Venetoclax
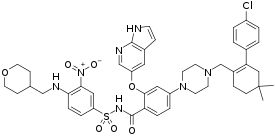 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Venclexta, Venclyxto |
| Other names | GDC-0199, ABT-199, RG-7601 |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | BCL-2 inhibitor[1] |
| Main uses | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML)[2][3] |
| Side effects | Low white blood cells, low red blood cell, high potassium, diarrhea, nausea, respiratory infections, tiredness[3] |
| Interactions | St. John’s wort[3] |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of use | By mouth (tablets) |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a616028 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Protein binding | >99.9%[2] |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP3A4, CYP3A5) |
| Elimination half-life | ~26 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (>99.9%; 20.8% as unchanged venetoclax) |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C45H50ClN7O7S |
| Molar mass | 868.45 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Venetoclax, sold under the brand names Venclexta and Venclyxto, is a medication used to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), or acute myeloid leukemia (AML).[2][3] It is taken by mouth.[3] It may be used on its own or together with other medications.[3]
Common side effects include low white blood cells, low red blood cell, high potassium, diarrhea, nausea, respiratory infections, and tiredness.[3] Other severe side effects may include sepsis, low potassium, tumor lysis syndrome, and bleeding.[3][1] It interacts with St. John’s wort.[3] It works by attaching to a protein called Bcl-2, blocking its activity, which results in the death of cancer cells.[3]
Venetoclax was approved for medical use in Europe and the United States in 2016.[3][1] In the United Kingdom 112 tablets of 100 mg costs the NHS about £4,800.[6] This amount in the United States costs about 12,600 USD as of 2021.[7]
Medical uses
CLL/SLL
In the US, venetoclax is indicated for adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL).[8][2] Indication does not depend on mutation status (e. g. 17p deletion, IGHV mutation, 12+).
In the EU, venetoclax monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) in the presence of 17p deletion or TP53 mutation in adults who are unsuitable for or have failed a B cell receptor pathway inhibitor and for the treatment of CLL in the absence of 17p deletion or TP53 mutation in adults who have failed both chemoimmunotherapy and a B cell receptor pathway inhibitor.[3]
Other types of leukemia
Venetoclax is also indicated as part of a combination therapy for acute myeloid leukemia (AML).[2] For this purpose it is used with azacitidine, decitabine, or low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed adults who are age 75 years or older, or those with other health problems where intensive chemotherapy cannot be used.[2]
Dosage
For CLL it is generally started at a dose of 20 mg daily and increased over five weeks to 400 mg daily.[3] This may be continued as long as it is working.[3]
Side effects
Common side effects of venetoclax include neutropenia (low white blood cell count), nausea, anemia, diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, fatigue, and thrombocytopenia (low platelet count). Major side effects include tumor lysis syndrome and severe neutropenia. Additionally, this drug may cause fertility problems in males.[2]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Venetoclax is a BH3-mimetic.[9] Venetoclax blocks the anti-apoptotic B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) protein, leading to programmed cell death of CLL cells. Overexpression of Bcl-2 in some lymphoid malignancies has sometimes shown to be linked with increased resistance to chemotherapy.[10]
Pharmacokinetics
The maximum plasma concentration achieved after oral administration occurred 5–8 hours after dose.[2] Steady state maximum concentration with low-fat meal conditions at the 400 mg once daily dose was found to be 2.1 ± 1.1 μg/mL. It is recommended that venetoclax be administered with a meal.[2]
The apparent volume of distribution for venetoclax is approximately 256–321 L. It is highly bound to human plasma protein. Within a concentration range of 1-30 μM (0.87-26 μg/mL), the fraction unbound in plasma was less than 0.01.[2]
Venetoclax is metabolized by CYP3A4/5 as proven by in-vitro studies.[2] Those using the drug should not consume grapefruit products because they contain CYP3A inhibitors.[2] Additionally, while using venetoclax it is not recommended to use other drugs which contain CYP3A inhibitors (i.e.: erythromycin, ciprofloxacin, diltiazem, dronedarone, fluconazole, verapamil).[2] Venetoclax is excreted from the body via the fecal route.[2]
History
In 2015, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted the breakthrough therapy designation to venetoclax for people with CLL or SLL who have relapsed, become intolerant to, or refractory to previous treatment.
