Communicable Disease: Chronic Viral Hepatitis
Congolese Refugee Health Profile
The World Health Organization estimates a 5-7% prevalence of active hepatitis B virus infection in the region of origin for Congolese refugees. During post-arrival screening exams in 4 large Congolese refugee-receiving states, 6.1% (124/2,355) of Congolese refugees screened from 2010–2013 had a detectable serum hepatitis B surface antigen, and indicator of active hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection (Figure 12). Data from a pilot health assessment conducted in refugee camps in Rwanda in 2012 showed that 3% of 416 refugees screened were infected with HBV (unpublished CDC data). There are no data available on the prevalence of different viral hepatitis infections in the camps in Burundi, Tanzania, or Uganda. For more information on HIV testing for Congolese refugees, refer to the Health Conditions to Consider in Post-Arrival Medical Screening of Congolese Refugees: HIV Infection section of this profile.
Figure 12: Communicable diseases found in Congolese refugees during domestic medical examinations in 6 states from 2010–2013 (n=2,355)*
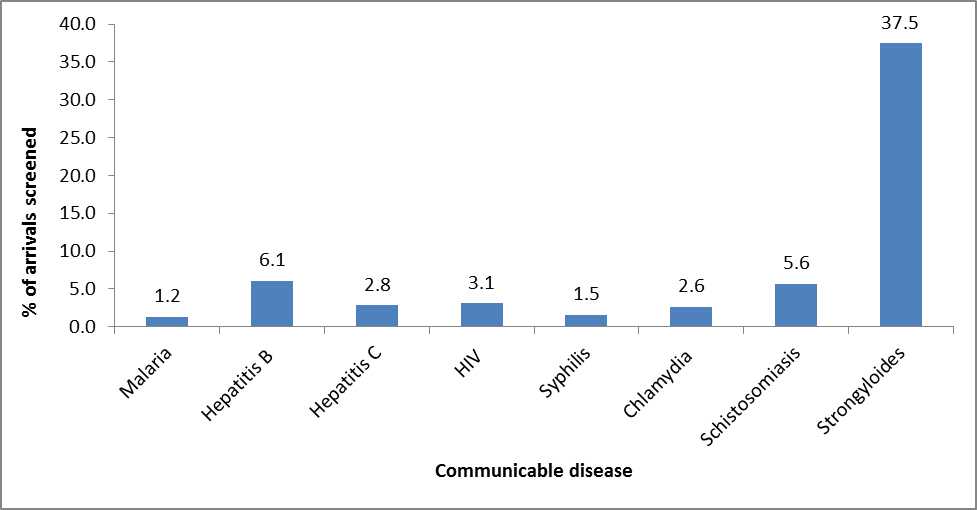
Source: Refugee health screening data from health departments in California, Colorado, Illinois, New York, Texas, and Indiana
- Page last reviewed: August 29, 2014
- Page last updated: August 29, 2014
- Content source:


 ShareCompartir
ShareCompartir