Energy policy of the European Union
Although the European Union has legislated, set targets, and negotiated internationally in the area of energy policy for many years, and evolved out of the European Coal and Steel Community, the concept of introducing a mandatory common European Union energy policy was only approved at the meeting of the European Council on October 27, 2005 in London. Following this the first policy proposals, Energy for a Changing World, were published by the European Commission, on January 10, 2007. The most well known energy policy objectives in the EU are 20/20/20 objectives, binding for all EU Member States. The EU is planning to increase the share of renewable energy in its final energy use to 20%, reduce greenhouse gases by 20% and increase energy efficiency by 20%.[2]
European Union total primary energy consumption by fuel in 2017[1]
| This article is part of a series on |
Politics of the European Union |
|---|
 |
|
The EU Treaty of Lisbon of 2007 legally includes solidarity in matters of energy supply and changes to the energy policy within the EU. Prior to the Treaty of Lisbon, EU energy legislation has been based on the EU authority in the area of the common market and environment. However, in practice many policy competencies in relation to energy remain at national member state level, and progress in policy at European level requires voluntary cooperation by members states.[3]
In 2007, the EU was importing 82% of its oil and 57% of its gas, which then made it the world's leading importer of these fuels.[4] Only 3% of the uranium used in European nuclear reactors was mined in Europe. Russia, Canada, Australia, Niger and Kazakhstan were the five largest suppliers of nuclear materials to the EU, supplying more than 75% of the total needs in 2009.[5] In 2015, the EU imports 53% of the energy it consumes.[6] In January 2014, the EU agreed to a 40% emissions reduction by 2030, compared to 1990 levels, and a 27% renewable energy target, which is expected to provide 70,000 full-time jobs and cut €33bn in fossil fuel imports.[7] The target is ambitious compared to other advanced economies but insufficient to limit warming to well below 2 °C, let alone 1.5 °C, and align with the Paris Agreement.[8]
In 2015, the Framework Strategy for Energy Union is launched as one of the European Commission's 10 Priorities.[9]
Energy Union
The Energy Union Strategy is a project[10][9] of the European Commission to coordinate the transformation of European energy supply. It was launched in February 2015, with the aim of providing secure, sustainable, competitive, affordable energy.[11]
Donald Tusk, President of the European Council, introduced the idea of an energy union when he was Prime Minister of Poland. Eurocommissioner Vice President Maroš Šefčovič called the Energy Union the biggest energy project since the European Coal and Steel Community.[12] The EU's reliance on Russia for its energy, and the annexation of Crimea by Russia have been cited as strong reasons for the importance of this policy.
The European Council concluded on 19 March 2015 that the EU is committed to building an Energy Union with a forward-looking climate policy on the basis of the commission's framework strategy, with five priority dimensions:
- Energy security, solidarity and trust
- A fully integrated European energy market
- Energy efficiency contributing to moderation of demand
- Decarbonising the economy
- Research, innovation and competitiveness.
The strategy includes a minimum 10% electricity interconnection target for all member states by 2020, which the Commission hopes will put downward pressure onto energy prices, reduce the need to build new power plants, reduce the risk of black-outs or other forms of electrical grid instability, improve the reliability of renewable energy supply, and encourage market integration.[14]
EU Member States agreed 25 January 2018 on the commission's proposal to invest €873 million in clean energy infrastructure.[15] The projects are financed by CEF (Connecting Europe Facility).[16]
- €578 million for the construction of the Biscay Gulf France-Spain interconnection, a 280 km long off-shore section and a French underground land section. This new link will increase the interconnection capacity between both countries from 2.8 GW to 5 GW.[17]
- €70 million to construct the SüdOstLink, 580 km of high-voltage cables laid fully underground. The power line will create an urgently needed link between the wind power generated in the north and the consumption centres in the south of Germany.
- €101 million for the CyprusGas2EU project to provide natural gas to Cyprus.
Earlier proposals
The possible principles of Energy Policy for Europe were elaborated at the commission's green paper A European Strategy for Sustainable, Competitive and Secure Energy on 8 March 2006.[21] As a result of the decision to develop a common energy policy, the first proposals, Energy for a Changing World were published by the European Commission, following a consultation process, on 10 January 2007.
