This article was co-authored by Brad Hurvitz. Brad Hurvitz is a Certified Swimming Instructor for My Baby Swims, an adolescent swimming school based in La Jolla, California. Brad is trained as an Infant Swimming Resource (ISR) instructor with ISR's Self-Rescue® program. He specializes in training children aged six months to six years of age survival skills like floating on their back to breathe and swimming back to the wall, while also educating parents on how to better keep their kids safe. He has a Master of Business Administration from Oregon State University.
There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 184,115 times.
Swimming, like all exercise, requires plenty of oxygen in your body to keep you from fainting. That's why it's so important to know how to hold your breath properly while swimming underwater. Knowing what to do will keep you safe and make it easier to swim, and it's simple to learn! Check out the tips below to learn how to safely hold your breath and control your breathing while you're swimming.
Steps
Controlling Your Breathing while Swimming
-
1Relax before and during your swim. A relaxed face and body muscles will help you hold more breath and breathe more effectively. Before you swim, loosen your limbs by shaking them out. Avoid clenching your teeth or jaw while swimming.[1]
- Hyperventilation is the practice of taking several quick breaths before you get in the water. Hyperventilation does not help you hold your breath. In fact, it can cause you to lose oxygen more quickly and black out.[2]
-
2Inhale deeply before you start swimming. Take a long, deep breath from the bottom of your lungs.[3] Your belly, not your chest or shoulders, should expand with the breath. Once you have a full inhalation, start swimming.[4]Advertisement
-
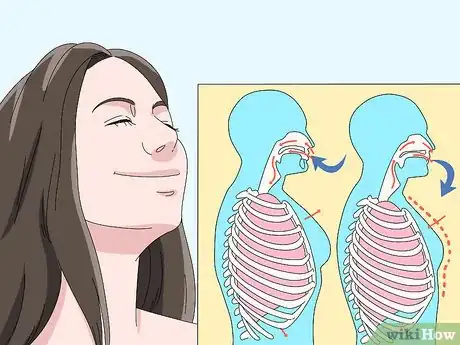
3Exhale slowly as your face enters the water. You can breathe out through your mouth or your nose, though it is recommended to exhale through your nose. Bubbles will rise up to the surface in a steady stream. Continue to exhale until you begin to pull up out of the water. Each exhale should be twice as long as your inhalation.[5]
-
4Come up to the surface when you need to inhale again. Let your mouth and nose break from the surface of the water. Inhale using your mouth. Your inhalation should only be half as long as your exhalation.[6]
- For some strokes, such as freestyle, you should turn your face to the side to take in a breath. Alternate which side you breathe on.[7]
- For strokes like the butterfly or breaststroke, you should inhale by lifting your head up above your arms until your nose and mouth break the surface of the water.
Practicing to Hold Your Breath Longer
-
1Practice holding your breath outside of the water. Breathing exercises can help expand your lung capacity. Practice in a comfortable, safe space, just in case you start to feel lightheaded. A bed or couch are ideal places to practice.[8]
- It is a good idea to have someone else nearby, just in case you faint.
-
2Push out air from your lungs to increase lung capacity. Stand up and bend over. Inhale deeply before trying to hold your breath for up to 20 seconds. As you hold your breath, raise your arms up over your head. When you can no longer hold your breath, exhale while lowering your arms.[9]
- Repeat this exercise up to 4 times every day.
-
3Do pursed lip breathing to strengthen your diaphragm. Breathe in deeply through your nose, filling the bottom of your lungs. Purse your lips and slowly exhale through your mouth. Your exhalation should be twice as long as your inhalation.[10]
- Spend about 5 minutes a day doing this exercise.
-
4Sing to expand your lung capacity. Singing in your free time can strengthen your diaphragm. Try singing songs that require you to hold long notes or hit high notes. This will help increase how much air you can store in your lungs.[11]
- Try to have at least 1 singing session a day. You can do it while you cook, clean, or take a shower.
Holding Your Breath while Sinking Underwater
-
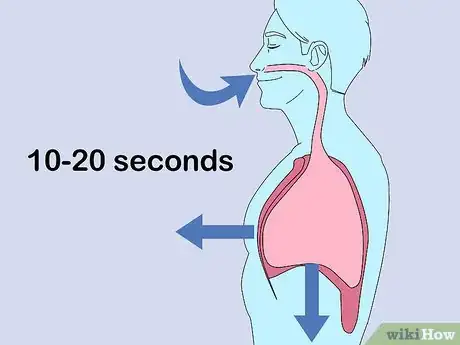
1Inhale deeply from the bottom of your lungs. Count to 10 or 20 seconds as you inhale. As you breathe, your belly should expand. If it does, you are reaching the deepest part of your lungs. If your chest and shoulders move, you are breathing from the top part of your lungs.[12]
- Avoid hyperventilation, which is the practice of taking quick, small breaths before you submerge yourself. This practice can increase your chances of blacking out.
- If inhaling for 10 seconds is too much, start out by taking in as much breath as you can. Each time you do it, try to inhale for a second longer.
