قائمة بالكائنات الحية حسب عدد الكروموسومات
تصف قائمة الكائنات الحية حسب عدد الكروموسوم الصيغة الصبغية أو أعداد الكروموسومات في خلايا النباتات والحيوانات والطلائعيات والكائنات الحية الأخرى المختلفة. يُعرف هذا العدد (عدد الكروموسومات في الخلية)، بالإضافة إلى المظهر البصري للكروموسوم، بالنمط النووي، [2][3][4] ويمكن العثور عليه بالنظر إلى الكروموسومات من خلال المجهر. يتم الانتباه إلى طولها، وموضع السنترومير، ونمط النطاق، وأي فروق بين الكروموسومات الجنسية وأي خصائص فيزيائية أخرى.[5] يعد إعداد ودراسة الأنماط النووية جزءاً من علم الوراثة الخلوية.
| الكائن الحي (الاسم العلمي) | عدد الكروموسومات | صورة | النمط النووي | ملاحظات | المصدر |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| النمل النطاط (Myrmecia pilosula) |
2/1 |  | 2 بالنسبة للإناث، أما الذكور فهي أحادية الشكل وبالتالي لديها 1؛ وهو أصغر عدد ممكن من الكروموسومات. أنواع النمل الأخرى لديها المزيد من الكروموسومات.[6] | [6] | |
| ديزي الأسترالي (Brachyscome dichromosomatica) |
12 |  | يمكن أن يحتوي هذا النوع على كروموسومات B أكثر من كروموسومات A في بعض الأحيان.
2n=6 |
[7] | |
| سوسيات عنكبوتية | 4–14 |  | العناكب (عائلة سوسيات عنكبوتية). الذكور أحادية الصبغة، بينما الإناث ثنائية الصبغية | [8] | |
| بعوضة الحمى الصفراء (Aedes aegypti) |
6 |  | _chromosomes.png.webp) |
يتم حفظ الرقم (2ن = 6) كروموسوم في جميع أفراد أسرة البعوضيات، باستثناء Chagasia bathana، التي لها (2ن = 8).[9] | [9] |
| الغزال الهندي مونتجاك (Muntiacus muntjak) |
6/7 |  | .png.webp) |
(2ن = 6) للإناث و7 للذكور. أقل عدد كروموسومي ثنائي الصبغيات في الثدييات.[10] | [11] |
| حشيشة الغراب | 8 |  | |||
| دروسفيلا (ذبابة فاكهة شائعة) |
8 | .jpg.webp) |  |
6 جسمية، 2 جنسية | [12] |
| رشاد أذن الفأر | 10 |  | .png.webp) |
||
| ولب المستنقعات (Wallabia bicolor) |
10/11 |  | .png.webp) |
10 عند الذكور، 11 عند الإناث | [13] |
| ديدان أسطوانية (ربداء رشيقة) |
12/11 |  |
12 للخنثى، 11 للذكور | ||
| سبانخ (Spinacia oleracea) |
12 |  | .png.webp) |
[14] | |
| فول (Vicia faba) |
12 |  | .png.webp) |
[15] | |
| ذبابة الروث الصفراء (Scathophaga stercoraria) |
12 |  | .png.webp) |
10 جسمية و2 جنسية. الذكور لديهم كروموسومات الجنس XY والإناث لديهم كروموسومات الجنس XX. الكروموسومات الجنسية هي أكبر الكروموسومات وتشكل 30٪ من الطول الكلي للمجموعة الصبغية في الإناث وحوالي 25٪ عند الذكور.[16] | [16] |
| عفن غروي (Dictyostelium discoideum) |
12 |  | [17] | ||
| خيار (Cucumis sativus) |
14 |  | [18] | ||
| شيطان تسمانيا (Sarcophilus harrisii) |
14 |  | .png.webp) |
||
| شيلم مزروع (Secale cereale) |
14 |  | [19] | ||
| بازلاء (Pisum sativum) |
14 |  | .png.webp) |
[19] | |
| شعير (Hordeum vulgare) |
14 |  | .png.webp) |
[20] | |
| صبر حقيقي | 14 |  |  |
[21] | |
| كوالا (Phascolarctos cinereus) |
16 |  | |||
| كنغر | 16 |  | يشمل ذلك العديد من أعضاء جنس كنغر، لكن ليس الكنغرأحمر (M. rufus ، 20) | [22] | |
| بلهارسية منسونية | 16 |  |  |
[23] | |
| بصل ويلزي (Allium Fistulosum) |
16 |  | _chromosomes.png.webp) |
[24] | |
| ثوم (Allium sativum) |
16 |  | .png.webp) |
[24] | |
| قارمة جربية (Sarcoptes scabiei) |
17/18 |  | _cell_-_17_chromosomes.png.webp) |
وفقًا لملاحظة خلايا البويضات الجنينية، فإن عدد الكروموسوم في سوس الحكة هو 17 أو 18. في حين أن سبب تباين الأرقام غير معروف، فقد ينشأ بسبب وجود نظام لتحديد الجنس Xo، حيث الذكور (2n = 17) تفتقر إلى كروموسوم الجنس وبالتالي يكون كروموسوم واحد أقل من الإناث (2n = 18).[25] | [25] |
| فجل (Raphanus sativus) |
18 | .jpg.webp) | [19] | ||
| جزر (جزر شائع) |
18 |  | .png.webp) |
جنس الجزر يضم حوالي 25 نوعا:
D. carota بها تسعة أزواج كروموسوم (2n = 2x = 18) كما أن D. capillifolius، وD. sahariensis وD. syrticus هم أنواع أخرى في هذا الجنس لديها 2n = 18 |
[26] |
| ملفوف (Brassica oleracea) |
18 |  | .png.webp) |
قنبيط أخضر، كرنب، كرنب أجعد، كرنب ساقي، كرنب بروكسل، والقرنبيط كلها من نفس النواع ولها نفس عدد الكروموسومات.[19] | [19] |
| حمضيات (Citrus x) |
18 |  | [27] | ||
| ماراكويا (Passiflora edulis) |
18 | [28] | |||
| ذيل الثعلب الأخضر (Setaria viridis) |
18 | _P.Beauv.P9130041.JPG.webp) | [29] | ||
| ذرة (Zea mays) |
20 | .JPG.webp) | [19] | ||
| قنب هندي (قنب مزروع) |
20 |  | |||
| قيطم مداري (Xenopus tropicalis) |
20 |  | _tropicalis).png.webp) |
[30] | |
| سيفالوتس (Cephalotus follicularis) |
20 |  | [31] | ||
| كاكاو (Theobroma cacao) |
20 |  |  |
[32] | |
| أوكالبتوس (Eucalyptus) |
22 |  | [33] | ||
| أبوسوم فيرجينيا (Didelphis virginiana) |
22 |  | [34] | ||
| فاصولياء (.Phaseolus sp) |
22 |  | .png.webp) |
[19] | |
| حلزون (حيوان) | 24 |  | |||
| شمام (Cucumis melo) |
24 |  | .png.webp) |
[35] | |
| أرز (Oryza sativa) |
24 |  | .png.webp) |
[19] | |
| كستناء حلو (Castanea sativa) |
24 |  | .png.webp) |
[36] | |
| طماطم (Solanum lycopersicum) |
24 |  | .png.webp) |
[37] | |
| زان أوروبي (Fagus sylvatica) |
24 |  | .png.webp) |
[38] | |
| ثلثان (Solanum dulcamara) |
24 |  | [39][40] | ||
| سنديان فليني (Quercus suber) |
24 |  | .png.webp) |
[41] | |
| ضفدع صالح الأكل (Pelophylax klepton esculentus) |
26 |  | .png.webp) |
ضفدع صالح الأكل هو الهجين الخصب لضفدع البركة وضفدع الماء الأخضر. | [42] |
| عفريت الماء (Ambystoma mexicanum) |
28 |  | .png.webp) |
[43] | |
| بق الفراش (Cimex lectularius) |
29–47 |  | 26 اوتوسومز وعدد متفاوت من الكروموسومات الجنسية من ثلاثة (X1X2Y) إلى 21 (X1X2Y + 18 Xs إضافية). | [44] | |
| زرافة (Giraffa camelopardalis) |
30 |  | .png.webp) |
[45] | |
| منك أمريكي (Neovison vison) |
30 |  | |||
| فستق (Pistacia vera) |
30 |  | [46] | ||
| خميرة (Saccharomyces cerivisiae) |
32 | 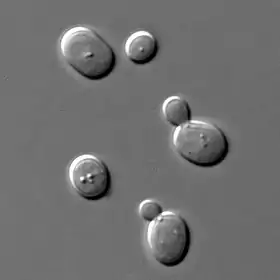 | |||
| نحل العسل الغربي (Apis mellifera) |
32/16 |  | .png.webp) |
32 للإناث (2n = 32) ، الذكور فردانية وبالتالي لديها 16 (1n = 16)..[47] | [47] |
| غرير أمريكي (Taxidea taxus) |
32 |  | |||
| برسيم حجازي (Medicago sativa) |
32 |  | .png.webp) |
البرسيم المزروع هو رباعي الصبغ، مع 2ن = 4x = 32.