It is claimed that they will lead to a 'post-industrial revolution', or a low-carbon economy, in the European Union, as well as increased competition in the energy markets, improved security of supply, and improved employment prospects. The commission's proposals have been approved at a meeting of the European Council on 8 and 9 March 2007.[22]
Key proposals[23] include:
- A cut of at least 20% in greenhouse gas emissions from all primary energy sources by 2020 (compared to 1990 levels), while pushing for an international agreement to succeed the Kyoto Protocol aimed at achieving a 30% cut by all developed nations by 2020.
- A cut of up to 95% in carbon emissions from primary energy sources by 2050, compared to 1990 levels.
- A minimum target of 10% for the use of biofuels by 2020.
- That the energy supply and generation activities of energy companies should be 'unbundled' from their distribution networks to further increase market competition.
- Improving energy relations with the EU's neighbours, including Russia.
- The development of a European Strategic Energy Technology Plan to develop technologies in areas including renewable energy, energy conservation, low-energy buildings, fourth generation nuclear reactor, coal pollution mitigation, and carbon capture and sequestration (CCS).
- Developing an Africa-Europe Energy partnership, to help Africa 'leap-frog' to low-carbon technologies and to help develop the continent as a sustainable energy supplier.
Many underlying proposals are designed to limit global temperature changes to no more than 2 °C above pre-industrial levels,[24] of which 0.8 °C has already taken place and another 0.5–0.7 °C is already committed.[25] 2 °C is usually seen as the upper temperature limit to avoid 'dangerous global warming'.[26] Due to only minor efforts in global Climate change mitigation it is highly likely that the world will not be able to reach this particular target. The EU might then not only be forced to accept a less ambitious global target. Because the planned emissions reductions in the European energy sector (95% by 2050) are derived directly from the 2 °C target since 2007, the EU will have to revise its energy policy paradigm.[27][28]
In 2014, negotiations about binding EU energy and climate targets until 2030 are set to start.[29][30] European Parliament voted in February 2014 in favour of binding 2030 targets on renewables, emissions and energy efficiency: a 40% cut in greenhouse gases, compared with 1990 levels; at least 30% of energy to come from renewable sources; and a 40% improvement in energy efficiency.[31]
Current policies
SET Plan
The FP7 research program only reserved a moderate amount of funding for energy research, although energy has recently emerged as one of the key issues of the European Union. A large part of FP7 energy funding is also devoted to fusion research, a technology that will not be able to help meet European climate and energy objectives until beyond 2050. More in the section on the page of the European Commission's participation in the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor - ITER - mega project built in the south of France.[32] The European Commission tried to redress this shortfall with the SET plan.[33]
The Steering Group on the implementation of the Strategic Energy Technologies Plan (SET Plan) on 26 June 2008 will set the agenda for an EU energy technology policy. It will enhance the coordination of national and European research and innovation efforts to position the EU in the forefront of the low-carbon technologies markets.[34][35]
The SET plan initiatives:
- European Wind Initiative
- focus on large turbines and large systems' validation and demonstration (relevant to on and off-shore applications). See also: European Technology Platform for Wind Energy
- Solar Europe Initiative
- focus on large-scale demonstration for photovoltaics and concentrated solar power
- Bioenergy Europe Initiative
- focus on 'next generation' biofuels within the context of an overall bio-energy use strategy. See also: European Biofuels Technology Platform
- European CO2 capture, transport and storage initiative
- focus on the whole system requirements, including efficiency, safety and public acceptance, to prove the viability of Zero Emission Fossil Fuel Power Plants at industrial scale.
