Giant cell arteritis
| Giant cell arteritis | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Temporal arteritis, cranial arteritis,[1] Horton disease,[2] senile arteritis,[1] granulomatous arteritis[1] | |
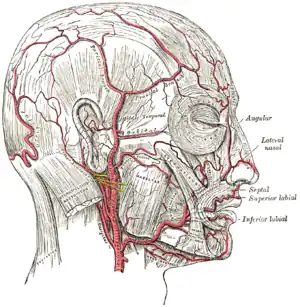 | |
| The arteries of the face and scalp. | |
| Specialty | Rheumatology, emergency medicine |
| Symptoms | Headache, pain over the temples, flu-like symptoms, double vision, difficulty opening the mouth[3] |
| Complications | Blindness, aortic dissection, aortic aneurysm, polymyalgia rheumatica[4] |
| Usual onset | Age greater than 50[4] |
| Causes | Inflammation of the small blood vessels within the walls of larger arteries[4] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms and blood tests, confirmed by biopsy of the temporal artery[4] |
| Differential diagnosis | Takayasu arteritis,[5] stroke, primary amyloidosis[6] |
| Treatment | Steroids, bisphosphonates, proton-pump inhibitor[4] |
| Prognosis | Life expectancy (typically normal)[4] |
| Frequency | ~ 1 in 15,000 people a year (> 50 years old)[2] |
Giant cell arteritis (GCA), also called temporal arteritis, is an inflammatory disease of large blood vessels.[4][7] Symptoms may include headache, pain over the temples, flu-like symptoms, double vision, and difficulty opening the mouth.[3] Complication can include blockage of the artery to the eye with resulting blindness, aortic dissection, and aortic aneurysm.[4] GCA is frequently associated with polymyalgia rheumatica.[4]
The cause is unknown.[2] The underlying mechanism involves inflammation of the small blood vessels that occur within the walls of larger arteries.[4] This mainly affects arteries around the head and neck, though some in the chest may also be affected.[4][8] Diagnosis is suspected based on symptoms, blood tests, and medical imaging, and confirmed by biopsy of the temporal artery.[4] However, in about 10% of people the temporal artery is normal.[4]
Treatment is typically with high doses of steroids such as prednisone or prednisolone.[4] Once symptoms have resolved the dose is then decreased by about 15% per month.[4] Once a low dose is reached, the taper is slowed further over the subsequent year.[4] Other medications that may be recommended include bisphosphonates to prevent bone loss and a proton-pump inhibitor to prevent stomach problems.[4]
It affects about 1 in 15,000 people over the age of 50 per year.[2] The condition typically only occurs in those over the age of 50, being most common among those in their 70s.[4] Females are more often affected than males.[4] Those of northern European descent are more commonly affected.[5] Life expectancy is typically normal.[4] The first description of the condition occurred in 1890.[1]
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms may include headache, pain over the temples, flu-like symptoms, double vision, and difficulty opening the mouth.[3]
- tenderness and sensitivity on the scalp
- jaw claudication (pain in jaw when chewing)
- acute visual loss (sudden blindness)
- acute tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- polymyalgia rheumatica (in 50%)[9]
The inflammation may affect blood supply to the eye; blurred vision or sudden blindness may occur. In 76% of cases involving the eye, the ophthalmic artery is involved, causing arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy.[10]
Giant cell arteritis may present with atypical or overlapping features.[11] Early and accurate diagnosis is important to prevent ischemic vision loss. Therefore, this condition is considered a medical emergency.[11]
While studies vary as to the exact relapse rate of giant cell arteritis, relapse of this condition can occur.[12] It most often happens at low doses of prednisone (<20 mg/day), during the first year of treatment, and the most common signs of relapse are headache and polymyalgia rheumatica.[12]
Associated conditions
The varicella-zoster virus (VZV) antigen was found in 74% of temporal artery biopsies that were GCA-positive, suggesting that the VZV infection may trigger the inflammatory cascade.[13]
