57,196,000 (1990) [44] | 59,396,000 (1994)[40] | 60,606,947 (2000)[78] | 63,878,267 (2011)[79] | (2008)[42] | 31,198,267 | |
| 2,520,000 (1967)[43] | 2,701,000 (1990) [44] | 2,915,000 (1994)[40] | 3,727,703[80] (2003) | 4,224,000[41] (2009) | - (2008)[42] | ||
| 5,600,000 (1967)[43] | 12,116,000 (1990) [44] | 13,844,000 (1994)[40] | 17,585,540 (2003) | 22,457,763 (2011)[81] | -(2008)[42] | ||
| 182,00 (1967)[43] | 503,000 (1990) [44] | 549,000 (1994)[40] | 667,238 (2003) | 1,234,596[82] (2010) | 75 (2008)[42] | ||
| 11,741,000 (1967)[43] | 16,993,000 (1990) [44] | 17,685,000 (1994)[40] | 19,607,519 (2002) | 20,238,000[49] (2009) | - (2008)[42] | ||
| 6,050,000 (1967)[43] | 6.712,000 (1990) [44] | 6,994,000 (1994)[40] | 7,261,200 (2002) | 7,866,500[83] (2010) | - (2008)[42] | ||
| 335,000 (1967)[43] | 381,000 (1990) [44] | 401,000 (1994)[40] | 439,539 (2001) | 511,840 (2011)[84] | - (2008)[42] | ||
| 19,105,056 (1966)[43] | 23,200,000 (1990)[44] | 22,736,000 (1994)[40] | 21,680,974 (2002) | 21,466,174[85] (2011) | - (2008)[42] | ||
(associated state of New Zealand) | 1,900 (1966)[43] | N/A (1990)[44] | N/A (1994)[40] | 2,134 (2002) | 1,398 (2009)[86] | N/A (2008)[42] | -502 |
(New Zealand territory) | 5,194 (1966)[43] | N/A (1990)[44] | N/A (1994)[40] | 1,445 (2001) | 1,416 (2009) | N/A (2008)[42] | -3,778 |
| 1,876,000 (1967)[43] | 2,420,000 (1990) [44] | 2,429,000 (1994)[40] | 2,695,867 (2003) | 2,847,232[57] (2010) | 74 (2008)[42] | 971,232 | |
| 32,031,000 (1967)[43] | 32,322,000 (1990)[44] | 34,180,000 (1994)[40] | 37,812,817 (2002) | 40,091,359 (2010) | 74 (2008)[42] | 8,060,359 | |
| 49,890,660 (1967)[43] | 56,440,000 (1990)[44] | 57,747,000 (1994)[40] | 59,551,000 (2001) | 63,136,180 (2011)[87] | 81 (2008)[42] | ||
| 52,334,000 (1967)[43] | 57,662,000 (1990)[44] | 57,193,000 (1994)[40] | 56,995,744 (2002) | 60,605,053[88] (2011) | 80 (2008)[42] | ||
| 774,000 (1967)[43] | 1,075,000 (1990)[44] | 1,104,000 (1994)[40] | 1,179,137 (2000) | 1,288,000 (2009)[49] | 75 (2008)[42] | 514,000 | |
| 4,717,000 (1967)[43] | 9,197,000 (1990)[44] | 10,322,000 (1994)[40] | 12,974,361 (2000) | 13,276,517 (2009) | 70 (2008)[42] | 8,559,517 | |
| 8,033,000 (1967)[43] | 10,609,000 (1990)[44] | 10,960,000 (1994)[40] | 11,177,743 (2002) | 11,239,363 (2009)[89] | 77 (2008)[42] | ||
| 246,000 (1967)[43] | 255,000 (1990) [44] | 261,000 (1994)[40] | 250,012 (2001) | 284,589 (2010)[39] | 73 (2008)[42] | 18,589 | |