- European electricity grid initiative
- focus on the development of the smart electricity system, including storage, and on the creation of a European centre to implement a research programme for the European transmission network. See also: European Technology Platform for the Electricity Networks of the Future
- Sustainable nuclear fission initiative
- focus on the development of Generation IV reactors technologies.[6] This includes the ESNII which comprises the Allegro reactor, MYRRHA and ASTRID.[36]
The budget for the SET plan is estimated at €71.5 billion.[37]
The IEA raised its concern that demand-side technologies do not feature at all in the six priority areas of the SET Plan.[33]
The EU resolution is available in EUR-Lex.[38]
European Energy Research Alliance (EERA)
The European Energy Research Alliance (EERA) [39] is founded by leading research institutes in the European Union, to expand and optimise EU energy research capabilities through the sharing of world-class national facilities and the joint realisation of national and European programmes. Formed in 2008, EERA intends to be a key actor of the EU Strategic Energy Technology Plan (SET Plan) and will contribute to accelerating the development of new low carbon technologies for the Union to move toward a low carbon economy.[40] In May 2017, Nils Anders Røkke from SINTEF was appointed EERA chairperson.[41]
Energy sources
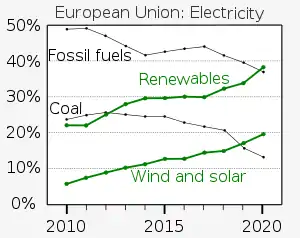
Under the requirements of the Directive on Electricity Production from Renewable Energy Sources, which entered into force in October 2001, the member states are expected to meet "indicative" targets for renewable energy production. Although there is significant variation in national targets, the average is that 22% of electricity should be generated by renewables by 2010 (compared to 13,9% in 1997). The European Commission has proposed in its Renewable Energy Roadmap21 a binding target of increasing the level of renewable energy in the EU's overall mix from less than 7% today to 20% by 2020.[44]
Europe spent €406 billion in 2011 and €545 billion in 2012 on importing fossil fuels. This is around three times more than the cost of the Greek bailout up to 2013. In 2012, wind energy avoided €9.6 billion of fossil fuel costs. EWEA recommends binding renewable energy target to support in replacing fossil fuels with wind energy in Europe by providing a stable regulatory framework. In addition, it recommends setting a minimum emission performance standard for all new-build power installations.[45]
For over a decade, the European Investment Bank has managed the European Local Energy Assistance (ELENA) facility on behalf of the European Commission, which provides technical assistance to any private or public entity in order to help prepare energy-efficient and renewable energy investments in buildings or innovative urban transportation projects.[46][47] The EU Modernisation Fund, formed in 2018 as part of the new EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) Directive and with direct engagement from the EIB12, targets such investments as well as energy efficiency and a fair transition across 10 Member States.
Energy markets
The EU promotes electricity market liberalisation and security of supply through Directive 2019/944
The 2004 Gas Security Directive[48] has been intended to improve security of supply in the natural gas sector.
Energy efficiency
IPEEC
At the Heiligendamm Summit in June 2007, the G8 acknowledged an EU proposal for an international initiative on energy efficiency tabled in March 2007, and agreed to explore, together with the International Energy Agency, the most effective means to promote energy efficiency internationally. A year later, on 8 June 2008, the G8 countries, China, India, South Korea and the European Community decided to establish the International Partnership for Energy Efficiency Cooperation, at the Energy Ministerial meeting hosted by Japan in the frame of the 2008 G8 Presidency, in Aomori.[49]
Buildings
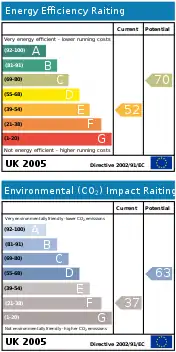
Buildings account for around 40% of EU energy requirements and have been the focus of several initiatives.[50] From 4 January 2006, the 2002 Directive on the energy performance of buildings[51] requires member states to ensure that new buildings, as well as large existing buildings undergoing refurbishment, meet certain minimum energy requirements. It also requires that all buildings should undergo 'energy certification' prior to sale, and that boilers and air conditioning equipment should be regularly inspected.