الأقارب البرية لديهم 2 ن = 16: 165.[19]:165 |
[19] |
| ثعلب أحمر (Vulpes vulpes) |
34 |  | بالإضافة إلى 3-5 ميكروسوم | [48] | |
| دوار الشمس (Helianthus annuus) |
34 |  | .png.webp) |
[49] | |
| نيص (Erethizon dorsatum) |
34 |  | [50] | ||
| خرشوف (Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus) |
34 |  |  |
[51] | |
| نمس أصفر (Cynictis penicillata) |
36 |  | |||
| ثعلب التبت (Vulpes ferrilata) |
36 |  | |||
| نجم البحر (Asteroidea) |
36 |  | |||
| باندا أحمر (Ailurus fulgens) |
36 |  | |||
| سرقاط (Suricata suricatta) |
36 |  | |||
| بفرة (Manihot esculenta) |
36 | .png.webp) |
[52] | ||
| دودة الأرض (Lumbricus terrestris) |
36 |  | |||
| قيطم أفريقي (Xenopus laevis) |
36 |  | .png.webp) |
[30] | |
| نبتة الناعورة (Aldrovanda vesiculosa) |
38 |  | [31] | ||
| ببر (Panthera tigris) |
38 |  |  |
||
| قضاعة بحرية (Enhydra lutris) |
38 |  | |||
| سمور (Martes zibellina) |
38 | ||||
| راكون شائع (Procyon lotor) |
38 | .jpg.webp) | [53] | ||
| خز الصنوبر الأوروبي (Martes martes) |
38 |  | |||
| خنزير (Sus) |
38 | .jpg.webp) |  |
||
| قضاعة آسيوية صغيرة المخالب (Aonyx cinerea) |
38 |  | |||
| أسد (Panthera leo) |
38 |  | |||
| دلق | 38 |  | نوع من الدلق (جنس) | ||
| منك أوروبي (Mustela lutreola) |
38 |  | |||
| قوطي (حيوان)mundi | 38 |  | |||
| قط (Felis silvestris catus) |
38 |  | .png.webp) |
||
| خز الزان (Martes foina) |
38 |  | |||
| خز أمريكي (Martes americana) |
38 |  | |||
| فأر (Mus musculus) |
40 |  |  |
[54] | |
| منجا (فاكهة) (Mangifera indica) |
40 |  | [19] | ||
| ضبع (Hyaenidae) |
40 |  | |||
| ابن مقرض (Mustela putorius furo) |
40 |  | |||
| ابن عرس أوروبي (Mustela putorius) |
40 |  | |||
| قندس (American) (Castor canadensis) |
40 |  | |||
| فول سوداني (Arachis hypogaea) |
40 | .jpg.webp) | .png.webp) |
[55] | |
| شره (Gulo gulo) |
42 |  | |||
| قمح (Triticum aestivum) |
42 | _at_Alnarp_1.jpg.webp) | .png.webp) |
[19] | |
| مكاك ريسوسي (Macaca mulatta) |
42 |  | .png.webp) |
[56] | |
| جرذ (Rattus norvegicus) |
42 |  | 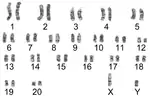 |
[57] | |
| شوفان (Avena sativa) |
42 |  | .png.webp) |
سداسي الصبغة (2ن = 6x = 42). توجد أيضاً أنواع مزروعة ثنائية الصبغة ورباعي الصبغة .[19] | [19] |
| باندا عملاقة (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) |
42 |  | |||
| فوسا (حيوان) (Cryptoprocta ferox) |
42 |  | |||
| أرنب أوروبي (Oryctolagus cuniculus) |
44 |  | .png.webp) |
||
| غرير أوروبي (Meles meles) |
44 |  | |||
| هلام البحر العادي (Aurelia aurita) |
44 |  | [58] | ||
| دلفين (Delphinidae Delphi) |
44 |  | |||
| بن عربي (Coffea arabica) |
44 |  |  |
من بين الأنواع 103 الموجودة في جنس بن، تعتبر قهوة أرابيكا هي النوع رباعي الصبغ الوحيد (2ن = 4x = 44) ، أما الأنواع المتبقية فهي ثنائية الصبغيات مع 2ن = 2x = 22.[59] | |