The disorder may co-exist (in about half of cases) with polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR),[9] which is characterized by sudden onset of pain and stiffness in muscles (pelvis, shoulder) of the body and is seen in the elderly. GCA and PMR are so closely linked that they are often considered to be different manifestations of the same disease process. PMR usually lacks the cranial symptoms, including headache, pain in the jaw while chewing, and vision symptoms, that are present in GCA.[14]
Giant cell arteritis can affect the aorta and lead to aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection.[15] Up to 67% of people with GCA having evidence of an inflamed aorta, which can increase the risk of aortic aneurysm and dissection.[15] Some recommend screening people with GCA for this complication by imaging the aorta. Screening should be done on a case-by-case basis based on the signs and symptoms of people with GCA.[15]
Mechanism
The pathological mechanism is the result of an inflammatory cascade that is triggered by an as of yet determined cause resulting in dendritic cells in the vessel wall recruiting T cells and macrophages to form granulomatous infiltrates.[15] These infiltrates erode the middle and inner layers of the arterial tunica media leading to conditions such as aneurysm and dissection.[15] Activation of T helper 17 (Th17) cells involved with interleukin (IL) 6, IL-17, IL-21 and IL-23 play a critical part; specifically, Th17 activation leads to further activation of Th17 through IL-6 in a continuous, cyclic fashion.[15] This pathway is suppressed with glucocorticoids,[16] and more recently it has been found that IL-6 inhibitors also play a suppressive role.[15]
Diagnosis
The symptoms that make the diagnosis most likely are limb claudication, jaw claudication, thickening of the temporal artery on biopsy, lack of a temporal artery pulse, a platelet count of greater than 400, temporal artery tenderness, and an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of greater than 100 mm/hour.[17] A ESR of less than 40 makes the diagnosis less likely.[17] Diagnosis is generally based on multiple features.[17]
Physical exam
- Palpation of the head reveals prominent temporal arteries with or without pulsation.
- The temporal area may be tender.
- Decreased pulses may be found throughout the body
- Evidence of ischemia may be noted on fundal exam.
- Bruits may be heard over the subclavian and axillary arteries
Laboratory tests
- ESR,[18] an inflammatory marker, >60 mm/hour (normal 1–40 mm/hour).
- C-reactive protein, another inflammatory marker, may be elevated.[18]
- LFTs, liver function tests, are abnormal particularly raised ALP- alkaline phosphatase
- Platelets may also be elevated.
Biopsy
The gold standard for diagnosing temporal arteritis is biopsy, which involves removing a small part of the vessel under local anesthesia and examining it microscopically for giant cells infiltrating the tissue.[19] However, a negative result does not definitively rule out the diagnosis; since the blood vessels are involved in a patchy pattern, there may be unaffected areas on the vessel and the biopsy might have been taken from these parts. Unilateral biopsy of a 1.5–3 cm length is 85-90% sensitive (1 cm is the minimum).[20] A characterised as intimal hyperplasia and medial granulomatous inflammation with elastic lamina fragmentation with a CD 4+ predominant T cell infiltrate, currently biopsy is only considered confirmatory for the clinical diagnosis, or one of the diagnostic criteria.
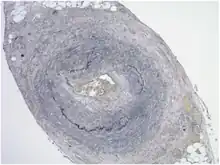 Histological features of temporal arteritis
Histological features of temporal arteritis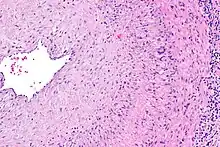 Intermediate magnification micrograph showing giant cell arteritis in a temporal artery biopsy. The arterial lumen is seen on the left. A giant cell is seen on the right at the interface between the thickened intima and media. H&E stain
Intermediate magnification micrograph showing giant cell arteritis in a temporal artery biopsy. The arterial lumen is seen on the left. A giant cell is seen on the right at the interface between the thickened intima and media. H&E stain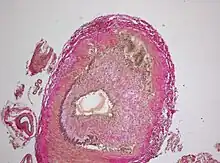 Histopathology of giant cell vasculitis in a cerebral artery. Elastica-stain.
Histopathology of giant cell vasculitis in a cerebral artery. Elastica-stain.