As part of the EU's SAVE Programme,[52] aimed at promoting energy efficiency and encouraging energy-saving behaviour, the Boiler Efficiency Directive[53] specifies minimum levels of efficiency for boilers fired with liquid or gaseous fuels. Originally, from June 2007, all homes (and other buildings) in the UK would have to undergo Energy Performance Certification before they are sold or let,[54] to meet the requirements of the European Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (Directive 2002/91/EC).[55]
Transport
Carbon dioxide emissions from transport have risen rapidly in recent years, from 21% of the total in 1990 to 28% in 2004.[56]
EU policies include the voluntary ACEA agreement, signed in 1998, to cut carbon dioxide emissions for new cars sold in Europe to an average of 140 grams of CO2/km by 2008, a 25% cut from the 1995 level. Because the target was unlikely to be met, the European Commission published new proposals in February 2007, requiring a mandatory limit of 130 grams of CO2/km for new cars by 2012, with 'complementary measures' being proposed to achieve the target of 120 grams of CO2/km that had originally been expected.[57][58]
In the area of fuels, the 2001 Biofuels Directive requires that 5,75% of all transport fossil fuels (petrol and diesel) should be replaced by biofuels by 31 December 2010, with an intermediate target of 2% by the end of 2005. In February 2007 the European Commission proposed that, from 2011, suppliers will have to reduce carbon emissions per unit of energy by 1% a year from 2010 levels, to result in a cut of 10% by 2020 Stricter fuel standards to combat climate change and reduce air pollution.[6]
Flights
Airlines can be charged for their greenhouse gas emissions on flights to and from Europe according to a court ruling in October 2011.[59]
Historically, EU aviation fuel was tax free and applied no VAT. Fuel taxation in the EU has been permitted since 2003 under the Energy Taxation Directive for domestic flights and on intra-EU flights on the basis of bilateral agreements. In 2018 Germany applied 19% VAT on domestic airline tickets. Many other member states had 0% VAT. Unlike air travel VAT is applied to bus and rail, which creates competitive distortions, artificially stimulate demand, drive uncontrolled growth in aviation emissions and constitute unjustifiable subsidies. Air fuel tax 33 cents/litre equal to road traffic would give €9.5 billion. Applying a 15% VAT in all air traffics within and from Europe would be equal to €15 billion.[60]
Industry
The European Union Emission Trading Scheme, introduced in 2005 under the 2003 Emission Trading Directive,[61] sets member state-level caps on greenhouse gas emissions for power plants and other large point sources.
Consumer goods
A further area of energy policy has been in the area of consumer goods, where energy labels were introduced to encourage consumers to purchase more energy-efficient appliances.[62]
External energy relations
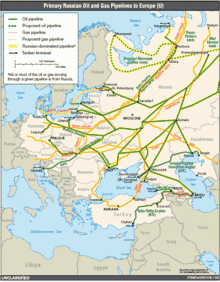
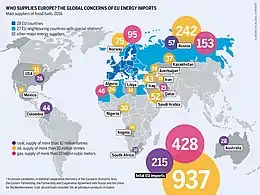
Beyond the bounds of the European Union, EU energy policy has included negotiating and developing wider international agreements, such as the Energy Charter Treaty, the Kyoto Protocol, the post-Kyoto regime and a framework agreement on energy efficiency; extension of the EC energy regulatory framework or principles to neighbours (Energy Community, Baku Initiative, Euro-Med energy cooperation) and the emission trading scheme to global partners; the promotion of research and the use of renewable energy.[63]
The EU-Russia energy cooperation will be based on a new comprehensive framework agreement within the post-Partnership and Cooperation Agreement (PCA), which will be negotiated in 2007. The energy cooperation with other third energy producer and transit countries is facilitated with different tools, such as the PCAs, the existing and foreseen Memorandums of Understanding on Energy Cooperation (with Ukraine, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan and Algeria), the Association Agreements with Mediterranean countries, the European Neighbourhood Policy Action Plans; Euromed energy cooperation; the Baku initiative; and the EU-Norway energy dialogue.[63] For the cooperation with African countries, a comprehensive Africa-Europe Energy partnership would be launched at the highest level, with the integration of Europe's Energy and Development Policies.[23]
For ensuring efficient follow-up and coherence in pursuing the initiatives and processes, for sharing information in case of an external energy crisis, and for assisting the EU's early response and reactions in case of energy security threats, the network of energy correspondents in the Member States was established in early 2007. After the Russian-Ukrainian Gas Crisis of 2009 the EU decided that the existing external measures regarding gas supply security should be supplemented by internal provisions for emergency prevention and response, such as enhancing gas storage and network capacity or the development of the technical prerequisites for reverse flow in transit pipelines.[64][65]
Just Transition Fund