| ظبي سابل (Hippotragus niger) |
46 | _adult_male.jpg.webp) | |||
| غُزلان ريفيز مونتجاك (Muntiacus reevesi) |
46 |  | |||
| إنسان (Homo sapiens) |
46 |  |  |
44 صبغي جسمي. and 2 صبغي جنسي (sex) | [60] |
| جاموس الماء (river type) (Bubalus bubalis) |
48 | ||||
| تبغ شائع (Nicotiana tabacum) |
48 | _in_a_field_in_Intercourse%252C_Pennsylvania..jpg.webp) | .png.webp) |
[61] | |
| بطاطس (Solanum tuberosum) |
48 | 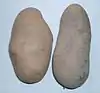 | .png.webp) |
هذا هو للبطاطا Solanum tuberosum الشائعة (رباعية الصبغة، 2n = 4x = 48). أنواع البطاطا المزروعة الأخرى قد تكون ثنائية الصبغة (2n = 2x = 24) ، أو ثلاثية الصبغة (2n = 3x = 36) ، أو رباعي الصيغة الصبغية (2n = 4x = 48) ، أو خماسي الصيغة الصبغية (2n = 5x = 60). معظم الأقارب البرية 2n = 24. | [62] |
| إنسان الغاب (Pongo) |
48 |  | .png.webp) |
||
| قواع (Lepus) |
48 |  | [63][64] | ||
| غوريلا (Gorilla) |
48 |  | |||
| فأر غزلاني (Peromyscus maniculatus) |
48 |  | |||
| شيمبانزي شائع (Pan troglodytes) |
48 |  | .png.webp) |
[65] | |
| قندس (Eurasian) (Castor fiber) |
48 |  | |||
| دانيو مخطط (Danio rerio) |
50 | .png.webp) |
[66] | ||
| جاموس الماء (swamp type) (Bubalus bubalis) |
50 |  |  |
||
| ظربان مخطط (Mephitis mephitis) |
50 | _DSC_0030.jpg.webp) | |||
| أناناس (أناناس) |
50 |  | [19] | ||
| ثعلب قزم (Vulpes macrotis) |
50 |  | |||
| دب أبو نظارة (Tremarctos ornatus) |
52 |  | |||
| خلد الماء (Ornithorhynchus anatinus) |
52 |  | .png.webp) |
عشرة كروموسومات جنسية. الذكور لديهم: X1Y1X2Y2X3Y3X4Y4X5Y5 والإناث لديها: X1X1X2X2X3X3X4X4X5X5. | [68] |
| قطن (قطن زغبي) |
52 |  | .png.webp) |
هذا للأنواع المزروعة G. hirsutum (تعدد الصيغ الصبغية، 2n = 4x = 52). هذه الأنواع تمثل 90 ٪ من إنتاج القطن في العالم. من بين 50 نوعًا من جنس جوسيبيوم، هناك 45 نوعًا ثنائي الصبغية (2n = 2x = 26) و5 أنواع allotetraploid (2n = 4x = 52). | [69] |
| خروف (Ovis orientalis aries) |
54 |  | .png.webp) |
||
| وبريات (Hyracoidea) |
54 |  | .png.webp) |
تعتبر الهيركسات أقرب الأقارب الأحياء للفيلة، [70] ولكن تم العثور على خيلانيات على صلة أوثق بالأفيال. | [71] |
| كلب الراكون (Nyctereutes procyonoides procyonoides) |
54 | .jpg.webp) | .png.webp) |
هذا الرقم مخصص لكلاب الراكون الصينية.[72][73] | [72] |
| كبوشاوات (Cebus x) |
54 |  | [74] | ||
| دودة القز (Bombyx mori) |
56 |  | .png.webp) |
هذا بالنسبة لأنواع دودة القز التوتية، دودة القز (2n = 56).[75] ربما أكثر من 99 ٪ من الحرير التجاري في العالم اليوم يأتي من هذا النوع. انواع العث الأخرى المنتجة للحرير، والتي تسمى دودة القز غير التوتية، لها أرقام كروموسوم مختلفة .[76] | [77] |
| فراولة (شليك) |
56 |  | .png.webp) |
[78] | |