-
2Submerge yourself in the water at the top of the inhalation. Once you can no longer take in any more breath, dive underwater or otherwise submerge yourself.[13]
-
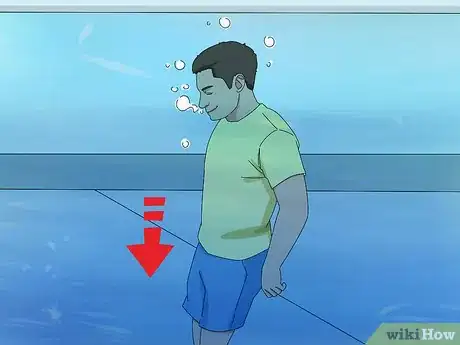
3Exhale while you are underwater. Holding your breath while underwater may cause you to blackout. Instead, slowly exhale through your mouth or nose while you are underwater. As you exhale, you should be pushing out a constant stream of bubbles from your nose or mouth.[14] Exhaling will not cause water to enter your nose or mouth.[15]
-
4Sink to the bottom of the pool to see if you are exhaling properly. If you exhale properly, your body will sink to the bottom. If you are not, your body will rise to the surface. As you get better at this exercise, try sitting on the bottom of the pool until you need air.[16]
-
5Rise back up as soon as you feel the urge to breathe. Unless you are an experienced free diver, you should not stay underwater for too long.[17] If you do, you might black out or drown. Instead, come back up for air once your exhalation is over or you feel the need to breathe.[18]
Community Q&A
-
QuestionWhat kind of exercises can I do to make me a better swimmer?
 Community AnswerAerobic and core exercises help lean out and strengthen your muscles, which lessens weight and cuts down on drag.
Community AnswerAerobic and core exercises help lean out and strengthen your muscles, which lessens weight and cuts down on drag. -
QuestionWhat if you're swimming, but it's just really hard for you to breathe and keep up with others? What if you have to stop in the middle of the pool? What are some good exercises to help prevent these issues?
 Community AnswerAll you need to do is take 2 big deep breaths and then keep going. It's ok if you stop in the middle of the pool. We all need to breathe.
Community AnswerAll you need to do is take 2 big deep breaths and then keep going. It's ok if you stop in the middle of the pool. We all need to breathe. -
QuestionHow can I hold it for five minutes?
 Community AnswerJust keep practicing and you will be able to go for a longer and longer amount of time. Five minutes might be unrealistic, though. Most Olympic swimmers can't even do that.
Community AnswerJust keep practicing and you will be able to go for a longer and longer amount of time. Five minutes might be unrealistic, though. Most Olympic swimmers can't even do that.
Warnings
- Never hold your breath entirely while you are swimming. This can cause you to black out, drown, or become light-headed.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Always swim and dive with other people watching, just in case you have a problem in the water. This is especially important when you are holding your breath.⧼thumbs_response⧽
- Hyperventilation (or the practice of taking quick, shallow breaths before submerging yourself) will not help you hold your breath. It can increase your chances of blacking out or drowning.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ http://www.humankinetics.com/news-and-excerpts/news-and-excerpts/five-tips-for-better-breathing-while-swimming
- ↑ http://www.usms.org/articles/articledisplay.php?aid=3063
- ↑ Brad Hurvitz. Certified Swimming Instructor. Expert Interview. 13 February 2020.
- ↑ https://www.artofmanliness.com/2015/08/17/how-to-hold-your-breath/
- ↑ http://www.humankinetics.com/news-and-excerpts/news-and-excerpts/five-tips-for-better-breathing-while-swimming
- ↑ http://www.humankinetics.com/news-and-excerpts/news-and-excerpts/five-tips-for-better-breathing-while-swimming
- ↑ https://www.active.com/triathlon/articles/proper-breathing-technique-for-swimming-875008
- ↑ https://www.artofmanliness.com/2015/08/17/how-to-hold-your-breath/
- ↑ https://lunginstitute.com/blog/increase-lung-capacity-5-easy-steps/
- ↑ http://www.lung.org/lung-health-and-diseases/protecting-your-lungs/breathing-exercises.html
- ↑ http://www.underwateraudio.com/blog/hold-your-breath-surprising-tips-on-increasing-lung-capacity/
- ↑ https://www.artofmanliness.com/2015/08/17/how-to-hold-your-breath/
- ↑ https://www.artofmanliness.com/2015/08/17/how-to-hold-your-breath/
- ↑ Brad Hurvitz. Certified Swimming Instructor. Expert Interview. 13 February 2020.
- ↑ http://www.usms.org/articles/articledisplay.php?aid=3250
- ↑ http://www.swimsmooth.com/exhalation.html
- ↑ Brad Hurvitz. Certified Swimming Instructor. Expert Interview. 13 February 2020.
- ↑ http://www.usms.org/articles/articledisplay.php?aid=3250
About This Article
To hold your breath while swimming, start by taking a long, deep breath so your belly, not your chest, expands. Then, slowly exhale out of your nose as you go underwater. When you feel like you need to inhale again, return to the surface and breathe in through your mouth. To practice holding your breath for longer periods of time, start by standing up on land and bending over. Then, inhale, hold your breath for 20 seconds, and raise your arms above your head. Finally, exhale while lowering your arms. To learn how to hold your breath while sinking underwater, scroll down!





























































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...