Just Transition Fund (JTF) was created in 2020 to boost investments in low-carbon energy. The fund was criticized for blanket ban on low-carbon nuclear power but also introduction of a loophole for fossil gas.[66] Having the largest workforce dedicated to the coal industry, Poland—followed by Germany and Romania—is the fund's largest receptor.[67] Amounting to €17.5 billion, the fund was approved by the European Parliament in May 2021.[67]
Policies under development
Documents leaked in late-2016 reveal that a confidential European Union impact assessment analyses four scenarios for paring back the 'priority dispatch' system afforded to renewable generation in many countries. Priority dispatch is mandated under the Renewable Energy Directive 2009/28/EC which expires in 2020. The assessment concludes that removing priority dispatch could increase carbon emissions by 45 million to 60 million tonnes per annum or up to 10%, with the aim of making European energy generators more flexible and cost-competitive.[68] In 2017, a systematic review based on experts perceptions concerning the EU targets for emissions, renewables, and efficiency, reflected a broad scepticism, highlighting that EU's GHG emission policies were not sufficient to achieve reduction targets, and that the EU's energy efficiency would not succeed. [69]
Solar anti-dumping levies
In 2013, a two-year investigation by the European Commission concluded that Chinese solar panel exporters were selling their products in the EU up to 88% below market prices, backed by state subsidies. In response, the European Council imposed tariffs on solar imported from China at an average rate of 47.6% beginning 6 June that year.[70][71]
The Commission reviewed these measures in December 2016 and proposed to extend them for two years until March 2019. However, in January 2017, 18 out of 28 EU member states voted in favour of shortening the extension period. In February 2017, the commission announced its intention to extend its anti-dumping measures for a reduced period of 18 months.[72][73]
Research and development
The European Union is active in the areas of energy research, development and promotion, via initiatives such as CEPHEUS (ultra-low energy housing), and programs under the umbrella titles of SAVE (energy saving) ALTENER (new and renewable energy sources), STEER (transport) and COOPENER (developing countries).[74] Through Fusion for Energy, the EU is participating in the ITER project.[75]
Public opinion

In a poll carried out for the European Commission in October and November 2005, 47% of the citizens questioned in the 27 countries of the EU (including the 2 states that joined in 2007) were in favour of taking decisions on key energy policy issues at a European level. 37% favoured national decisions and 8% that they be tackled locally.[76]
A similar survey of 29,220 people in March and May 2006 indicated that the balance had changed in favour of national decisions in these areas (42% in favour), with 39% backing EU policy making and 12% preferring local decisions. There was significant national variation with this, with 55% in favour of European level decision making in the Netherlands, but only 15% in Finland.[77]
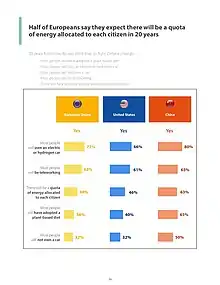
A comprehensive public opinion survey was performed in May and June 2006.[78] The authors propose following conclusions:
- Energy issues are considered to be important but not at first glance.
- EU citizens perceive great future promise in the use of renewable energies. Despite majority opposition, nuclear energy also has its place in the future energy mix.
- Citizens appear to opt for changing the energy structure, enhancing research and development and guaranteeing the stability of the energy field rather than saving energy as the way to meet energy challenges.
- The possible future consequences of energy issues do not generate deep fears in Europeans' minds.
- Europeans appear to be fairly familiar with energy issues, although their knowledge seems somewhat vague.
- Energy issues touch everybody and it is therefore hard to distinguish clear groups with differing perceptions. Nevertheless, rough distinction between groups of citizens is sketched.
Example European countries
Germany
In September 2010, the German government adopted a set of ambitious goals to transform their national energy system and to reduce national greenhouse gas emissions by 80 to 95% by 2050 (relative to 1990).[79] This transformation became known as the Energiewende. Subsequently, the government decided to the phase-out the nation's fleet of nuclear reactors, to be complete by 2022.[80] As of 2014, the country is making steady progress on this transition.[81]
See also
- CHP Directive
- Directorate-General for Energy
- Energy Charter Treaty
- Energy Community
- Energy conservation
- Energy diplomacy
- Energy efficiency in Europe (study)
- Energy in Europe
- EU Energy Efficiency Directive 2012
- European Atomic Forum
- European Climate Change Programme
- European Commissioner for Energy
- European countries by electricity consumption per person
- European countries by fossil fuel use (% of total energy)
- European Ecodesign Directive
- European Green Deal
- European Pollutant Emission Register (EPER)
- Global strategic petroleum reserves
- Internal Market in Electricity Directive
- INOGATE
- List of electricity interconnection level
- Renewable energy in the European Union
- Special economic zone
- Transport in Europe
References
- "Statistical Review of World Energy (June 2018)" (PDF). bp.com.