| 131,377 (1967)[43] | 164,000 (1990) [44] | 164,000 (1994)[40] | 178,173 (2003) | 179,000 (2009)[41] | N/A (2008)[42] | ||
| 7,765,981 (1967)[43] | 8,559,000 (1990) [44] | 8,794,000 (1994)[40] | 8,920,705 (2002) | 9,354,462 (2009) | 81 (2008)[42] | ||
| 4,664,000 (1967)[43] | 4,986,000 (1990) [44] | 5,095,000 (1994)[40] | 5,175,783 (2002) | 5,374,781 (2010) | N/A (2008)[42] | ||
| 9,440,000 (1967)[43] | 10,525,000 (1990)[44] | 9,830,000 (1994)[40] | 10,355,824 (2001) | 10,647,763[90] (2011) | N/A (2008)[42] | ||
| 7,323,981 (1967)[43] | 7,712,000 (1990) [44] | 8,031,000 (1994)[40] | 8,032,926 (2001) | 8,404,252 (2011) | N/A (2008)[42] | ||
| 1,738,000 (1967)[43] | 4,545,000 (1990)[44] | 5,225,000(1994)[40] | 5,499,074 (2002) | 6,420,000 (2009)[41] | 77 (2008)[42] | ||
| 12,385,000 (1967)[43] | 21,550,000 (1990)[44] | 23,080,000(1994)[40] | 27,949,639 (2002) | 29,496,000 (2010) | 70 (2008)[42] | ||
| 528,000 (1967)[43] | 965,000 (1990) [44] | 1,050,000 (1994)[40] | 1,345,479 (2002) | 1,647,000[41] (2009) | 48 (2008)[42] | ||
| 5,203,066 (1967)[43] | 10,020,000 (1990)[44] | 10,674,000 (1994)[40] | 10,766,500 (2003) | 18,498,000[49][91] (2009) | 38 (2008)[42] | ||
| 277,000 (1967)[43] | 348,000 (1990)[44] | 389,000 (1994)[40] | 474,214 (2000) | 676,000 (2009)[49] | 61 (2008)[42] | ||
| 2,505,000 (1967)[43] | 4,736,000 (1990)[44] | 5,246,000 (1994)[40] | 8,500,500 (2002) | 8,791,832 (2009) | 59 (2008)[42] | ||
| 2,770,000 (1967)[43] | 4,139,000 (1990)[44] | 4,742,000 (1994)[40] | 5,635,967 (2002) | 6,800,000[92] (2011) | 56 (2008)[42] | ||
| 10,500,000 (1967)[43] | 18,961,000 (1990)[44] | 21,360,000 (1994)[40] | 25,284,463 (2002) | 29,331,000[49] (2009) | - (2008)[42] | ||
| 25,781,090 (1966)[43] | 54,608,000 (1990)[44] | 59,778,000 (1994)[40] | 66,622,704 (2002) | 75,330,000 (2010)[93] | 71 (2008)[42] | 49,548,910 | |
| 20,014,880 (1966)[43] | 26,603,000 (1990)[44] | 29,248,000(1994)[40] | 31,081,900 (2001) | 32,623,490 (2011)[94] | 81 (2008)[42] | ||
| 199,118,000 (1967)[43] | 249,995,000 (1990)[44] | 260,650,00(1994)[40] | 281,421,906 (2000) | 308,745,538 (2010)[95] | 78 (2008)[42] | ||
| 7,931,000 (1967)[43] | 18,795,000 (1990)[44] | 20,621,000 (1994)[40] | 24,227,297 (2002) | 32,369,558 (2009) | 52 (2008)[42] |
- Notes
- * Eritrea left Ethiopia in 1991.
- † Split into the nations of Sudan and South Sudan during 2011.
- ‡ Japan and the Ryukyu Islands merged in 1972.
