987
Year 987 (CMLXXXVII) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
| Millennium: | 1st millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | |
| Decades: | |
| Years: |
| 987 by topic |
|---|
| Leaders |
|
| Categories |
|
| Gregorian calendar | 987 CMLXXXVII |
| Ab urbe condita | 1740 |
| Armenian calendar | 436 ԹՎ ՆԼԶ |
| Assyrian calendar | 5737 |
| Balinese saka calendar | 908–909 |
| Bengali calendar | 394 |
| Berber calendar | 1937 |
| Buddhist calendar | 1531 |
| Burmese calendar | 349 |
| Byzantine calendar | 6495–6496 |
| Chinese calendar | 丙戌年 (Fire Dog) 3683 or 3623 — to — 丁亥年 (Fire Pig) 3684 or 3624 |
| Coptic calendar | 703–704 |
| Discordian calendar | 2153 |
| Ethiopian calendar | 979–980 |
| Hebrew calendar | 4747–4748 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | 1043–1044 |
| - Shaka Samvat | 908–909 |
| - Kali Yuga | 4087–4088 |
| Holocene calendar | 10987 |
| Iranian calendar | 365–366 |
| Islamic calendar | 376–377 |
| Japanese calendar | Kanna 3 / Eien 1 (永延元年) |
| Javanese calendar | 888–889 |
| Julian calendar | 987 CMLXXXVII |
| Korean calendar | 3320 |
| Minguo calendar | 925 before ROC 民前925年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | −481 |
| Seleucid era | 1298/1299 AG |
| Thai solar calendar | 1529–1530 |
| Tibetan calendar | 阳火狗年 (male Fire-Dog) 1113 or 732 or −40 — to — 阴火猪年 (female Fire-Pig) 1114 or 733 or −39 |

King Hugh I (Capet) (r. 987–996)
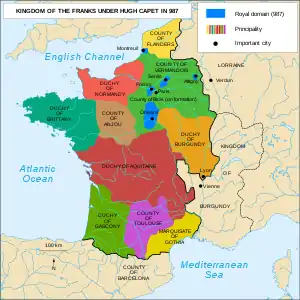
France during the reign of Hugh Capet.
Events
Byzantine Empire
- February 7 – Bardas Phokas (the Younger) and Bardas Skleros, two members of the military elite, begin a wide-scale rebellion against Emperor Basil II. They overrun Anatolia, and Phokas declares himself Emperor. Basil applies for military assistance from Prince Vladimir the Great, ruler of Kievan Rus', who agrees to help him and sends a Varangian army (6,000 men).[1]
Europe
- May 21 – King Louis V dies during a hunting accident in the Forest of Halatte near the town of Senlis. His death at age 20 ends the Carolingian Dynasty founded by Charlemagne (the Great) (see 800). The late King's uncle, Charles (Duke of Lower Lorraine), lays claim to the throne. Being a vassal of King Otto III, the Frankish nobles balk at the prospect of his ascension.
- July 3 – Hugh Capet, Count of Paris, is elected and crowned King of France at Noyon (Picardy), by Adalbero (Archbishop of Reims). He becomes the first monarch of the Capetian Dynasty, who rules the kingdom until 1328. Empress-regent Theophanu (the mother of Otto III) leads an expedition to Lower Lorraine, to ensure it remains as part of the Holy Roman Empire.
- Al-Mansur, the de facto ruler of Al-Andalus, occupies the city of Coimbra (modern Portugal).[2] The domination of the Andalusian authorities in the north of Gharb al-Andalus, leads to the submission of the Counts of Portugal to the Caliphate of Córdoba. But it also illustrates the limited ability of the Muslims to repopulate, or at least govern directly, these remote areas.
- December – The 15-year-old Robert (the son of Hugo Capet) is crowned co-ruler of France around Christmas at Orléans.[3]
- The population of Bari revolts against the Byzantine Empire.[4]
- Sweyn Forkbeard (father of Cnut the Great) overthrows his father, Harald Bluetooth, Viking King of Denmark and Norway.
Africa
- The Zirid Dynasty fails to reconquer the western part of the Maghreb (Land of Atlas), which they have recently lost to the Umayyad Caliphate.[5]
Art
- An extension of the Prayer Hall, Great Mosque of Córdoba at Córdoba (modern Spain), is made.
Births
Deaths
- January 10 – Pietro I Orseolo, doge of Venice (b. 928)
- March 30 – Arnulf II (the Younger), Frankish nobleman
- May 21 – Louis V, king of the West Frankish Kingdom
- July 21 – Geoffrey I (Greymantle), Frankish nobleman
- November 16 – Shen Lun, Chinese scholar-official
- Abu'l-Fawaris Ahmad ibn Ali, Ikhshidid governor
- Adalbert I, Frankish nobleman (approximate date)
- Beatrice of France, duchess regent of Upper Lorraine
- Erluin I, Frankish Benedictine monk and abbot
- Otto I (or Eudes), Frankish nobleman (approximate date)
- Owain ap Hywel Dda, king of Deheubarth (Wales)
- Severus ibn al-Muqaffa, Coptic Orthodox bishop
- Střezislava, Bohemian noblewoman (approximate date)
- Ziyar ibn Shahrakuya, Buyid general (approximate date)
References
- Raffaele D'Amato (2010). Osprey: MAA - 459: The Varangian Guard 988–1453, p. 6. ISBN 978-1-84908-179-5.
- Picard, Christophe (2000). Le Portugal musulman (VIIIe-XIIIe siècle). L'Occident d'al-Andalus sous domination islamique. Paris: Maisonneuve & Larose. p. 109. ISBN 2-7068-1398-9.
- Robert Fawtier, The Capetian Kings of France, transl. Lionel Butler and R.J. Adam, (Macmillan, 1989), p.48.
- France, John (1991). "The occasion of the coming of the Normans to southern Italy". Journal of Medieval History. 17 (1): 183–203. doi:10.1016/0304-4181(91)90033-H.
- Gilbert Meynier (2010). L'Algérie cœur du Maghreb classique. De l'ouverture islamo-arabe au repli (658-1518). Paris: La Découverte; p. 45.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.