| غور (حيوان) (Bos gaurus) |
56 |  | |||
| فيل (Elephantidae) |
56 |  | |||
| ماموث صوفي (Mammuthus primigenius) |
58 |  | مُنقَرِض؛ الأنسجة من الجثة المجمدة | ||
| قطاس أليف (Bos mutus) |
60 |  | |||
| ماعز (Capra aegagrus hircus) |
60 |  |  |
||
| بقرة (Bos primigenius) |
60 |  |  |
||
| بيسون أمريكي (Bison bison) |
60 |  | |||
| ثعلب البنغال (Vulpes bengalensis) |
60 |  | |||
| Gypsy moth (Lymantria dispar dispar) |
62 |  | |||
| حمار (Equus africanus asinus) |
62 |  | |||
| مكاو قرمزي (مكاو قرمزي) |
62–64 | _-Panama-8a.jpg.webp) | .png.webp) |
[79] | |
| بغل | 63 |  | semi-infertile (odd number of chromosomes – between donkey (62) and horse (64) makes انقسام منصف much more difficult) | ||
| كابياء خنزيرية (Cavia porcellus) |
64 | .jpg.webp) | .png.webp) |
||
| ظربان مرقط (Spilogale x) |
64 |  | |||
| خيل (Equus ferus caballus) |
64 |  | .png.webp) |
||
| فنك (Vulpes zerda) |
64 |  | [48] | ||
| آكل النمل الشوكي | 63/64 |  | 63 (X1Y1X2Y2X3Y3X4Y4X5, male) and 64 (X1X1X2X2X3X3X4X4X5X5, female)[80] | ||
| شنشيلة (Chinchilla lanigera) |
64 |  | [50] | ||
| مدرع ثماني الحزم (Dasypus novemcinctus) |
64 |  |  |
[81] | |
| ثعلب رمادي (Urocyon cinereoargenteus) |
66 |  | [48] | ||
| أيل أحمر (Cervus elaphus) |
68 |  | |||
| الإلكة (Wapiti) (Cervus canadensis) |
68 |  | |||
| صقر رودسايد (Rupornis magnirostris) |
68 |  | [82] | ||
| أيل أبيض الذيل (Odocoileus virginianus) |
70 | _grazing_-_20050809.jpg.webp) | |||
| عنب الثعلب الأسود (مغد أسود) |
72 |  | [83] | ||
| ثعلب خفاشي الأذنين (Otocyon megalotis) |
72 | .jpg.webp) | [48] | ||
| دب الشمس (Helarctos malayanus) |
74 |  | |||
| الدب الكسلان (Melursus ursinus) |
74 |  | |||
| دب قطبي (Ursus maritimus) |
74 |  | |||
| دب بني (Ursus arctos) |
74 | _running.jpg.webp) | |||
| دب أسود آسيوي (Ursus thibetanus) |
74 |  | |||
| دب أسود أمريكي (Ursus americanus) |
74 |  | |||
| ذئب ذو العرف (Chrysocyon brachyurus) |
76 |  | |||
| ذئب رمادي (Canis lupus) |
78 |  | |||
| ابن آوى الذهبي (Canis aureus) |
78 |  | [48] | ||
| حمامة "بالإنجليزية: Dove" (Columbidae) |
78 |  | Based on African collared dove | [84] | |
| كلب (Canis lupus familiaris) |
78 |  | .png.webp) |
Normal dog karyotype is composed of 38 pairs of قطعة مركزية صبغي جسميs and two قطعة مركزية صبغي جنسيs.[85][86] | [87] |
| كلب أسترالي (Canis lupus dingo) |
78 |  | [48] | ||
| كلب الدول (Cuon alpinus) |
78 |  | |||
| قيوط (Canis latrans) |
78 |  | [48] | ||
| دجاج (Gallus gallus domesticus) |
78 |  | |||
| كلب بري إفريقي (Lycaon pictus) |
78 | .jpg.webp) | [48] | ||
| نابنط (Nepenthes rafflesiana) |
78 |  | [31] | ||
| دجاج رومي (Meleagris) |
80 |  | [88] | ||
| قصب السكر (قصب السكر المخزني) |
80 |  | .png.webp) |
