Trichothiodystrophy
| Trichothiodystrophy | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Amish brittle hair syndrome, BIDS syndrome, brittle hair–intellectual impairment–decreased fertility–short stature syndrome[1] | |
 | |
| This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.[1] | |
Trichothiodystrophy (TTD) is an autosomal recessive inherited disorder characterised by brittle hair and intellectual impairment. The word breaks down into tricho – "hair", thio – "sulphur", and dystrophy – "wasting away" or literally "bad nourishment". TTD is associated with a range of symptoms connected with organs of the ectoderm and neuroectoderm. TTD may be subclassified into four syndromes: Approximately half of all patients with trichothiodystrophy have photosensitivity, which divides the classification into syndromes with or without photosensitivity; BIDS and PBIDS, and IBIDS and PIBIDS. Modern covering usage is TTD-P (photosensitive), and TTD.[2][3]
Symptoms and signs
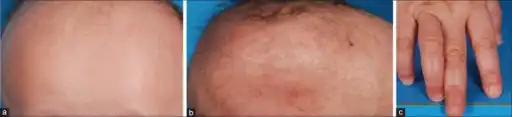
Features of TTD can include photosensitivity, icthyosis, brittle hair and nails, intellectual impairment, decreased fertility and short stature. A more subtle feature associated with this syndrome is a "tiger tail" banding pattern in hair shafts, seen in microscopy under polarized light.[4] The acronyms PIBIDS, IBIDS, BIDS and PBIDS give the initials of the words involved. BIDS syndrome, also called Amish brittle hair brain syndrome and hair-brain syndrome,[5] is an autosomal recessive[6] inherited disease. It is nonphotosensitive. BIDS is characterized by brittle hair, intellectual impairment, decreased fertility, and short stature.[7]: 501 There is a photosensitive syndrome, PBIDS.[8]
BIDS is associated with the gene MPLKIP (TTDN1).[9] IBIDS syndrome, following the acronym from ichthyosis, brittle hair and nails, intellectual impairment and short stature, is the Tay syndrome or sulfur-deficient brittle hair syndrome, first described by Tay in 1971.[10] (Chong Hai Tay was the Singaporean doctor who was the first doctor in South East Asia to have a disease named after him.) Tay syndrome should not be confused with the Tay–Sachs disease.[7]: 485 [11][12][13] It is an autosomal recessive[14] congenital disease.[7]: 501 [15] In some cases, it can be diagnosed prenatally.[16] IBIDS syndrome is nonphotosensitive.
Cause
The photosensitive form is referred to as PIBIDS, and is associated with ERCC2[11] and ERCC3.[17]
Photosensitive forms
All photosensitive TTD syndromes have defects in the nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway, which is a vital DNA repair system that removes many kinds of DNA lesions. This defect is not present in the nonphotosensitive TTD's.[18] These type of defects can result in other rare autosomal recessive diseases like xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne syndrome.[19]
DNA repair
Currently, mutations in four genes are recognized as causing the TTD phenotype, namely TTDN1, XPB, XPD and TTDA.[20] Individuals with defects in XPB, XPD and TTDA are photosensitive, whereas those with a defect in TTDN1 are not. The three genes, XPB, XPD and TTDA, encode protein components of the multi-subunit transcription/repair factor IIH (TFIIH). This complex factor is an important decision maker in NER that opens the DNA double helix after damage is initially recognized. NER is a multi-step pathway that removes a variety of different DNA damages that alter normal base pairing, including both UV-induced damages and bulky chemical adducts. Features of premature aging often occur in individuals with mutational defects in genes specifying protein components of the NER pathway, including those with TTD[21] (see DNA damage theory of aging).
Diagnosis
The evaluation of this condition is done via the following:[22]
- Detailed medical history
- Physical exam
- MRI imaging
- Laboratory testing
Treatment
In terms of management of an individual with this condition would benefit from the following:[22]
- Protection from exposure to sun
- Special education
- Physical therapy
- Skin softening emollients
- Prophylactic antibiotics
See also
References
- 1 2 "Trichothiodystrophy". Genetics Home Reference. Archived from the original on 20 February 2018. Retrieved 19 February 2018.
