Essex-Lopresti fracture
| Essex-Lopresti fracture | |
|---|---|
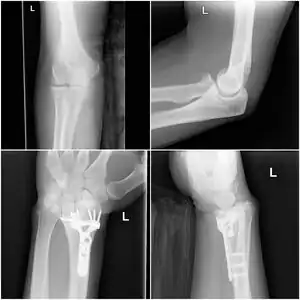 | |
| Collated key points (combination of radial head fracture with dislocation of the distal radial ulnar joint, requiring pinning) | |
| Specialty | Orthopaedics |
| Symptoms | Dislocation of the forearm |
| Complications | Mal-Union |
| Treatment | Open reduction and internal fixation with plates |
| Prognosis | Good if treated early |
| Deaths | Rare |
The Essex-Lopresti fracture is a break in the forearm near the wrist with concomitant dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint and disruption of the interosseous membrane.[1]
The injury is named after Peter Essex-Lopresti who described it in 1951.[2][3]
Cause
It is generally as a result of falling from a height.[1]
Diagnosis
The injury can be difficult to diagnose initially as the attention is focused on the injury to the radial head, leading to the distal radio-ulnar injury being overlooked. The examination finding of tenderness of the distal radio-ulnar joint suggests an Essex-Lopresti injury in people who have sustained high energy forearm trauma. Plain radiography shows the radial head fracture, with dorsal subluxation of the ulna often seen on lateral view of the pronated wrist.[1]
Management
The radial head fracture is usually managed by open reduction internal fixation; if the fracture is too comminuted, a radial head implant can be used. Excision of the radial head should be avoided, as the radius will migrate proximally leading to wrist pain and loss of pronation and supination of the wrist. Delayed treatment of the radial head fracture will also lead to proximal migration of the radius.[4]
The distal radio-ulnar joint dislocation can be reduced by supination of the forearm, and may be pinned in place for 6 weeks to allow healing of the interosseous membrane.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Essex Lopresti Fracture". Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics. 22 July 2020. Archived from the original on 7 May 2021. Retrieved 7 May 2021.
- ↑ Essex-Lopresti, P. (May 1951). "Fractures of the radial head with distal radio-ulnar dislocation; report of two cases". The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British Volume. 33B (2): 244–247. ISSN 0301-620X. PMID 14832324. Archived from the original on 2021-08-28. Retrieved 2021-05-08.
- ↑ Mostofi, Seyed B. (2004). Who's Who in Orthopedics. London: Springer. pp. 99–100. ISBN 1-85233-786-9. Archived from the original on 2021-08-28. Retrieved 2021-05-08.
- ↑ Edwards, GS Jr.; Jupiter JB (Sep 1988). "Radial head fractures with acute radioulnar dislocation. Essex-Lopresti revisited". Clin Orthop Relat Res (234): 61–9. PMID 3409602.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |