wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 39 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 40 testimonials and 95% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 911,929 times.
Learn more...
Chords are what make music interesting and give it character. They are some of the most basic and important things for every pianist to know, and they're really easy to learn! We'll show you the rules, and then let you go practice!
Steps
Chord Basics
-
1Understand what a chord is. A chord is three or more notes. Complex chords may have many notes, but you need a minimum of three.
- The chords discussed here will all be composed of three notes: a root, a third and a fifth.[1]
-
2Find the root of the chord. Every major chord is built on a note called the tonic, or root of the chord. This is the note that the chord is named after and will be the lowest note in the chord.[2]
- For a C major chord, C is the tonic. It will be the bottom note of your chord.
- You will play the tonic note with your thumb in your right hand, or with your pinkie in your left hand.
Advertisement -
3Find the major third. The second note in a major chord is the major third, which gives the chord its character. It will be four semitones, or half-steps, above the root. It is called a third because when you play a scale in that key, it will be the third note that you hit.
- For a C major chord, E is the third. It is four half steps above C. You can count them on your piano (C#, D, D#, E).
- You will play the third with your middle finger, regardless of which hand you’re using.
- Try playing the root and the third together, to get a sense of how that interval is supposed to sound.
-
4Find the fifth. The top note in a major chord is called the fifth because if you play a scale it will be the fifth note that you hit. It anchors the chord and makes it complete. It is seven semi-tones above the root.[3]
- For a C major chord, G is the fifth. You can count the seven semi-tones up from the root on your piano. (C#, D, D#, E, F, F#, G.)
- You play the fifth with your pinkie in your right hand, or your thumb in your left.
-
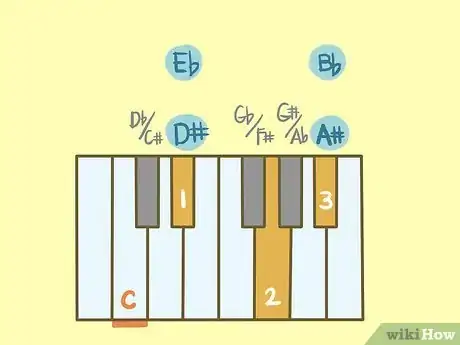
5Understand that there are at least two ways to spell a chord. All notes can be written at least two different ways, for example Eb and D# are the same note. Therefore, an Eb major chord would sound the same as D# major chord.
- The notes Eb, G, Bb create an Eb chord. The notes D#, F𝄪 (F##), A# create a D# Major chord, which sounds exactly like an Eb chord.
- The two chords are called enharmonic equivalents because they sound exactly the same but are written differently.[4]
- A few of the common enharmonic equivalents are noted below, but otherwise the article presents only the most common notation of a major chord.
-
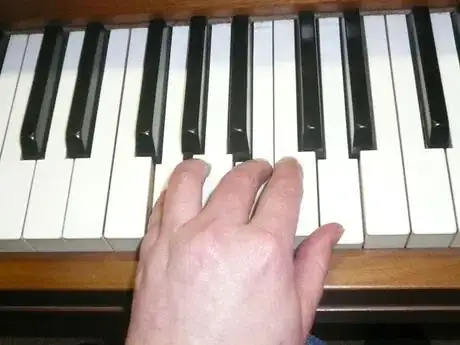
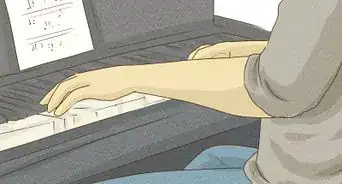
6Review proper hand position. In order to play a piece of piano music well, you need to consistently use the correct hand position, even when you’re just practicing chords.
- Keep your fingers tall and curved, as if they are diving into the keys. Use the natural curve of your fingers.
- Use the weight of your arms rather than the strength of your fingers to push on the keys.[5]
- Play on the tips of your fingers, including if possible the pinkie and thumb which tend to lie flat if you’re not paying attention.
- Keep your fingernails trimmed close so that you can play using the tips of your fingers.
Playing Chords
-
1Use three fingers. Notice that you will only use fingers 1, 3 and 5 (thumb, middle, pinkie) to play the three notes of each chord. Your index and ring fingers may rest on, but not press down any keys.
- Notice that your fingers advance one half-step (one key) up the keyboard each time you change chords.
-
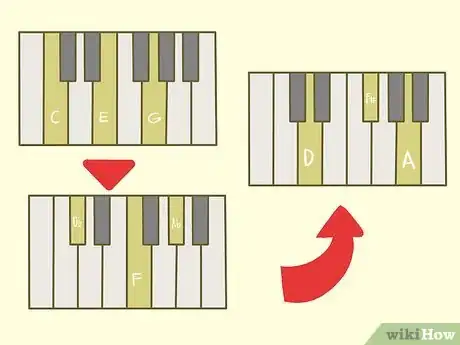
2Play C Major. The three notes will be C, E, G. Remember, C = tonic (0), E = major third (4 semi-tones), G = fifth (7 semi-tones).