هذا العدد لقصب السكر المخزني.[89] حوالي 70٪ من سكر العالم يأتي من هذا النوع.[90] الأنواع الأخرى في جنس قصب السكر، والمعروفة باسم قصب السكر، لها أعداد كروموسوم في النطاق 2n = 40-128.[91] | [89] |
| Pigeon (حماميات) |
80 |  | [92] | ||
| القرش الابيض الكبير (Carcharodon carcharias) |
82 |  | [93] | ||
| قنفذ من جنسErinaceus (قنفذ الغابات) | 88 | .jpg.webp) | |||
| قنفذ من جنس Atelerix (قنفذ أفريفي) | 90 |  | |||
| سرخس العنب (Sceptridium) |
90 |  | |||
| فأر السلطعون بيتير (Ichthyomys pittieri) |
92 | كان يُعتقد سابقًا أنه أعلى رقم في الثدييات، مرتبطًا بأنسوم Anotomys. | [94] | ||
| جمبري (ذلاف semisulcatus) |
86–92 |  | [95] | ||
| الفئران المائية (Anotomys leander) |
92 | كان يُعتقد سابقًا أنه أعلى رقم في الثدييات، وهو مرتبط بـ Ichthyomys pittieri. | [94] | ||
| Kamraj (fern) (Helminthostachys zeylanica) |
94 |  | |||
| سمك الشبوط (الشبوط) |
100 |  | .png.webp) |
[96] | |
| الجرذ اللزج الأحمر (Tympanoctomys barrerae) |
102 |  | .jpg.webp) |
أكبر عدد معروف في الثدييات، يُعتقد أنه رباعي الصبغيات أو allotetraploid.[97] | [98] |
| قرموط الكلاريس (Clarias batrachus) |
104 |  | .png.webp) |
[99] | |
| السمكة ذات المجداف (Polyodon spathula) |
120 |  | [100] | ||
| جلكيات مألوفة (Petromyzontinae) |
174 |  | [101] | ||
| أفعى جرسية (أفعى مجلجلة) |
184 |  | [102] | ||
| سلطعون الملك الأحمر (Paralithodes camtschaticus) |
208 |  | |||
كنباث الحقول |
216 |  | |||
| توت أسود | 308 |  | 44-ploid | [103] | |
| أطلس أزرق (Polyommatus atlantica) |
448-452 |  | .png.webp) |
2n = حوالي 448–452. Highest number of chromosomes in the non-تعدد الصيغ الصبغية حقيقيات النوى organisms.[104] | [104] |
| أفعى اللسان (Ophioglossum) |
1260 |  | [105] | ||
| البروتوزوا الهدبي (Tetrahymena thermophila) |
10 (in micronucleus) | 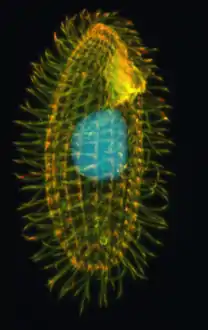 | 50x = 12,500 (in macronucleus, except minichromosomes) 10,000x = 10,000 (macronuclear minichromosomes)[107] |
||
| هدبيات (Oxytricha trifallax) |
15600 |  | النواة الصبغية النانوية ؛ ampliploid. كروموسومات MAC × 1900 مستوى الصيغة الصبغية = 2.964 × 107 كروموسومات | [108][109][110] |

نمط نووي لإنسان، يبين 22 زوج من الكروموسومات الجسمية وكلاً من XX للأنثى، وXY للذكر، تمثل الاحتمالات بالنسبة لزوج الكروموسومات الجنسية
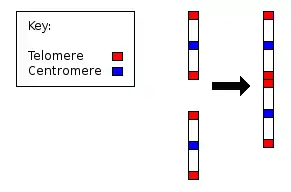
يترك انصهار الكروموسومات السلفية بقايا مميزة من التيلوميرات، وبقايا السنترومير. نظرًا لأن القردة العليا الأخرى غير البشرية تحتوي على 48 كروموسوم، يُعتقد أن الكروموسوم البشري 2 هو النتيجة النهائية لدمج كروموسومين اثنين.[1]
المراجع
- Avarello؛ وآخرون (1992)، "Evidence for an ancestral alphoid domain on the long arm of human chromosome 2"، Human Genetics، 89 (2): 247–9، doi:10.1007/BF00217134، PMID 1587535.