In April 2016, the FDA approved venetoclax for use in those with CLL who have 17p deletion (deletion located on the chromosome 17 short arm) and who have been treated with at least one prior therapy.[11][12][13][14] Based on overall response rate, the indication was approved under accelerated FDA approval.[2]
The efficacy of venetoclax was tested in a single-arm clinical trial of 106 participants with CLL who have a 17p deletion and who had received at least one prior therapy.[12] Trial participants took venetoclax orally every day, beginning with 20 mg and increasing over a five-week period to 400 mg.[12] Results showed that 80 percent of trial participants experienced a complete or partial remission of their cancer.[12] The trial was conducted in the US, Canada, France, Germany, Poland, the United Kingdom, and Australia.[14]
The application for venetoclax was granted priority review and accelerated approval along with breakthrough therapy designation and orphan drug designation.[12]
Venetoclax was approved for use in the European Union in December 2016.[3]
In June 2018, the FDA granted regular approval to venetoclax for people with CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), with or without 17p deletion, who have received at least one prior therapy.[15]
Approval was based on MURANO (NCT02005471), a randomized (1:1), multicenter, open-label trial of venetoclax with rituximab (VEN+R) versus bendamustine with rituximab (B+R) in 389 participants with CLL who had received at least one prior line of therapy.[15] Participants in the VEN+R arm completed a 5-week ramp-up venetoclax scheduleand then received venetoclax 400 mg once daily for 24 months measured from the rituximab start date.[15] Rituximab was initiated after venetoclax ramp-up and given for 6 cycles (375 mg/m2 intravenously on cycle 1 day 1 and 500 mg/m2 intravenously on day 1 of cycles 2–6, with a 28-day cycle length).[15] The comparator arm received 6 cycles of B+R (bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of each 28-day cycle and rituximab at the above described dose and schedule).[15]
The application for venetoclax in combination with rituximab was granted priority review along with a breakthrough therapy designation.[15]
In November 2018, in the United States, venetoclax was approved in combination with azacitidine or decitabine or low-dose cytarabine for the treatment of newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in adults who are age 75 years or older, or who have comorbidities that preclude use of intensive induction chemotherapy.[16]
Accelerated approval was based on two open-label non-randomized trials in participants with newly diagnosed AML who were >= 75 years of age or had comorbidities that precluded the use of intensive induction chemotherapy.[16] Efficacy was established based on the rate of complete remission (CR) and CR duration.[16]
Study M14-358 (NCT02203773) was a non-randomized, open-label clinical trial of venetoclax in combination with azacitidine (n=67) or decitabine (n=13) in newly diagnosed participants with AML.[16] In combination with azacitidine, 25 participants achieved a CR (37%, 95% CI: 26, 50) with a median observed time in remission of 5.5 months (range: 0.4–30 months).[16] In combination with decitabine, 7 participants achieved a CR (54%, 95% CI: 25, 81) with a median observed time in remission of 4.7 months (range: 1.0–18 months).[16] The observed time in remission is the time from start of CR to data cut-off date or relapse from CR.[16] In a phase 3 study of azacitidine and venetoclax in untreated acute myeloid leukemia not eligible for standard induction chemotherapy, the addition of venetoclax to azacitidine resulted in an improvement in median overall survival (14.7 months versus 9.6 months) and improved complete remission rates.[17]
Study M14-387 (NCT02287233) was a non-randomized, open-label trial of venetoclax in combination with low-dose cytarabine (n=61) in newly diagnosed participants with AML, including participants with previous exposure to a hypomethylating agent for an antecedent hematologic disorder.[16] In combination with low-dose cytarabine, 13 participants achieved a CR (21%, 95% CI: 12, 34) with a median observed time in remission of 6 months (range: 0.03–25 months).[16]
In May 2019, the label was extended by accelerated approval to include all adults with CLL/SLL disregarding prior treatment or mutation status.[8]
Approval was based on CLL14 (NCT02242942), a randomized (1:1), multicenter, open label, actively controlled trial of venetoclax in combination with obinutuzumab (VEN+G) versus obinutuzumab in combination with chlorambucil (GClb) in 432 participants with previously untreated CLL with coexisting medical conditions.[8]
The major efficacy outcome was progression-free survival (PFS) assessed by an independent review committee.[8] The trial demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in PFS for participants who received VEN+G compared with those who received GClb (HR 0.33; 95% CI: 0.22, 0.51; p<0.0001).[8] Median PFS was not reached in either arm after a median follow-up duration of 28 months.[8] The overall response rate was 85% in VEN+G arm compared to 71% in GClb arm, p=0.0007.[8] The trial also demonstrated statistically significant improvements in rates of minimal residual disease negativity (less than one CLL cell per 104 leukocytes) in bone marrow and peripheral blood.[8] Overall survival data were not mature at this analysis.[8]
The FDA used the Real-Time Oncology Review and Assessment Aid Pilot Program for this application and granted priority review as well as orphan drug and breakthrough therapy designations.[8] Approval was granted 3.7 months ahead of the Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) date.[8]
Society and culture
AbbVie Inc. manufactures Venclexta.[12] It is marketed by both Abbvie and Genentech USA, which is a member of the Roche Group.[12] AbbVie and Genentech are both commercializing the drug within the United States, but only AbbVie has rights to do so outside of the U.S.[18]
According to Reuters 2016 Drugs to Watch, the 2020 forecast sales for venetoclax are US$1.48 billion.[19]: 3, 7–8 Competition as well as potential for combination is expected from other drugs such as ibrutinib and idelalisib, both of which were also approved in 2014 to treat CLL.[19]: 7–8 [20]
Research
As of 2016, venetoclax had been tested to treat other hematological cancers, including non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, multiple myeloma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma.[19]: 7–8
On 13 June 2020 at the European Hematology Association (EHA) annual congress, AbbVie and Roche announced the results of a Phase III trial that showed a 34 percent reduction in the risk of death in AML patients who were ineligible for intensive chemotherapy treated with venetoclax plus azacitidine compared to azacitidine plus placebo.[25][26][27]
References
- 1 2 3 "Venetoclax Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 31 May 2021. Retrieved 13 September 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 "Venclexta- venetoclax kit Venclexta- venetoclax tablet, film coated". DailyMed. 12 November 2019. Archived from the original on 15 June 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 "Venclyxto EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Archived from the original on 16 April 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2020. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- 1 2 "Venetoclax (Venclexta) Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 29 May 2019. Archived from the original on 19 January 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- ↑ "Venclyxto 10 mg film-coated tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 21 April 2020. Archived from the original on 26 April 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- ↑ BNF (80 ed.). BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. September 2020 – March 2021. p. 1066. ISBN 978-0-85711-369-6.
