This article was medically reviewed by Allison Romero, PT, DPT. Dr. Allison Romero is a Pelvic Health Specialist, Physical Therapist, and the Owner of Reclaim Pelvic Therapy in the San Francisco Bay Area. With over a decade of experience, Allison specializes in comprehensive pelvic physical therapy treatments for pelvic floor dysfunction. She holds a Bachelor of Science in Kinesiology and Exercise Science from Sonoma State University and a Doctor of Physical Therapy from the University of Southern California. Allison is a board certified Physical Therapist in California and is a member of the American Physical Therapy Association-Section on Women’s Health and the International Pelvic Pain Society.
There are 18 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 100% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status.
This article has been viewed 984,471 times.
You might find that you sometimes have to urinate more often. This unusual need to empty your bladder may be the result of drinking lots of fluids, weak pelvic floor muscles, or even surgery. If you find that you have urinary incontinence, you can try strengthening your pelvic muscles and other measures such as limiting how much you drink in order to have to use the bathroom less often. If you find you are urinating more often than is normal for you, consult your doctor, as this may indicate a more serious health issue.
Steps
Performing Kegel Exercises to Strengthen Pelvic Muscles
-
1Recognize the benefits of Kegel exercises. Kegel exercises are a way to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles that may be weak from pregnancy, childbirth, surgery, aging, or being overweight.[1] [2] Anyone can do these discreet exercises at any time of day and they may help with urinary and fecal incontinence.[3]
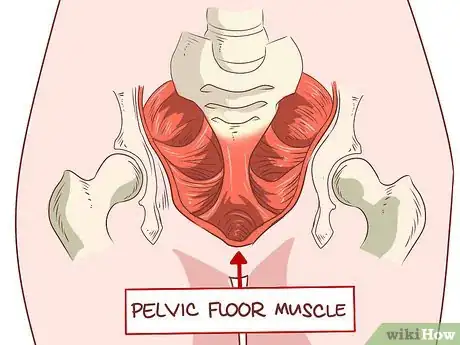
- The pelvic floor muscles support the uterus, bladder, small intestine, and rectum.[4]
- Kegels work by forcing you to relax and contract your pelvic floor muscles.[5]
- Kegels may work for anyone to help prevent urinary incontinence, especially during pregnancy.[6]
- If you have severe urinary leakage when you sneeze, cough, or laugh due to weakened pelvic floor muscles, Kegel exercises may be less effective.[7]
-
2Identify your pelvic floor muscles. You might be unsure where your pelvic floor muscles, but identifying them is very easy. This can help ensure that you’re doing Kegel exercises properly and strengthen your pelvic muscles more effectively.[8]Advertisement
-
3Empty your bladder. After you’ve identified your pelvic muscles, you’re ready to do Kegel exercises. You’ll need to empty your bladder to most effectively train your pelvic floor.[12]
-
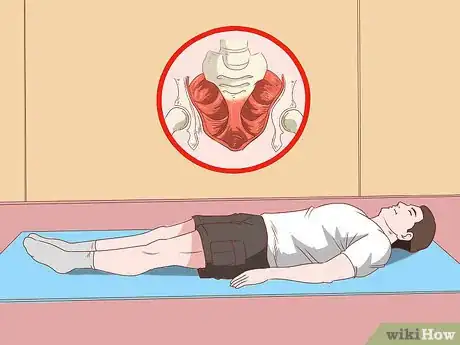
4Lie on your back. While you’re first getting the hang of doing Kegels, or if you’re having a hard time identifying your pelvic muscles, lie on your back. This can help you more effectively contract your pelvic floor muscles.[15]
- Make sure to lie on your back only after you’ve completely emptied your bladder.[16]
-
5Contract your pelvic floor muscles. Either on your back or, if you’re a more advanced practitioner of Kegels, someplace else you choose, contract your pelvic muscles. Hold them for a count of five and then relax for a count of five.[17]
- Pretend that you're pulling your pubic bone toward your tailbone. While you won't actually move either of these bones, you will engage your pelvic floor muscles in the process.[18]
- Try four or five sets of Kegel exercises.[19]
- Eventually work up to contracting your pelvic floor muscles for 10 seconds and then relaxing them for 10 seconds.[20]
- Don’t hold your breath when you are contracting your muscles. Allow your breath to flow naturally.[21]
-
6
-
7Practice Kegel exercise three times a day. Repeat your Kegel exercises at least three times a day. This can help you strengthen your pelvic floor muscles most effectively and help minimize incontinence.[24]
-
8Notice a stronger pelvic floor. If you practice your Kegels regularly, you should notice a stronger pelvic floor within a few months. You may also notice a decrease in how often you need to urinate.[27]
Using Behavioral Techniques to Control Urination
-
1Train your bladder. Bladder training is a behavioral technique in which you delay urination following the urge to use the bathroom. This technique may help increase the length of time between trips to the bathroom.[28]
-
2Try double voiding. Double voiding is a technique whereby you urinate twice in a short amount of time. This technique may help you empty your bladder and avoid so-called overflow incontinence.