- Right hand fingering will place your thumb on C, your middle finger on E and your pinkie on G.
- Left hand fingering will place your pinkie on C, your middle finger on E and your thumb on G.
-
3Play Db Major. The three notes will be Db, F, Ab. Remember, Db = tonic (0), F = major third (4 semi-tones), Ab = fifth (7 semi-tones). The enharmonic equivalent of this chord is C# Major. Notice that Db could also be noted as C#. F can also be written in music as E#. Ab can also be written as G#. The notes you play will be the same whether it is written as Db Major or C# Major.
- Right hand fingering will place your thumb on Db, your middle finger on F and your pinkie on Ab.
- Left hand fingering will place your pinkie on Db, your middle finger on F and your thumb on Ab.
-
4Play D Major. The three notes will be D, F#, A. Remember, D = tonic (0), F# = major third (4 semi-tones), A = fifth (7 semi-tones).
- Right hand fingering will place your thumb on D, your middle finger on F# and your pinkie on A.
- Left hand fingering will place your pinkie on D, your middle finger on F# and your thumb on A.
-
5Play Eb Major. The three notes will be Eb, G, Bb. Remember, Eb = tonic (0), G = major third (4 semi-tones), Bb = fifth (7 semi-tones).
- Right hand fingering will place your thumb on Eb, your middle finger on G and your pinkie on Bb.
- Left hand fingering will place your pinkie on Eb, your middle finger on G and your thumb on Bb.
-
6Play E Major. The three notes will be E, G#, B. Remember, E = tonic (0), G# = major third (4 semi-tones), B = fifth (7 semi-tones).
- Right hand fingering will place your thumb on E, your middle finger on G# and your pinkie on B.
- Left hand fingering will place your pinkie on E, your middle finger on G# and your thumb on B.
-
7Play F Major. The three notes will be F, A, C. Remember, F = tonic (0), A = major third (4 semi-tones), C = fifth (7 semi-tones).
- Right hand fingering will place your thumb on F, your middle finger on A and your pinkie on C.
- Left hand fingering will place your pinkie on F, your middle finger on A and your thumb on C.
-
8Play F# Major. The three notes will be F#, A#, C#. Remember, F# = tonic (0), A# = major third (4 semi-tones), C# = fifth (7 semi-tones). The enharmonic equivalent of this chord is Gb Major which will be written as Gb, Bb, Db. Note that F# can also be written as Gb. A# can also be written as Bb. C# can also be written as Db. So the notes you play to make a major chord will be the same in F# Major and Gb Major.
- Right hand fingering will place the thumb on F#, the middle finger on A# and the pinkie on C#.
- Left hand fingering will place the pinkie on F#, the middle finger on A# and the thumb on C#.
-
9Play G Major. The three notes will be G, B, D. Remember, G = tonic (0), B = major third (4 semi-tones), D = fifth (7 semi-tones).
- Right hand fingering will place the thumb on G, the middle finger on B and the pinkie on D.
- Left hand fingering will place the pinkie on G, the middle finger on B and the thumb on D.
-
10Play Ab Major. The three notes will be Ab, C, Eb. Remember, Ab = tonic (0), C = major third (4 semi-tones), Eb = fifth (7 semi-tones). The enharmonic equivalent of this chord is G# Major which will be written as G#, B#, D#. Note that Ab can also be written as G#. C can also be written as B#. Eb can also be written as D#. The notes you play to make a major chord will be the same for Ab Major and G# major, although they will be noted differently.
- Right hand fingering will place your thumb on Ab, your middle finger on C and your pinkie on Eb.
- Left hand fingering will place your pinkie on Ab, your middle finger on C and your thumb on Eb.
-
11Play A Major. The three notes will be A, C#, E. Remember, A = tonic (0), C# = major third (4 semi-tones), E = fifth (7 semi-tones).
- Right hand fingering will place your thumb on A, your middle finger on C# and your pinkie on E.
- Left hand fingering will place your pinkie on A, your middle finger on C# and your thumb on E.
-
12Play Bb Major. The three notes will be Bb, D, F. Remember, Bb = tonic (0), D = major third (4 semi-tones), F = fifth (7 semi-tones).
- Right hand fingering will place the thumb on Bb, the middle finger on D and the pinkie on F.
- Left hand fingering will place the pinkie on Bb, the middle finger on D, and the thumb on F.
-
13Play B Major. The three notes will be B, D#, F#. Remember, B = tonic (0), D# = major third (4 semi-tones), F# = fifth (7 semi-tones).