Medical imaging
Radiological examination of the temporal artery with ultrasound yields a halo sign. Contrast-enhanced brain MRI and CT is generally negative in this disorder. Recent studies have shown that 3T MRI using super high resolution imaging and contrast injection can non-invasively diagnose this disorder with high specificity and sensitivity.[21]
Treatment
GCA is considered a medical emergency due to the potential of irreversible vision loss.[11] Corticosteroids, typically high-dose prednisone (1 mg/kg/day), should be started as soon as the diagnosis is suspected (even before the diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy) to prevent irreversible blindness secondary to ophthalmic artery occlusion. Steroids do not prevent the diagnosis from later being confirmed by biopsy, although certain changes in the histology may be observed towards the end of the first week of treatment and are more difficult to identify after a couple of months.[22] The dose of corticosteroids is generally slowly tapered over 12–18 months.[23] Oral steroids are at least as effective as intravenous steroids,[24] except in the treatment of acute visual loss where intravenous steroids appear to offer significant benefit over oral steroids.[25] Short-term side effects of prednisone are uncommon but can include mood changes, avascular necrosis, and an increased risk of infection.[26] Some of the side effects associated with long-term use include weight gain, diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, avascular necrosis, glaucoma, cataracts, cardiovascular disease, and an increased risk of infection.[27][28] It is unclear if adding a small amount of aspirin is beneficial or not as it has not been studied.[29] Injections of tocilizumab may also be used.[30] Tocilizumab is a humanized antibody that targets the interleukin-6 receptor, which is a key cytokine involved in the progression of GCA.[31] Tocilizumab has been found to be effective at minimizing both recurrence, and flares of GCA when used both on its own and with corticosteroids.[31] Long term use of tocilizumab requires further investigation.[31][32] Tocilizumab may increase the risk of gastrointestinal perforation and infections, however it does not appear that there are more risks than using corticosteroids.[31][32]
Epidemiology
Giant cell arteritis typically only occurs in those over the age of 50;[4] particularly those in their 70s.[18] It affects about 1 in 15,000 people over the age of 50 per year.[2] It is more common in women than in men, by a ratio of 2:1,[4] and more common in those of Northern European descent, as well as in those residing further from the Equator.[5]
Terminology
The terms "giant cell arteritis" and "temporal arteritis" are sometimes used interchangeably, because of the frequent involvement of the temporal artery. However, other large vessels such as the aorta can be involved.[33] Giant-cell arteritis is also known as "cranial arteritis" and "Horton's disease."[34] The name (giant cell arteritis) reflects the type of inflammatory cell involved.[35]
References
- 1 2 3 4 Nussinovitch, Udi (2017). The Heart in Rheumatic, Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases: Pathophysiology, Clinical Aspects and Therapeutic Approaches. Academic Press. p. 367. ISBN 9780128032688. Archived from the original on 2017-10-22.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Orphanet: Giant cell arteritis". www.orpha.net. Archived from the original on 14 September 2017. Retrieved 14 September 2017.
- 1 2 3 "Giant Cell Arteritis". National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. 13 April 2017. Archived from the original on 22 October 2017. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ (July 2014). "Clinical practice. Giant-cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica". The New England Journal of Medicine. 371 (1): 50–7. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1214825. PMC 4277693. PMID 24988557.
- 1 2 3 Johnson, Richard J.; Feehally, John; Floege, Jurgen (2014). Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 300. ISBN 9780323242875. Archived from the original on 2017-10-22.
- ↑ Ferri, Fred F. (2010). Ferri's Differential Diagnosis E-Book: A Practical Guide to the Differential Diagnosis of Symptoms, Signs, and Clinical Disorders. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 195. ISBN 978-0323081634. Archived from the original on 2017-10-22.
- ↑ Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F, et al. (January 2013). "2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides". Arthritis and Rheumatism. 65 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1002/art.37715. PMID 23045170. S2CID 20891451.
- ↑ "Giant Cell Arteritis". National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. 13 April 2017. Archived from the original on 22 October 2017. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- 1 2 Hunder, Gene G. "Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell (temporal) arteritis". uptodate.com. Wolters Kluwer. Archived from the original on 25 September 2015. Retrieved 23 September 2015.
- ↑ Hayreh (April 3, 2003). "Ocular Manifestations of GCA". University of Iowa Health Care. Archived from the original on 2007-10-25. Retrieved 2007-10-15.
- 1 2 3 Rana AQ, Saeed U, Khan OA, Qureshi AR, Paul D (October 2014). "Giant cell arteritis or tension-type headache?: A differential diagnostic dilemma". Journal of Neurosciences in Rural Practice. 5 (4): 409–11. doi:10.4103/0976-3147.140005. PMC 4173245. PMID 25288850.