- The most effective way to “double void” is to empty your bladder and then waiting a few minutes and trying to urinate again.[31]
-
3Schedule bathroom breaks. Waiting to urinate too long may exacerbate or cause incontinence. By scheduling regular bathroom breaks instead of waiting for the need to go, you may help strengthen your pelvic floor and control incontinence.[32]
- Use the bathroom every two to four hours depending on how often you usually go and how much you drink. The more you drink, the more often you may need to use the bathroom.[33]
-
4Drink fewer liquids. It’s important to get enough water to maintain hydration and your overall health. But drinking too much water isn’t good and may cause you to have to use the bathroom more often.[34]
-
5Limit foods and drinks that irritate the bladder. Certain foods and drinks may irritate or stimulate urination. By reducing your consumption of alcohol, caffeine, and acidic foods, you may help control your incontinence.[37]
- Reduce your intake of coffee, caffeinated teas, sodas, and milk[38]
- Try and eat less acidic foods such as tomatoes, citrus fruits, and nuts.[39]
- Eating too many salty foods may require you to drink and urinate more often.[40]
- Limit how much protein you eat because it requires the body to excrete certain by-products in your urine, making you have to go more frequently.[41]
-
6Take diuretics only when instructed by your doctor. Diuretics, which are sometimes called water pills, may make you have to urinate more often.[42] If you are taking diuretics to treat high blood pressure, edema, kidney disorders, or diabetes insipidus (diabetes that causes frequent urination), talk to your doctor about alternative treatments.[43] Be aware that if your doctor has prescribed diuretics, it may, in fact, be important for you to urinate frequently.
- Never discontinue prescribed medication without consulting your doctor first.
-
7Recognize abnormal urination. Most people urinate every three to four hours during the day. If you find that you’re urinating more often than normal, see your doctor.
-
8See your doctor. If you are experiencing more frequent urination or incontinence, see your doctor. She can rule out other conditions such as a urinary tract infection, bladder stones, diabetes, prostate issues, and other more serious conditions.[47]
- See your doctor if you frequent urination and/ or incontinence has no apparent cause, including drinking more liquids, alcohol, or caffeine.[48]
- If you have any of the following signs, it’s also important to see your doctor: blood in your urine, red or dark brown urine, painful urination, pain in your side, difficulty urinating or emptying your bladder, an overwhelming urge to use the bathroom, and loss of bladder control.[49]
- Keep a log of when you go to the bathroom. A precise diary, which need not cover a great span of time, may help your doctor understand your problem.
Expert Q&A
-
QuestionHow do I know if I'm doing Kegels right?
 Allison Romero, PT, DPTDr. Allison Romero is a Pelvic Health Specialist, Physical Therapist, and the Owner of Reclaim Pelvic Therapy in the San Francisco Bay Area. With over a decade of experience, Allison specializes in comprehensive pelvic physical therapy treatments for pelvic floor dysfunction. She holds a Bachelor of Science in Kinesiology and Exercise Science from Sonoma State University and a Doctor of Physical Therapy from the University of Southern California. Allison is a board certified Physical Therapist in California and is a member of the American Physical Therapy Association-Section on Women’s Health and the International Pelvic Pain Society.