- # India and Sikkim merged in 1975.
| Population growth 1990–2012 (%)[96] | |
|---|---|
| Africa | 73.3% |
| Middle East | 68.2% |
| Asia (excl. China) | 42.8% |
| China | 19.0% |
| OECD Americas | 27.9% |
| Non-OECD Americas | 36.6% |
| OECD Europe | 11.5% |
| OECD Asia Oceania | 11.1% |
| Non-OECD Europe and Eurasia | -0.8% |

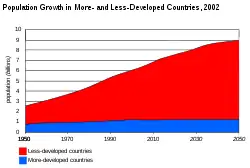
Future population
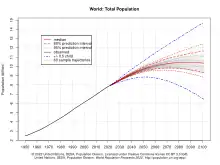
Population projections are attempts to show how the human population statistics might change in the future.[97] These projections are an important input to forecasts of the population's impact on this planet and humanity's future well-being.[98] Models of population growth take trends in human development, and apply projections into the future.[99] These models use trend-based-assumptions about how populations will respond to economic, social and technological forces to understand how they will affect fertility and mortality, and thus population growth.[99]
The 2019 projections from the United Nations Population Division show that annual world population growth peaked at 2.1% in 1968, has since dropped to 1.1%, and could drop even further to 0.1% by 2100, which would be a growth rate not seen since pre-industrial revolution days.[100] Based on this, the UN Population Division projects the world population, which is 7.8 billion as of 2020, to level out around 2100 at 10.9 billion (the median line),[101][102] assuming a continuing decrease in the global average fertility rate from 2.5 births per woman during the 2015–2020 period to 1.9 in 2095–2100, according to the medium-variant projection.[103] A 2014 projection has the population continuing to grow into the next century.[104]
However, estimates outside of the United Nations have put forward alternative models based on additional downward pressure on fertility (such as successful implementation of education and family planning goals in the Sustainable Development Goals) which could result in peak population during the 2060-2070 period rather than later.[99][105]
According to the UN, about two-thirds of the predicted growth in population between 2020 and 2050 will take place in Africa.[106] It is projected that 50% of births in the 5-year period 2095-2100 will be in Africa.[107] Other organizations project lower levels of population growth in Africa based particularly on improvement in women's education and successfully implementing family planning.[108]
By 2100, the UN projects the population in Sub-Saharan Africa will reach 3.8 billion, IHME projects 3.1 billion, and IIASA is the lowest at 2.6 billion. In contrast to the UN projections, the models of fertility developed by IHME and IIASA incorporate women's educational attainment, and in the case of IHME, also assume successful implementation of family planning.[109]
See also
- List of countries by population growth rate
- Demographic history
- Demographic transition
- Density dependence
- Ecological overshoot
- Epidemiological transition
- Human population planning
- Irruptive growth
- Overshoot (population)
- Population decline
- Population density
- World population
- Estimates of historical world population
References
- "Absolute increase in global population per year". Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 28 February 2021. Retrieved 15 February 2020.
- "World Population Prospects 2017 – Data Booklet (ST/ESA/SER.A/401)" (PDF). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. 2017. p. 3. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 7, 2022. Retrieved April 13, 2022.
- "World Population 2017". Retrieved 2020-04-01.
- "World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision: Key Findings and Advance Tables" (PDF). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. p. 2. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 26, 2019. Retrieved January 5, 2019.
- Roser, Max (2013-05-09). "Future Population Growth". Our World in Data.
- "Black death 'discriminated' between victims". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 29 January 2008. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 2008-11-03.
- Population Reference Bureau. "2013 World Population Factsheet" (PDF). Population Reference Bureau. Retrieved 5 December 2014.
- Roser, Max; Ritchie, Hannah; Ortiz-Ospina, Esteban (2013-05-09). "World Population Growth". Our World in Data.
- Vollset, Stein Emil; Goren, Emily; Yuan, Chun-Wei; Cao, Jackie; Smith, Amanda E.; Hsiao, Thomas; Bisignano, Catherine; Azhar, Gulrez S.; Castro, Emma; Chalek, Julian; Dolgert, Andrew J.; Frank, Tahvi; Fukutaki, Kai; Hay, Simon I.; Lozano, Rafael; Mokdad, Ali H.; Nandakumar, Vishnu; Pierce, Maxwell; Pletcher, Martin; Robalik, Toshana; Steuben, Krista M.; Wunrow, Han Yong; Zlavog, Bianca S.; Murray, Christopher J L. (July 14, 2020). "Fertility, mortality, migration, and population scenarios for 195 countries and territories from 2017 to 2100: a forecasting analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study". Lancet (pdf). 396 (10258): 1285–1306. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30677-2. PMC 7561721. PMID 32679112.
- Stokstad, Erik (5 May 2019). "Landmark analysis documents the alarming global decline of nature". Science. AAAS. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
Driving these threats are the growing human population, which has doubled since 1970 to 7.6 billion, and consumption. (Per capita of use of materials is up 15% over the past 5 decades.)
- Crist, Eileen; Ripple, William J.; Ehrlich, Paul R.; Rees, William E.; Wolf, Christopher (2022). "Scientists' warning on population" (PDF). Science of the Total Environment. 845: 157166. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157166. PMID 35803428.
- United Nations Environment Programme (2021). Making Peace with Nature: A scientific blueprint to tackle the climate, biodiversity and pollution emergencies. Nairobi. https://www.unep.org/resources/making-peace-nature
- "United Nations - World Population Prospects 2017". Archived from the original on 2018-03-22. Retrieved 2017-07-07.
- Greenwood, B. (19 June 2014). "The contribution of vaccination to global health: past, present and future". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society. 369 (1645): 20130433. doi:10.1098/rstb.2013.0433. PMC 4024226. PMID 24821919.
- Armelagos, George J., Alan H. Goodman, and Kenneth H. Jacobs. "The origins of agriculture: Population growth during a period of declining health." Population and Environment 13.1 (1991): 9-22.
- Smil, Vaclav (1999). "Detonator of the population explosion" (PDF). Nature. 400 (6743): 415. Bibcode:1999Natur.400..415S. doi:10.1038/22672. S2CID 4301828.
- McKeown, Thomas (1976). The Modern Rise of Population. London, UK: Edward Arnold. ISBN 9780713159868.
- McKeown T, Brown RG (1955). "Medical evidence related to English population changes in the eighteenth century". Population Studies. 9 (2): 119–141. doi:10.1080/00324728.1955.10404688. JSTOR 2172162.
- McKeown T, Brown RG, Record RG (1972). "An interpretation of the modern rise of population in Europe". Population Studies. 26 (3): 345–382. doi:10.1080/00324728.1972.10405908. JSTOR 2173815. PMID 11630563.
- McKeown T, Record RG (1962). "Reasons for the Decline of Mortality in England and Wales during the Nineteenth Century". Population Studies. 16 (2): 94–122. doi:10.2307/2173119. JSTOR 2173119.
- McKeown T, Record RG, Turner RD (1975). "An Interpretation of the Decline of Mortality in England and Wales during the Twentieth Century". Population Studies. 29 (3): 391–422. doi:10.1080/00324728.1975.10412707. JSTOR 2173935. PMID 11630508.
- Korotayev, A. V.; Malkov, A. S. (2016). "Compact Mathematical Model of the World System Economic and Demographic Growth, 1 CE–1973 CE". International Journal of Mathematical Models and Methods in Applied Sciences. 10: 200–209.
- Deaton, Angus (2013). The Great Escape. Health, wealth, and the origins of inequality. Princeton and Oxford: Princeton University Press. pp. 91–93. ISBN 978-0-691-15354-4.
McKeown's views, updated to modern circumstances, are still important today in debates between those who think that health is primarily determined by medical discoveries and medical treatment and those who look to the background social conditions of life.
- Association of Public Health Epidemiologists in Ontario Archived 2008-05-22 at the Wayback Machine
- Reece, Jane; Urry, Lisa; Cain, Michael; Wasserman, Steven; Minorsky, Peter; Jackson, Robert (2014). Campbell Biology. Pearson.
- Stewart, James; Clegg, Daniel (2012). Brief Applied Calculus. Brooks/Cole Cengage Learning.
- "World Population Prospects 2017". Archived from the original on 2017-07-11.