- 1 2 "UpToDate". www.uptodate.com. Archived from the original on 2021-08-28. Retrieved 2019-11-25.
- ↑ Gilden D, White T, Khmeleva N, Heintzman A, Choe A, Boyer PJ, et al. (May 2015). "Prevalence and distribution of VZV in temporal arteries of patients with giant cell arteritis". Neurology. 84 (19): 1948–55. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000001409. PMC 4433460. PMID 25695965.
- ↑ "Giant cell arteritis". BMJ Best Practice. Archived from the original on 2019-11-11. Retrieved 2019-11-25.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chen, John; Warrington, Kenneth; Garrity, James; Prasad, Sashank (2017). "Is Routine Imaging of the Aorta Warranted in Patients With Giant Cell Arteritis?". Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology. 37 (3): 314–319. doi:10.1097/WNO.0000000000000538. ISSN 1070-8022. PMID 28614098. Archived from the original on 2019-09-27. Retrieved 2019-11-25.
- ↑ Weyand, Cornelia M.; Goronzy, Jörg J. (2014-07-03). Solomon, Caren G. (ed.). "Giant-Cell Arteritis and Polymyalgia Rheumatica". New England Journal of Medicine. 371 (1): 50–57. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1214825. ISSN 0028-4793. PMC 4277693. PMID 24988557.
- 1 2 3 van der Geest, Kornelis S. M.; Sandovici, Maria; Brouwer, Elisabeth; Mackie, Sarah L. (17 August 2020). "Diagnostic Accuracy of Symptoms, Physical Signs, and Laboratory Tests for Giant Cell Arteritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". JAMA Internal Medicine. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3050.
- 1 2 3 Mackie, SL; Dejaco, C; Appenzeller, S; Camellino, D; Duftner, C; Gonzalez-Chiappe, S; Mahr, A; Mukhtyar, C; Reynolds, G; de Souza, AWS; Brouwer, E; Bukhari, M; Buttgereit, F; Byrne, D; Cid, MC; Cimmino, M; Direskeneli, H; Gilbert, K; Kermani, TA; Khan, A; Lanyon, P; Luqmani, R; Mallen, C; Mason, JC; Matteson, EL; Merkel, PA; Mollan, S; Neill, L; Sullivan, EO; Sandovici, M; Schmidt, WA; Watts, R; Whitlock, M; Yacyshyn, E; Ytterberg, S; Dasgupta, B (1 March 2020). "British Society for Rheumatology guideline on diagnosis and treatment of giant cell arteritis". Rheumatology (Oxford, England). 59 (3): e1–e23. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kez672. PMID 31970405.
- ↑ Cahais J, Houdart R, Lupinacci RM, Valverde A (June 2017). "Operative technique: Superficial temporal artery biopsy". Journal of Visceral Surgery. 154 (3): 203–207. doi:10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2017.05.001. PMID 28601496.
- ↑ Ypsilantis E, Courtney ED, Chopra N, Karthikesalingam A, Eltayab M, Katsoulas N, et al. (November 2011). "Importance of specimen length during temporal artery biopsy". The British Journal of Surgery. 98 (11): 1556–60. doi:10.1002/bjs.7595. PMID 21706476. S2CID 20149393.
- ↑ Bley TA, Uhl M, Carew J, Markl M, Schmidt D, Peter HH, et al. (October 2007). "Diagnostic value of high-resolution MR imaging in giant cell arteritis". AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology. 28 (9): 1722–7. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0638. PMID 17885247.
- ↑ Font RL, Prabhakaran VC (February 2007). "Histological parameters helpful in recognising steroid-treated temporal arteritis: an analysis of 35 cases". The British Journal of Ophthalmology. 91 (2): 204–9. doi:10.1136/bjo.2006.101725. PMC 1857614. PMID 16987903.
- ↑ Mackie, SL; Dejaco, C; Appenzeller, S; Camellino, D; Duftner, C; Gonzalez-Chiappe, S; Mahr, A; Mukhtyar, C; Reynolds, G; de Souza, AWS; Brouwer, E; Bukhari, M; Buttgereit, F; Byrne, D; Cid, MC; Cimmino, M; Direskeneli, H; Gilbert, K; Kermani, TA; Khan, A; Lanyon, P; Luqmani, R; Mallen, C; Mason, JC; Matteson, EL; Merkel, PA; Mollan, S; Neill, L; Sullivan, EO; Sandovici, M; Schmidt, WA; Watts, R; Whitlock, M; Yacyshyn, E; Ytterberg, S; Dasgupta, B (1 March 2020). "British Society for Rheumatology guideline on diagnosis and treatment of giant cell arteritis". Rheumatology (Oxford, England). 59 (3): e1–e23. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kez672. PMID 31970405.