Allison Romero, PT, DPTDr. Allison Romero is a Pelvic Health Specialist, Physical Therapist, and the Owner of Reclaim Pelvic Therapy in the San Francisco Bay Area. With over a decade of experience, Allison specializes in comprehensive pelvic physical therapy treatments for pelvic floor dysfunction. She holds a Bachelor of Science in Kinesiology and Exercise Science from Sonoma State University and a Doctor of Physical Therapy from the University of Southern California. Allison is a board certified Physical Therapist in California and is a member of the American Physical Therapy Association-Section on Women’s Health and the International Pelvic Pain Society.
Pelvic Health Specialist Pretend you're sucking up a smoothie through a straw. Women can imagine this motion through the vagina, while men can imagine this through the penis and rectum.
Pretend you're sucking up a smoothie through a straw. Women can imagine this motion through the vagina, while men can imagine this through the penis and rectum. -
QuestionWhat is bladder leakage a sign of?
 Allison Romero, PT, DPTDr. Allison Romero is a Pelvic Health Specialist, Physical Therapist, and the Owner of Reclaim Pelvic Therapy in the San Francisco Bay Area. With over a decade of experience, Allison specializes in comprehensive pelvic physical therapy treatments for pelvic floor dysfunction. She holds a Bachelor of Science in Kinesiology and Exercise Science from Sonoma State University and a Doctor of Physical Therapy from the University of Southern California. Allison is a board certified Physical Therapist in California and is a member of the American Physical Therapy Association-Section on Women’s Health and the International Pelvic Pain Society.
Allison Romero, PT, DPTDr. Allison Romero is a Pelvic Health Specialist, Physical Therapist, and the Owner of Reclaim Pelvic Therapy in the San Francisco Bay Area. With over a decade of experience, Allison specializes in comprehensive pelvic physical therapy treatments for pelvic floor dysfunction. She holds a Bachelor of Science in Kinesiology and Exercise Science from Sonoma State University and a Doctor of Physical Therapy from the University of Southern California. Allison is a board certified Physical Therapist in California and is a member of the American Physical Therapy Association-Section on Women’s Health and the International Pelvic Pain Society.
Pelvic Health Specialist Bladder leakage can be a sign of anything from tight pelvic muscles to a pelvic floor injury. I recommend you see your doctor or a physical therapist so they can diagnose what's going on.
Bladder leakage can be a sign of anything from tight pelvic muscles to a pelvic floor injury. I recommend you see your doctor or a physical therapist so they can diagnose what's going on. -
QuestionWhy can't I stop feeling like I have to pee?
 Allison Romero, PT, DPTDr. Allison Romero is a Pelvic Health Specialist, Physical Therapist, and the Owner of Reclaim Pelvic Therapy in the San Francisco Bay Area. With over a decade of experience, Allison specializes in comprehensive pelvic physical therapy treatments for pelvic floor dysfunction. She holds a Bachelor of Science in Kinesiology and Exercise Science from Sonoma State University and a Doctor of Physical Therapy from the University of Southern California. Allison is a board certified Physical Therapist in California and is a member of the American Physical Therapy Association-Section on Women’s Health and the International Pelvic Pain Society.
Allison Romero, PT, DPTDr. Allison Romero is a Pelvic Health Specialist, Physical Therapist, and the Owner of Reclaim Pelvic Therapy in the San Francisco Bay Area. With over a decade of experience, Allison specializes in comprehensive pelvic physical therapy treatments for pelvic floor dysfunction. She holds a Bachelor of Science in Kinesiology and Exercise Science from Sonoma State University and a Doctor of Physical Therapy from the University of Southern California. Allison is a board certified Physical Therapist in California and is a member of the American Physical Therapy Association-Section on Women’s Health and the International Pelvic Pain Society.
Pelvic Health Specialist Oftentimes, tight pelvic floor muscles can cause us to feel like we have to urinate, even we don't. I recommend doing some deep breathing to help relax your muscles. If you keep having issues, talk to your doctor.