- Obrecht, Matevz; Denac, Matjaz (2013). "A sustainable energy policy for Slovenia : considering the potential of renewables and investment costs". Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy. 5 (3): 032301. doi:10.1063/1.4811283.
- Braun, Jan Frederik (24 February 2012). "EU Energy Policy under the Treaty of Lisbon Rules: Between a new policy and business as usual". Politics and Institutions, EPIN Working Papers. p. 14. Retrieved 21 August 2012.
- "Low-carbon economy' proposed for Europe". NBC News. Associated Press. 10 January 2007.
- "ESA-AnnualReport2009-100908.indd" (PDF). Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- "Press corner". European Commission – European Commission.
- Limiting climate change could have huge economic benefits, study finds Stopping global warming at two degrees would create nearly half a million jobs in Europe and save over a million lives in China, analysis of emissions pledges says, Guardian 31.3.2015
- Robiou du Pont; Meinshausen (2018). "Warming assessment of the bottom-up Paris Agreement emissions pledges". Nature Communications. 9 (1): 4810. Bibcode:2018NatCo...9.4810R. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-07223-9. PMC 6240108. PMID 30446653.
- "European Commission". European Commission – European Commission.
- "Energy Union and Climate" (PDF).
- "ENERGY UNION PACKAGE COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND THE COUNCIL The Paris Protocol – A blueprint for tackling global climate change beyond 2020 - (SWD(2015) 17 final)". European Commission. 25 February 2015.
- "Will EU states play ball on Energy Union?". EurActiv – EU News & policy debates, across languages.
- "Press". www.consilium.europa.eu.
- "ENERGY UNION PACKAGE COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND THE COUNCIL - Achieving the 10% electricity interconnection target Making Europe's electricity grid fit for 2020". European Commission. 25 February 2015.
- "European Commission – PRESS RELEASES – Press release – More growth and jobs: EU invests €873 million in clean energy infrastructure". europa.eu.
- "CEF Energy – Innovation and Networks Executive Agency – European Commission". Innovation and Networks Executive Agency.
- "Biscay Gulf Interconnector – 4C Offshore". www.4coffshore.com.
- State of the Energy Union 2015, COM/2015/0572 final, published 18 November 2015, accessed 30 December 2018
- European Commission, Second Report on the State of the Energy Union, published 1 February 2017, accessed 30 December 2018
- European Commission, Third Report on the State of the Energy Union, COM(2017) 688 final, published 23 November 2017, accessed 30 December 2018
- "EUR-Lex – 52006DC0105 – EN – EUR-Lex". eur-lex.europa.eu.
- "EU sticks out neck in global climate change battle". EUobserver.
- "EUR-Lex – 52007DC0001 – EN – EUR-Lex". eur-lex.europa.eu.
- New EU energy plan – more security, less pollution, press release by European Commission
- Oliver Geden (2010), What Comes After the Two-Degree Target?, SWP Comments 19
- Randalls, Samuel (2010). "History of the 2 °C climate target". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change. 1 (4): 598–605. doi:10.1002/wcc.62.