- ↑ "BestBets: Steroids and Temporal Arteritis". Archived from the original on 2009-02-27.
- ↑ Chan CC, Paine M, O'Day J (September 2001). "Steroid management in giant cell arteritis". The British Journal of Ophthalmology. 85 (9): 1061–4. doi:10.1136/bjo.85.9.1061. PMC 1724128. PMID 11520757.
- ↑ Richards, Robert N. (March 2008). "Side Effects of Short-Term Oral Corticosteroids". Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 12 (2): 77–81. doi:10.2310/7750.2008.07029. ISSN 1203-4754. PMID 18346404.
- ↑ Youssef, Jameel; Novosad, Shannon A.; Winthrop, Kevin L. (2016). "Infection Risk and Safety of Corticosteroid Use". Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America. 42 (1): 157–176. doi:10.1016/j.rdc.2015.08.004. ISSN 0889-857X. PMC 4751577. PMID 26611557.
- ↑ Oray, Merih; Samra, Khawla Abu; Ebrahimiadib, Nazanin; Meese, Halea; Foster, C. Stephen (2016-04-02). "Long-term side effects of glucocorticoids". Expert Opinion on Drug Safety. 15 (4): 457–465. doi:10.1517/14740338.2016.1140743. ISSN 1474-0338. PMID 26789102.
- ↑ Mollan SP, Sharrack N, Burdon MA, Denniston AK (August 2014). "Aspirin as adjunctive treatment for giant cell arteritis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (8): CD010453. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010453.pub2. PMID 25087045.
- ↑ "Press Announcements - FDA approves first drug to specifically treat giant cell arteritis". www.fda.gov. Archived from the original on 26 January 2018. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 Mariano, Vincent J.; Frishman, William H. (2018). "Tocilizumab in Giant Cell Arteritis". Cardiology in Review. 26 (6): 321–330. doi:10.1097/CRD.0000000000000204. ISSN 1061-5377. PMID 29570475.
- 1 2 Rinden, T.; Miller, E.; Nasr, R. (2019-07-01). "Giant cell arteritis: An updated review of an old disease". Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 86 (7): 465–472. doi:10.3949/ccjm.86a.18103. ISSN 0891-1150. PMID 31291180.
- ↑ Walter MA, Melzer RA, Graf M, Tyndall A, Müller-Brand J, Nitzsche EU (May 2005). "[18F]FDG-PET of giant-cell aortitis". Rheumatology. 44 (5): 690–1. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh551. PMID 15728420.
- ↑ James, William D.; Elston, Dirk; Treat, James R.; Rosenbach, Misha A.; Neuhaus, Isaac (2020). "35.Cutaneous vascular diseases". Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (13th ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. pp. 849–850. ISBN 978-0-323-54753-6. Archived from the original on 2022-10-01. Retrieved 2022-10-01.
- ↑ "giant cell arteritis" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
External links
- Mackie, SL; Dejaco, C; Appenzeller, S; Camellino, D; Duftner, C; Gonzalez-Chiappe, S; Mahr, A; Mukhtyar, C; Reynolds, G; de Souza, AWS; Brouwer, E; Bukhari, M; Buttgereit, F; Byrne, D; Cid, MC; Cimmino, M; Direskeneli, H; Gilbert, K; Kermani, TA; Khan, A; Lanyon, P; Luqmani, R; Mallen, C; Mason, JC; Matteson, EL; Merkel, PA; Mollan, S; Neill, L; Sullivan, EO; Sandovici, M; Schmidt, WA; Watts, R; Whitlock, M; Yacyshyn, E; Ytterberg, S; Dasgupta, B (1 March 2020). "British Society for Rheumatology guideline on diagnosis and treatment of giant cell arteritis". Rheumatology. Oxford, England. 59 (3): e1–e23. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kez672. PMID 31970405.
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|