Oftentimes, tight pelvic floor muscles can cause us to feel like we have to urinate, even we don't. I recommend doing some deep breathing to help relax your muscles. If you keep having issues, talk to your doctor.
Warnings
- Urinating more frequently than is normal for you can be the sign of serious medical conditions such as diabetes, prostate disease, bladder or urinary tract infections, etc. If you believe you are urinating more than normal, you must be evaluated by your doctor before pursuing any home treatment.⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ Allison Romero, PT, DPT. Pelvic Health Specialist. Expert Interview. 2 December 2020.
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000141.htm
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ https://www.health.harvard.edu/bladder-and-bowel/step-by-step-guide-to-performing-kegel-exercises
- ↑ https://www.health.harvard.edu/bladder-and-bowel/step-by-step-guide-to-performing-kegel-exercises
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ Allison Romero, PT, DPT. Pelvic Health Specialist. Expert Interview. 2 December 2020.
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ Allison Romero, PT, DPT. Pelvic Health Specialist. Expert Interview. 2 December 2020.
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000141.htm
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ https://www.health.harvard.edu/bladder-and-bowel/step-by-step-guide-to-performing-kegel-exercises
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ https://www.health.harvard.edu/bladder-and-bowel/step-by-step-guide-to-performing-kegel-exercises
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ Allison Romero, PT, DPT. Pelvic Health Specialist. Expert Interview. 2 December 2020.
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/kegel-exercises/art-20045283
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279430/
- ↑ https://www.health.harvard.edu/healthbeat/training-your-bladder
- ↑ https://www.ucsfhealth.org/education/bladder-training
- ↑ https://www.lhsc.on.ca/women-s-health/timed-toileting-and-double-voiding
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/basics/treatment/con-20037883
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/basics/treatment/con-20037883
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/basics/treatment/con-20037883
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/water/NU00283
- ↑ https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/bladder-control-problems/prevention
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/basics/treatment/con-20037883
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/basics/treatment/con-20037883
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/basics/treatment/con-20037883
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/basics/treatment/con-20037883
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/basics/treatment/con-20037883
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/in-depth/diuretics/art-20048129
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/in-depth/diuretics/art-20048129?pg=2
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/frequent-urination/basics/definition/sym-20050712
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/frequent-urination/basics/definition/sym-20050712
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/frequent-urination/basics/definition/sym-20050712
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/frequent-urination/basics/when-to-see-doctor/sym-20050712
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/frequent-urination/basics/when-to-see-doctor/sym-20050712
- ↑ http://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/frequent-urination/basics/when-to-see-doctor/sym-20050712
About This Article
Urinating too often can be inconvenient, but there are simple exercises you can do to strengthen your bladder. Try waiting 5 to 10 minutes after you feel the urge to pee before you go to the bathroom. If you can, only go every 2 to 4 hours to help train your bladder. Kegel exercises are also a great way to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles after pregnancy or childbirth, or from general ageing. All you need to do is empty your bladder, then lie on your back and contract your pelvic floor muscles for a few seconds. These are the same muscles you’d use to stop urinating midstream. Practice tensing your pelvic floor muscles for 10 repetitions 3 times a day. For more tips from our Medical co-author, including how to avoid foods and drinks that irritate your bladder, read on!









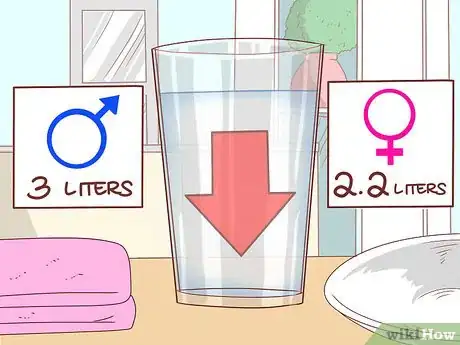























































Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...