- Oliver Geden (2012), The End of Climate Policy as We Knew it, SWP Research Paper 2012/RP01
- Oliver Geden (2012), Impending Paradigm Shift. International Climate Negotiations and their Impact on EU Energy Policy, in: KAS International Reports, 9/2012, pp. 22–34
- Severin Fischer/Oliver Geden (2013), Updating the EU's Energy and Climate Policy. New Targets for the Post-2020 Period, FES International Policy Analysis
- Oliver Geden/Severin Fischer (2014), Moving Targets. Negotiations on the EU’s Energy and Climate Policy Objectives for the Post-2020 Period and Implications for the German Energy Transition, SWP Research Paper 2014/RP03
- European parliament votes for stronger climate targets The Guardian 5.2.2014
- "ITER & Beyond". Iter.org. Archived from the original on 20 May 2009. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- "International Energy Agency – Energy Publications". Iea.org. Archived from the original on 29 April 2009. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- "Energy revolution kick- off meeting, Rapid – Press Release, 26 june 2008 – EUROPA". Europa.eu. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- A European strategic energy technology plan (SET-plan) – 'Towards a low carbon future', Communication from the Commission COM(2007) 723 final
- "ESNII".
- "What is the SET-Plan?". setis.ec.europa.eu.
- "CE2009294EN.01003501.xml". eur-lex.europa.eu.
- "European Energy Research Alliance (EERA)". eera-set.eu. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- European Commission (28 October 2008). "Fostering "green" energy technologies: Leading EU research institutes launch the European Energy Research Alliance — Press release IP/08/1587". European Commission. Brussels, Belgium. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- "EERA announced Nils Røkke (SINTEF) as new Chairman during EERA high level political event — EERA". www.eera-set.eu. 5 May 2008. Archived from the original on 23 October 2017.
- "The European Power Sector in 2020 / Up-to-Date Analysis on the Electricity Transition" (PDF). ember-climate.org. Ember and Agora Energiewende. 25 January 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 January 2021.
- "Labelling provision in Directive 2003/54/EC" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 February 2014. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- "Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council: Renewable Energy Roadmap: Renewable Energies in the 21st century; building a sustainable future – COM(2006) 848 final". Retrieved 27 January 2007.
- Avoiding fossil fuel costs with wind energy EWEA March 2014
- Bank, European Investment (14 December 2020). The EIB Group Climate Bank Roadmap 2021-2025. European Investment Bank. ISBN 978-92-861-4908-5.
- "ELENA – European Local ENergy Assistance". EIB.org. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- "Council Directive 2004/67/EC of 26 April 2004 concerning measures to safeguard security of natural gas supply". Eur-lex.europa.eu. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- "Rapid – Press Releases – EUROPA – The International Partnership for Energy Efficiency Cooperation (IPEEC)". Europa.eu. 8 June 2008. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- Energy Efficiency in Buildings, European Commission, Directorate-General for Energy and Transport
- "Directive 2002/91/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2002 on the energy performance of buildings". Eur-lex.europa.eu. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- For an Energy-Efficient Millennium: SAVE 2000, Directorate-General for Energy
- "Council Directive 92/42/EEC of 21 May 1992 on efficiency requirements for new hot-water boilers fired with liquid or gaseous fuels". Eur-lex.europa.eu. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- "[ARCHIVED CONTENT] DCLG News Release – Department for Communities and Local Government". Archived from the original on 19 September 2012.
- European Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (Directive 2002/91/EC), Official Journal of the European Communities, published 02-12-16. Retrieved 2008-06-02.
- Mulvey, Stephen (7 February 2007). "EU car CO2 fight only beginning –". BBC News. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- "Commission plans legislative framework to ensure the EU meets its target for cutting CO2 emissions from cars". Europa.eu. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- Bilefsky, Dan (6 February 2007). "EU to compromise on auto emissions – Europe – International Herald Tribune". The New York Times. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- Fiona Harvey (6 October 2011). "Airlines can be charged for carbon pollution, court rules". the Guardian.
- Taxing aviation fuels in the EU Jasper Faber and Aoife O’Leary Delft November 2018
- "Directive 2003/87/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 13 October 2003 establishing a scheme for greenhouse gas emission allowance trading within the Community and amending Council Directive 96/61/EC". Eur-lex.europa.eu. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- "Directive 2010/30/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 May 2010 on the indication by labelling and standard product information of the consumption of energy and other resources by energy-related products". Eur-lex.europa.eu. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- External energy relations – from principles to action. Communication from the Commission to the European Council COM(2006) 590 final
- Effective Provisions for Emergency Prevention and Response in the Gas Sector. German Institute for International and Security Affairs, Comment 21/2009
- Oliver Geden/Jonas Graetz: The EU’s Policy to Secure Gas Supplies. Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zurich, CSS Analyses 159 (2014)
- Simon, Frédéric (7 July 2020). "MEPs ban nuclear from green transition fund, leave loophole for gas". www.euractiv.com. Retrieved 7 July 2020.