- ↑ "Venclexta Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 16 January 2021. Retrieved 13 September 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 "FDA approves venetoclax for CLL and SLL". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 15 May 2019. Archived from the original on 25 April 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ Roberts AW, Huang D (January 2017). "Targeting BCL2 With BH3 Mimetics: Basic Science and Clinical Application of Venetoclax in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Related B Cell Malignancies". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 101 (1): 89–98. doi:10.1002/cpt.553. PMC 5657403. PMID 27806433.
- ↑ "Center for Drug Evaluation and Research - Application 208573Orig1s000 - Division Director Summary Review" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 November 2016. Retrieved 21 November 2016.
- ↑ "Venclexta Tablets". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 19 May 2016. Archived from the original on 31 March 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "FDA approves new drug for chronic lymphocytic leukemia in patients with a specific chromosomal abnormality". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 11 April 2016. Archived from the original on 8 February 2019. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ "Venetoclax (Venclexta) Tablets". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 11 April 2016. Archived from the original on 25 April 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 "Drug Trials Snapshot: Venclexta". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 11 April 2016. Archived from the original on 25 April 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 3 4 5 6 "FDA approves venetoclax for CLL or SLL, with or without 17p deletion, after one prior therapy". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 8 June 2018. Archived from the original on 25 April 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "FDA approves venetoclax in combination for AML in adults". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 21 November 2018. Archived from the original on 25 April 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ DiNardo, C.D.; Jonas, B.A.; Pullarkat, V.; Thirman, M.J.; Garcia, J.S.; Wei, A.H.; et al. (August 2020). "Azacitidine and Venetoclax in Previously Untreated Acute Myeloid Leukemia". The New England Journal of Medicine. 383 (7): 617–629. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2012971. PMID 32786187.
- ↑ "Inside the development of Venclexta, AbbVie's new leukemia drug". BioPharma Dive. Archived from the original on 22 December 2019. Retrieved 16 November 2016.
- 1 2 3 "Drugs to Watch 2016 - Market Insight Report" (pdf). Thomson Reuters. February 2016. Archived (PDF) from the original on 31 May 2021. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ↑ "Ibrutinib and Idelalisib Continue to Impress in CLL, May Eventually Replace Chemotherapy for Some Patients". OncLive. Archived from the original on 11 October 2018. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- ↑ "United States Patent: 9174982". patft.uspto.gov. Archived from the original on 11 October 2018. Retrieved 21 November 2016.
- ↑ "venetoclax". drugcentral.org. Archived from the original on 13 August 2020. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- ↑ "Apoptosis-inducing agents for the treatment of cancer and immune and autoimmune diseases - Patent US9174982 - PubChem". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 15 June 2020. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- ↑ "Venetoclax | US Patents | Expiry | Expiration | Dates". PharmaCompass.com. Archived from the original on 31 May 2021. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- ↑ "BRIEF-Roche Reports Positive Phase 3 Results For Venclexta/Venclyxto Combination In Acute Myeloid Leukaemia". Reuters. 13 June 2020. Archived from the original on 17 July 2020. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- ↑ "EHA: AbbVie, Roche cement Venclexta's place in AML with survival win". FiercePharma. Archived from the original on 31 May 2021. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- ↑ "Venclexta/Venclyxto (venetoclax) Plus Azacitidine Demonstrates Statistically Significant Overall Survival Benefit and Improved Remission Rates in Treatment-Naïve Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients". AbbVie. Archived from the original on 30 April 2021. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
External links
- "Venetoclax". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 3 June 2021. Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- AusPAR: Venetoclax. Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) (Report). October 2020. Archived from the original on 31 May 2021. Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- "FDA In Brief: FDA warns about safety concerns related to investigational use of Venclexta (venetoclax) for multiple myeloma". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 21 March 2019. Archived from the original on 20 December 2020. Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- "FDA Warns about the risks associated with the investigational use of Venclexta in Multiple Myeloma". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 21 March 2019. Archived from the original on 16 January 2021. Retrieved 12 July 2021.
| Identifiers: |
|---|