- "The World Factbook". 20 November 2015. Retrieved 4 January 2016.
- "BBC NEWS - South Asia - The end of India's green revolution?". 2006-05-29.
- "International Programs". Archived from the original on 2009-07-01.
- "UN population projections". Archived from the original on 2010-09-14. Retrieved 2009-05-23.
- "Japan sees biggest population fall". the Guardian. Associated Press. 2009-01-02.
- Carrington, Damien (September 18, 2014). "World population to hit 11bn in 2100 – with 70% chance of continuous rise". The Guardian. Retrieved December 19, 2016.
- Gerland, P.; Raftery, A. E.; Ev Ikova, H.; Li, N.; Gu, D.; Spoorenberg, T.; Alkema, L.; Fosdick, B. K.; Chunn, J.; Lalic, N.; Bay, G.; Buettner, T.; Heilig, G. K.; Wilmoth, J. (September 14, 2014). "World population stabilization unlikely this century". Science. 346 (6206): 234–7. Bibcode:2014Sci...346..234G. doi:10.1126/science.1257469. ISSN 1095-9203. PMC 4230924. PMID 25301627.
- Hook, Chris (December 20, 2019). "Earth's population set to soar to 7.75 billion people by New year's Eve". Seven News. Retrieved January 2, 2020.
- Silk, John (21 December 2019). "World's population to hit 7.75 billion in 2019". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 14 March 2021.
- "World Population Prospects - Population Division - United Nations". Archived from the original on 2011-05-07. Retrieved 2012-05-28.
- "East Asia/Southeast Asia :: China — The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Retrieved 2019-05-15.
- Barbados: People. World Factbook of CIA
- The British Collins Longman Student Atlas, the 1996 and in 1998 publications, ISBN 978-0-00-448879-0 for the 1998 edition, ISBN 0-00-448365-0 for the 1996 edition
- "World Population Prospects: The 2008 Revision: Selected Tables: Annex Tables" (PDF). United Nations. 2009. Table A.1. Total Population by Sex in 2009 and Sex Ratio by Country in 2009. Retrieved 2009-03-12. NB: The preliminary results of the National population census in Guinea-Bissau put the figure at 1,449,230, according to email information by the Instituto Nacional de Estudos e Pesquisa, Bissau.
- 'Modern School Atlas (96th edition)', ISBN 978-1-84907-013-3.
- The British Oxford economic atlas of the World 4th edition, ISBN 0-19-894107-2
- The British Collins Atlas of the World, the 1993 edition, ISBN 0-00-448038-4
- Ethiopia Central Statistics Office -- Population Projection for mid-2008 Archived January 5, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- Central Intelligence Agency (2009). "Niger". The World Factbook. Retrieved January 10, 2010.
- "Mali preliminary 2009 census". Institut National de la Statistique. Archived from the original on April 18, 2010. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- Central Intelligence Agency (2009). "Senegal". The World Factbook. Retrieved January 10, 2010.
- "World Population Prospects, Table A.1" (PDF). United Nations. 2010. Retrieved 2009-03-12.
- The World Factbook- Congo, Democratic Republic of the. Central Intelligence Agency.
- "Central Agency for Population Mobilisation and Statistics — Population Clock (July 2008)". Msrintranet.capmas.gov.eg. Archived from the original on 2010-09-08. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- "Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas)". The World Factbook. CIA. Retrieved 5 March 2010.
- "Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadística". Dane.gov.co. Archived from the original on 2015-09-05. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- IBGE. Censo 2010: população do Brasil é de 190.732.694 pessoas.
- "INEGI 2010 Census Statistics". inegi.org.mx. Retrieved 2010-11-25.
- Central Intelligence Agency (2011). "Nauru". The World Factbook. Retrieved 12 February 2011.
- "The World Factbook". 19 October 2021.
- "Population clock". Australian Bureau of Statistics website. Commonwealth of Australia. Retrieved 12 April 2011. The population estimate shown is automatically calculated daily at 00:00 UTC and is based on data obtained from the population clock on the date shown in the citation.