- "EU lawmakers give final approval to bloc's green transition fund". euractiv.com. 19 May 2021.
- Neslen, Arthur (1 November 2016). "Renewables could lose European power grid priority, documents reveal". The Guardian. London, United Kingdom. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 1 November 2016.
- Khanam, Tahamina; Rahman, Abul; Mola-Yudego, Blas; Pelkonen, Paavo; Perez, Yanick; Pykalainen, Jouni (2017). "Achievable or unbelievable? Expert perceptions of the European Union targets for emissions, renewables, and efficiency". Energy Research & Social Science. 34: 144-153. doi:10.1016/j.erss.2017.06.040.
- Chee, Foo Yun (28 February 2017). "EU wins court backing on anti-dumping duties on Chinese solar panels". Reuters.
- "EU imposes China solar panel duties". BBC News. 4 June 2013.
- "EU to Shorten Extension on Anti-Dumping Duties of Chinese Solar Imports_EnergyTrend PV". pv.energytrend.com. Archived from the original on 6 September 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2017.
- "EU softens proposal on extension of Chinese solar panel duties". businessinsider.com.
- Projects, European Commission, Directorate-General for Energy and Transport
- "Fusion for Energy". Fusionforenergy.europa.eu. Retrieved 23 April 2011.
- Special Eurobarometer 247. Attitudes towards Energy, January 2006
- Special Eurobarometer 258. Energy Issues, November 2006
- Special Eurobarometer 262: Energy Technologies: Knowledge, Perception, Measures, January 2007
- Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology (BMWi); Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety (BMU) (28 September 2010). Energy concept for an environmentally sound, reliable and affordable energy supply (PDF). Berlin, Germany: Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology (BMWi). Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- Bruninx, Kenneth; Madzharov, Darin; Delarue, Erik; D'haeseleer, William (2013). "Impact of the German nuclear phase-out on Europe's electricity generation — a comprehensive study". Energy Policy. 60: 251–261. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2013.05.026. Retrieved 12 May 2016.
- The Energy of the Future: Fourth "Energy Transition" Monitoring Report — Summary (PDF). Berlin, Germany: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi). November 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2016. Retrieved 9 June 2016.
External links
- Official website
- European information campaign on the opening of the energy markets and on energy consumers' right.
- European Strategic Energy Technology Plan, Towards A Low Carbon Future.
- Eurostat – Statistics Explained – all articles on energy
- ManagEnergy, for energy efficiency and renewable energies at the local and regional level.
- BBC Q&A: EU energy proposals
- 2006 Energy Green Paper
- Collective Energy Security: A New Approach for Europe
- Berlin Forum on Fossil Fuels.
- The post-industrial revolution.
- Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency – Meeting the European Union 2 °C climate target: global and regional emission implications
- German Institute for International and Security Affairs – Perspectives for the European Union's External Energy Policy
- Energy Law Research Forum
- The Liberalisation of the Power Industry in the European Union and its Impact on Climate Change – A Legal Analysis of the Internal Market in Electricity.
- Torsten H. Fransson Lecture: Implementing Clean Energy Goals in the EU – European Union Center at the University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign.
In the media
- 8 Sep 2008 New Europe (neurope.eu) : Energy security and Europe.
- 10 Jan 2007, BBC: EU plans 'industrial revolution'
- 10 Jan 2007, BBC: EU's energy plans – how revolutionary?
- 10 Jan 2007, Reuters: EU puts climate change at heart of energy policy
- 10 Jan 2007, Xinhua: EU to build competitive internal energy market
- 10 Jan 2007, Deutsche Welle: Germany Wary About EU Energy Policy
- 10 Jan 2007, UK Government: UK Ministers strongly welcome EU energy proposals
- 9 Jan 2007, Greenpeace: Fine wrapping conceals lack of substance
- 14 Dec 2006, opendemocracy.net: Russia, Germany and European energy policy
- 20 Nov 2006, eupolitix.com: Barroso calls for strong EU energy policy