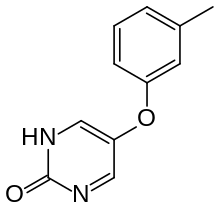
Tolimidone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | CP-26154, MLR-1023 |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.230.742 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H10N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 202.213 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
Tolimidone (CP-26154; MLR-1023) is a compound which was discovered by scientists at Pfizer, was found to stimulate secretion of gastric mucosa, and was in development by Pfizer as a drug candidate to treat gastric ulcers but was abandoned.[1][2][3][4] After the patent on the compound expired, scientists at the company Melior Discovery identified it as a potential drug candidate for diabetes through a phenotypic screen.[5] The company proceeded to show that MLR-1023 is an allosteric activator of Lyn kinase with an EC50 of 63 nM.[6][7] As of 2012 Melior was repurposing it for diabetes.[1][8] In June 2016, the company reported positive results from their Phase 2a clinical study in diabetic subjects[9][10]
References
- 1 2 Saporito, Michael S.; Lipinski, Christopher A.; Reaume, Andrew G. (2012). "Chapter 9:Phenotypic In Vivo Screening to Identify New, Unpredicted Indications for Existing Drugs and Drug Candidates". In Barratt, Michael J.; Frail, Donald E. (eds.). Drug Repositioning: Bringing New Life to Shelved Assets and Existing Drugs. John Wiley & Sons. p. 270. ISBN 9781118274392.
- ↑ "Tolimidone". AdisInsight. Retrieved 26 August 2017.
- ↑ Lipinski, C. A.; Stam, J. G.; Pereira, J. N.; Ackerman, N. R.; Hess, H. J. (1980). "Bronchodilator and antiulcer phenoxypyrimidinones". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 23 (9): 1026–31. doi:10.1021/jm00183a012. PMID 7411545.
Compound 3 has been assigned the nonproprietary (USAN) name tolimidone
- ↑ Lipinski CA, Reaume AG (May 2020). "High throughput in vivo phenotypic screening for drug repurposing: Discovery of MLR-1023 a novel insulin sensitizer and novel Lyn kinase activator with clinical proof of concept". Bioorg Med Chem. 28 (8): 115425. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115425. PMID 32201192.
- ↑ Lipinski CA, Reaume AG (May 2020). "High throughput in vivo phenotypic screening for drug repurposing: Discovery of MLR-1023 a novel insulin sensitizer and novel Lyn kinase activator with clinical proof of concept". Bioorg Med Chem. 28 (8): 115425. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115425. PMID 32201192.
- ↑ Ochman AR, Lipinski CA, Handler JA, Reaume AG, Saporito MS (2012). "The Lyn kinase activator MLR-123 is a novel insulin receptor potentiator that elicits a rapid-onset and durable improvement in glucose homeostasis in animal models of type 2 diabetes". J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 342 (1): 23–32. doi:10.1124/jpet.112.192187. PMID 22431203. S2CID 7288053.
- ↑ Saporito MS, Ochman AR, Lipinski CA, Handler JA, Reaume AG (2011). "MLR-1023 is potent and selective allosteric activator of Lyn kinase in vitro that improves glucose tolerance in vivo". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 342 (1): 15–22. doi:10.1124/jpet.112.192096. PMID 22473614. S2CID 26419896.
- ↑ "Melior Discovery website press releases".
- ↑ "Melior Pharmaceuticals Announces Positive Phase 2A Results in Type 2 Diabetes Study".
- ↑ Lee MK, Kim SG, Watkins E, Moon MK, Rhee SY, Frias JP, Chung CH, Lee SH, Block B, Cha BS, Park HK, Kim BJ, Greenway F (May 2020). "A Novel Non-PPARgamma Insulin Sensitizer: MLR-1023 Clinical Proof-of-concept in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus". J. Diabetes Complications. 34 (5): 107555. doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107555. PMID 32019723.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.