- "IFs Forecast - Version 7.00-Google Public Data Explorer".
- "Wzrasta liczba ludności Polski - Wiadomości - WP.PL". Wiadomosci.wp.pl. 2010-07-23. Archived from the original on 2013-10-05. Retrieved 2010-07-27.
- Hungarian Central Statistical Office. Retrieved 25 July 2010.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-09-05. Retrieved 2011-12-31.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Total population at 1 January". Eurostat. 11 March 2011. Retrieved 29 April 2011.
- "CSO – Population and Migration Estimates April 2010" (PDF). September 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2010. Retrieved 21 September 2010.
- Communiqué of the National Bureau of Statistics of People's Republic of China on Major Figures of the 2010 Population Census Archived November 8, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- "Statistics Bureau Home Page/Population Estimates Monthly Report".
- "Provisional Population Totals - Census 2011". Indian Census Bureau 2011. Retrieved 2011-03-29.
- "Population (Mid Year Estimates) & Land Area". Statistics Singapore. 31 August 2010. Archived from the original on 2010-09-14.
- Monaco, The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 7 June 2010.
- "Πίνακας 1. Πληθυσμός κατά φύλο και ηλικία" (PDF). National Statistical Service of Greece: Population census of 18 March 2001. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 25, 2009.
- "Total population". Eurostat. 1 January 2010. Retrieved 8 January 2010.
- "Hagstova F?roya". Archived from the original on 2013-12-10. Retrieved 2015-12-10. (Faroese)
- Bevölkerungsstatistik 30. Juni 2009 Archived 2013-11-14 at the Wayback Machine, Landesverwaltung Liechtenstein.
- "총인구, 인구성장률 : 지표상세화면". Index.go.kr. Retrieved 2010-10-29.
- 한반도 인구 7천400만명 시대 임박. Joins (in Korean). 2009-10-01. Archived from the original on 2010-04-17. Retrieved 2010-04-14.
- "Brunei". CIA World Factbook. 2011. Retrieved 2011-01-13.
- "Laporan Kiraan Permulaan 2010". Jabatan Perangkaan Malaysia. p. iii. Archived from the original on July 8, 2011. Retrieved 31 January 2011.
- "Population and Housing Census 2000, National Statistical Office". Web.nso.go.th. 2000-04-01. Archived from the original on 2017-11-14. Retrieved 2010-04-25.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-16. Retrieved 2011-07-16.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Central Intelligence Agency. March 2011 est". Cia.gov. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- "Central Intelligence Agency. March 2011 est". Cia.gov. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- "REMARKABLE GROWTH EXPATS OUTNUMBER BAHRAINIS IN 2010 CENSUS". Bahraini Census 2010. 2010-11-28. Archived from the original on February 19, 2011. Retrieved 14 February 2011.
- "Population size and population composition". Swiss Federal Statistical Office. Swiss Federal Statistical Office, Neuchâtel. 2010. Archived from the original on 2016-06-28. Retrieved 2011-04-29.
- "Population: 511 840 habitants au 1er janvier 2011", Le Portail des statistiques: Grand-Duché de Luxembourg, 3 May 2011. (in French) Retrieved 4 May 2011.
- "Romania - Population". epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 26 May 2011.
- "Niue". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2009-07-20.
- "Population totale par sexe et âge au 1er janvier 2011, France métropolitaine". INSEE (in French). Government of France. Retrieved 20 January 2011.
- "Monthly demographic balance: January–November 2010" (PDF) (in Italian). Istat. 28 March 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 July 2012. Retrieved 2 April 2011.
- Anuario Estadístico de Cuba 2009. Edición 2010 Archived 2010-07-16 at the Wayback Machine, Oficina Nacional de Estadísticas, República de Cuba. Accessed on November 6, 2010. Note: An exchange rate of 1 CUC to 1.08 USD was used to convert GDP.
- Pordata, "Base de Dados Portugal Contemporâneo". Accessed on March 7, 2011.