- ↑ Lambert WC, Gagna CE, Lambert MW (2010). "Trichothiodystrophy: Photosensitive, TTD-P, TTD, Tay syndrome". Adv Exp Med Biol. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 685: 106–10. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-6448-9_10. ISBN 978-1-4419-6447-2. PMID 20687499.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Giacaman, A.; Ferrando, J. (1 February 2022). "[Translated article] Keys to the Diagnosis of Hair Shaft Disorders: Part I". Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas. 113 (2): T141–T149. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2022.01.021. ISSN 0001-7310. PMID 35244576. Archived from the original on 20 April 2022. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ↑ Liang, Christine; Kraemer, Kenneth H.; Morris, Andrea; Schiffmann, Raphael; Price, Vera H.; Menefee, Emory; DiGiovanna, John J. (February 2005). "Characterization of tiger tail banding and hair shaft abnormalities in trichothiodystrophy". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 52 (2): 224–232. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.09.013.
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 234050
- ↑ Baden, H. P.; Jackson, C. E.; Weiss, L.; Jimbow, K.; Lee, L.; Kubilus, J.; Gold, R. J. (Sep 1976). "The physicochemical properties of hair in the BIDS syndrome". American Journal of Human Genetics. 28 (5): 514–521. PMC 1685097. PMID 984047.
- 1 2 3 Freedberg, et al. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-138076-0.
- ↑ Hashimo S, and Egly JM. Trichothiodystrophy view from the molecular basis of DNA repair transcription factor TF11H.www.oxfordjournals.org/content/18/R2/R224
- ↑ Nakabayashi K, Amann D, Ren Y, et al. (March 2005). "Identification of C7orf11 (TTDN1) gene mutations and genetic heterogeneity in nonphotosensitive trichothiodystrophy". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 76 (3): 510–6. doi:10.1086/428141. PMC 1196401. PMID 15645389.
- ↑ Tay CH (1971). "Ichthyosiform erythroderma, hair shaft abnormalities, and mental and growth retardation. A new recessive disorder". Arch Dermatol. 104 (1): 4–13. doi:10.1001/archderm.104.1.4. PMID 5120162.
- 1 2 Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 601675
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ↑ Hashimoto S, and Egly JM, www.oxfordjournals.org/content/18/R2/R224
- ↑ Stefanini M, B. E.; Botta, E.; Lanzafame, M.; Orioli, D. (January 2010). "Trichothiodystrophy: from basic mechanisms to clinical implications". DNA Repair. 9 (1): 2–10. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.10.005. PMID 19931493.
- ↑ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (10th ed.). Saunders. p. 575. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.
- ↑ Kleijer WJ, van der Sterre ML, Garritsen VH, Raams A, Jaspers NG (Dec 2007). "Prenatal diagnosis of xeroderma pigmentosum and trichothiodystrophy in 76 pregnancies at risk". Prenat. Diagn. 27 (12): 1133–1137. doi:10.1002/pd.1849. PMID 17880036. S2CID 23534246.
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 616390
- ↑ Hashimoto S, and Egly JM http://www.oxfordjournals.org/content/18/R2/R224%5B%5D
- ↑ Peserico, A.; Battistella, P. A.; Bertoli, P. (1 January 1992). "MRI of a very rare hereditary ectodermal dysplasia: PIBI(D)S". Neuroradiology. 34 (4): 316–317. doi:10.1007/BF00588190. PMID 1528442. S2CID 31063628.
- ↑ Theil AF, Hoeijmakers JH, Vermeulen W (2014). "TTDA: big impact of a small protein". Exp. Cell Res. 329 (1): 61–8. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.07.008. PMID 25016283.
- ↑ Edifizi D, Schumacher B (2015). "Genome Instability in Development and Aging: Insights from Nucleotide Excision Repair in Humans, Mice, and Worms". Biomolecules. 5 (3): 1855–69. doi:10.3390/biom5031855. PMC 4598778. PMID 26287260.
- 1 2 "Trichothiodystrophy". NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders). Archived from the original on 26 February 2021. Retrieved 1 September 2021.
External links
- NIH document on Tay syndrome Archived 2019-12-14 at the Wayback Machine
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|