- Concise Oxford Dictionary
- White 1973
- Stebbins, G.L. (1950)، "Chapter XII: The Karyotype"، Variation and evolution in plants، Columbia University Press.
- King, R.C.؛ Stansfield؛ Mulligan (2006)، A dictionary of genetics (ط. 7th)، Oxford University Press، ص. 242.
- Crosland, M.W.J., Crozier, R.H. (1986)، "Myrmecia pilosula, an ant with only one pair of chromosomes"، Science، 231 (4743): 1278، Bibcode:1986Sci...231.1278C، doi:10.1126/science.231.4743.1278، PMID 17839565.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: صيانة CS1: أسماء متعددة: قائمة المؤلفون (link) - Leach؛ وآخرون (1995)، "Organisation and origin of a B chromosome centromeric sequence from Brachycome dichromosomatica"، Chromosoma، 103 (10): 708–714، doi:10.1007/BF00344232، PMID 7664618.
- Helle, W.؛ Bolland, H. R.؛ Gutierrez, J. (1972)، "Minimal chromosome number in false spider mites (Tenuipalpidae)"، Experientia، 28 (6): 707، doi:10.1007/BF01944992.
- Francesco Giannelli؛ Hall, Jeffrey C.؛ Dunlap, Jay C.؛ Friedmann, Theodore (1999)، Advances in Genetics, Volume 41 (Advances in Genetics)، Boston: Academic Press، ص. 2، ISBN 978-0-12-017641-0.
- "Rapid and parallel chromosomal number reductions in muntjac deer inferred from mitochondrial DNA phylogeny."، Mol Biol Evol، 17 (9): 1326–33، 2000، doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026416، PMID 10958849.
- Wurster, Doris H.؛ Kurt Benirschke (12 يونيو 1970)، "Indian Momtjac, Muntiacus muntiak: A Deer with a Low Diploid Chromosome Number"، Science، 168 (3937): 1364–1366، Bibcode:1970Sci...168.1364W، doi:10.1126/science.168.3937.1364، PMID 5444269.
- "Drosophila Genome Project"، المركز الوطني لمعلومات التقانة الحيوية، مؤرشف من الأصل في 9 أبريل 2010، اطلع عليه بتاريخ 14 أبريل 2009.
- Toder (يونيو 1997)، "Comparative chromosome painting between two marsupials: origins of an XX/XY1Y2 sex chromosome system."، Mammalian Genome، 8 (6): 418–22، doi:10.1007/s003359900459، PMID 9166586.
- "Evidence for a Common Origin of Homomorphic and Heteromorphic Sex Chromosomes in Distinct Spinacia Species."، G3 (Bethesda)، 5 (8): 1663–73، 2015، doi:10.1534/g3.115.018671، PMC 4528323، PMID 26048564.
- "Genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in Vicia faba: a pilot study on the environmental monitoring of nanoparticles."، Int J Environ Res Public Health، 9 (5): 1649–62، 2012، doi:10.3390/ijerph9051649، PMC 3386578، PMID 22754463.
- "The karyotype of the yellow dung fly, Scathophaga stercoraria, a model organism in studies of sexual selection"، J Insect Sci، 10 (118): 1–11، 2010، doi:10.1673/031.010.11801، PMC 3016996، PMID 20874599.
- "First of six chromosomes sequenced in Dictyostelium discoideum"، Genome News Network، مؤرشف من الأصل في 8 سبتمبر 2017، اطلع عليه بتاريخ 29 أبريل 2009.
- Zhang؛ Cheng؛ Li؛ Yang؛ Wang؛ Li؛ Chen؛ Lou (2015)، "Chromosomal structures and repetitive sequences divergence in Cucumis species revealed by comparative cytogenetic mapping"، BMC Genomics، 16 (1): 730، doi:10.1186/s12864-015-1877-6، PMC 4583154، PMID 26407707.
- Simmonds, NW (ed.) (1976)، Evolution of crop plants، New York: Longman، ISBN 978-0-582-44496-6.