- "Population Forecast to 2060 by International Futures hosted by Google Public Data Explorer". Retrieved 2011-07-13.
- "Background notes - Laos". US Dept. of State. Retrieved 2011-01-20.
- "Official Iranian Population clock". Amar.org.ir. Archived from the original on 2011-07-22. Retrieved 2011-07-13.
- "Estimated population of Canada, 1605 to present". Statistics Canada. 6 July 2009. Retrieved 2011-04-17.
- "Resident Population Data – 2010". U.S. Census Bureau. 2010. Archived from the original on 2011-10-28. Retrieved 2010-12-22.
- CO2 Emissions from Fuel Combustion Archived 2015-12-02 at the Wayback Machine Population 1971–2014 IEA (PDF Page 74, marked page 72)
- "Population Projections". United States Census Bureau.
- Kaneda, Toshiko (June 2014). "Understanding Population Projections: Assumptions Behind the Numbers" (PDF). Population Reference Bureau.
- Roser, Max (2013-05-09). "Future Population Growth". Our World in Data.
- Roser, Max (June 18, 2019). "Two centuries of rapid global population growth will come to an end". Our World in Data.
- "World Population Prospects 2019". United Nations, Dept of Economic and Social Affairs. 2019.
- "World Population Prospects 2019, Population Data, File: Total Population Both Sexes, Medium Variant tab". United Nations Population Division. 2019.
- "World Population Prospects 2019, Dept of Economic and Social Affairs, File: Total Fertility". United Nations Population Division. 2019.
- Gerland, P.; Raftery, A. E.; Ev Ikova, H.; Li, N.; Gu, D.; Spoorenberg, T.; Alkema, L.; Fosdick, B. K.; Chunn, J.; Lalic, N.; Bay, G.; Buettner, T.; Heilig, G. K.; Wilmoth, J. (September 14, 2014). "World population stabilization unlikely this century". Science. AAAS. 346 (6206): 234–7. Bibcode:2014Sci...346..234G. doi:10.1126/science.1257469. ISSN 1095-9203. PMC 4230924. PMID 25301627.
- Vollset, Stein Emil; Goren, Emily; Yuan, Chun-Wei; Cao, Jackie; Smith, Amanda E.; Hsiao, Thomas; Bisignano, Catherine; Azhar, Gulrez S.; Castro, Emma; Chalek, Julian; Dolgert, Andrew J. (2020-10-17). "Fertility, mortality, migration, and population scenarios for 195 countries and territories from 2017 to 2100: a forecasting analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study". The Lancet. 396 (10258): 1285–1306. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30677-2. ISSN 0140-6736. PMC 7561721. PMID 32679112.
- "World Population Prospects 2019, Population Data, File: Population Growth Rate, Median Variant tab". United Nations Population Division. 2019.
- "World's Population is Projected to Nearly Stop Growing by the end of the Century". June 17, 2019.
- Kaneda, Toshiko; Falk, Marissa; Patierno, Kaitlyn (March 27, 2021). "Understanding and Comparing Population Projections in Sub-Saharan Africa". Population Reference Bureau.
- "Understanding and Comparing Population Projections in Sub-Saharan Africa". Population Reference Bureau.
External links
- "World Population Prospects". Website of the United Nations Population Division. Archived from the original on 2017-07-11.
- "Food Production and Population Growth". Daniel Quinn, Alan D. Thornhill, PhD. Ecofuture. Population and Sustainability Media, Non-fiction.
- "Probabilistic Population Projections, 2nd Revision". Website of the United Nations Population Division. Archived from the original on 2013-10-04.
- "Population Growth and the Food Supply". Population Institute of Canada.
- "World population growth and trends 1950-2050". US Census. Archived from the original on 2010-07-07.
- "World population: focus on youth, Annual World Population Data Sheet". Population Reference Bureau.
- "Feeding the Ten Billion-Plants and Population Growth". PGR Newsletter FAO-Bioversity L.T. Evans. 2000. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-64685-5. Published in Issue No. 125, page 39 to 40 - (5802) characters