- Right hand fingering will place the thumb on B, the middle finger on D# and the pinkie on F#.
- Left hand fingering will place the pinkie on B, the middle finger on D# and the thumb on F#.
Practicing
-
1Practice playing all three notes at once. When you feel comfortable playing each chord individually, try skipping up the scale with each major chord. Start with a C major chord, then play a Db major, then D major and so on.
- Begin by doing this exercise with only one hand. When you feel confident, play both hands at once.
- Listen for false notes. The ratio between the notes should always remain the same, so if one chord suddenly sounds different, review whether you are hitting the correct notes.
-
2Try arpeggios. An arpeggio is when each note is struck in sequence from lowest to highest. To play a C Major arpeggio with your right hand, strike the C with your thumb and release. Strike E with your middle finger and release. Strike G with your pinkie and release.[6]
- When you have mastered this motion, try to make it fluid rather than choppy. Strike and release each note quickly, so there is scarcely any time between notes.
-
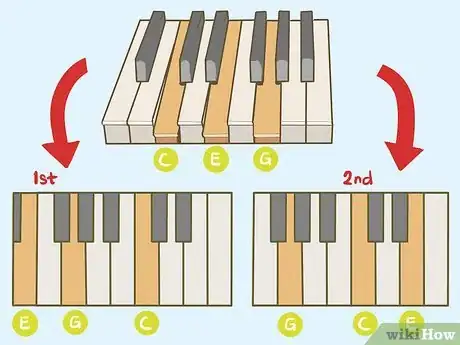
3Practice playing the major chords in different inversions. Inversions of a chord use the same notes, but place a different note on the bottom. For example, a C major chord is C, E, G. The first inversion of the C-major chord is E, G, C. The second inversion is G, C, E. [7]
- Challenge yourself by making a major chord with every note on the scale, in every inversion.
-
4Look for chords in sheet music. Once you are familiar with how to construct and play a chord, find a piece of music that has chords written. Look to see if you can identify major chords that you have practiced.
Community Q&A
-
QuestionHow do I play inversions?
 Community AnswerAn inversion is when you use all the same notes you normally do in a chord but you've changed which one you start with. For example: C major chord starts with the note C and has E and G above it (1, 3, 5). If you want to play the 1st inversion of this chord you will begin the chord on E, and play G and C (from the next octave) above it. In second inversion, you will start with G, and play C and E above it (from the octave above it).
Community AnswerAn inversion is when you use all the same notes you normally do in a chord but you've changed which one you start with. For example: C major chord starts with the note C and has E and G above it (1, 3, 5). If you want to play the 1st inversion of this chord you will begin the chord on E, and play G and C (from the next octave) above it. In second inversion, you will start with G, and play C and E above it (from the octave above it). -
QuestionCan I learn piano without classes?
 Community AnswerCheck out these additional tips for how to learn piano on wikiHow.
Community AnswerCheck out these additional tips for how to learn piano on wikiHow. -
QuestionHow do I read chords in sheet music?
 Community AnswerIn sheet music, chords are made up of two or more notes stacked on top of each other on the staff. You read them the same way you read any other note in sheet music -- by memorizing which line or space corresponds to each note. To play a chord, you just play all the stacked notes at the same time.
Community AnswerIn sheet music, chords are made up of two or more notes stacked on top of each other on the staff. You read them the same way you read any other note in sheet music -- by memorizing which line or space corresponds to each note. To play a chord, you just play all the stacked notes at the same time.
References
- ↑ http://www.elpin.com/tutorials/musicalchord.php
- ↑ http://www.piano-keyboard-guide.com/chord-inversions-explained-root-position-first-and-second-inversions/
- ↑ http://www.musictheory.net/lessons/40
- ↑ https://boldmusiclessons.com/enharmonic-equivalents/
- ↑ http://www.true-piano-lessons.com/piano-fingering.html
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i4Zsvtvm_g0
- ↑ http://www.piano-keyboard-guide.com/chord-inversions-explained-root-position-first-and-second-inversions/
About This Article
To play major chords on a keyboard, start by identifying the note that the chord is built on, such as the C key for a C major chord, and putting your right thumb on it. Next, find the second note of the chord, which will be 4 half-steps from the first note, and place your middle finger on it. Then, rest your thumb on the top note of the chord, which is 7 half-steps from the first note. When you want to play the chord, keep your fingers tall and curved, and push down on the keys simultaneously with the tips of your fingers. To learn how to play specific chords like Db Major or F Major, read on.












































-of-a-Song-Step-9.webp)


















-of-a-Song-Step-9.webp)