{{استشهاد بكتاب}}:|مؤلف=has generic name (مساعدة)[بحاجة لرقم الصفحة] - Schubert؛ Ruban؛ Houben (2016)، "Chromatin Ring Formation at Plant Centromeres"، Front Plant Sci، 7: 28، doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00028، PMC 4753331، PMID 26913037.
- "High frequency microcloning of Aloe vera and their true-to-type conformity by molecular cytogenetic assessment of two years old field growing regenerated plants."، Bot Stud، 54 (1): 46، 2013، doi:10.1186/1999-3110-54-46، PMC 5430365، PMID 28510900.
- Rofe, R. H. (ديسمبر 1978)، "G-banded chromosomes and the evolution of macropodidae"، Australian Mammalogy، 2: 50–63، ISSN 0310-0049، مؤرشف من الأصل في 8 أبريل 2019.
- "The genome of the blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni."، Nature، 460 (7253): 352–8، 2009، Bibcode:2009Natur.460..352B، doi:10.1038/nature08160، PMC 2756445، PMID 19606141.
- "Chromosome dynamics visualized with an anti-centromeric histone H3 antibody in Allium."، PLOS ONE، 7 (12): e51315، 2012، Bibcode:2012PLoSO...751315N، doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051315، PMC 3517398، PMID 23236469.
- "Quantitative PCR-based genome size estimation of the astigmatid mites Sarcoptes scabiei, Psoroptes ovis and Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus."، Parasit Vectors، 5: 3، 2012، doi:10.1186/1756-3305-5-3، PMC 3274472، PMID 22214472.
- Dunemann؛ Schrader؛ Budahn؛ Houben (2014)، "Characterization of centromeric histone H3 (CENH3) variants in cultivated and wild carrots (Daucus sp.)"، PLOS ONE، 9 (6): e98504، Bibcode:2014PLoSO...998504D، doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0098504، PMC 4041860، PMID 24887084.
- Hynniewta؛ Malik؛ Rao (2011)، "Karyological studies in ten species of Citrus(Linnaeus, 1753) (Rutaceae) of North-East India"، Comp Cytogenet، 5 (4): 277–87، doi:10.3897/CompCytogen.v5i4.1796، PMC 3833788، PMID 24260635.
- Souza, Margarete Magalhães, Telma N. Santana Pereira, and Maria Lúcia Carneiro Vieira. "Cytogenetic studies in some species of Passiflora L.(Passifloraceae): a review emphasizing Brazilian species." Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology 51.2 (2008): 247–258. https://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132008000200003 نسخة محفوظة 2020-08-18 على موقع واي باك مشين.
- Nani؛ Cenzi؛ Pereira؛ Davide؛ Techio (2015)، "Ribosomal DNA in diploid and polyploid Setaria (Poaceae) species: number and distribution"، Comp Cytogenet، 9 (4): 645–60، doi:10.3897/CompCytogen.v9i4.5456، PMC 4698577، PMID 26753080.
- Matsuda؛ Uno؛ Kondo؛ Gilchrist؛ Zorn؛ Rokhsar؛ Schmid؛ Taira (أبريل 2015)، "A New Nomenclature of Xenopus laevis Chromosomes Based on the Phylogenetic Relationship to Silurana/Xenopus tropicalis."، Cytogenetic and Genome Research، 145 (3–4): 187–191، doi:10.1159/000381292، PMID 25871511.
- Kondo (مايو 1969)، "Chromosome Numbers of Carnivorous Plants"، Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club، 96 (3): 322–328، doi:10.2307/2483737، JSTOR 2483737.
- da Silva؛ Souza؛ Lemos؛ Lopes؛ Patrocínio؛ Alves؛ Marcellino؛ Clement؛ Micheli؛ Gramacho, KP (2017)، "Genome size, cytogenetic data and transferability of EST-SSRs markers in wild and cultivated species of the genus Theobroma L. (Byttnerioideae, Malvaceae)"، PLOS ONE، 12 (2): e0170799، Bibcode:2017PLoSO..1270799D، doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0170799، PMC 5302445، PMID 28187131.
- Balasaravanan؛ Chezhian؛ Kamalakannan؛ Ghosh؛ Yasodha؛ Varghese؛ Gurumurthi (2005)، "Determination of inter- and intra-species genetic relationships among six Eucalyptus species based on inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR)"، Tree Physiol، 25 (10): 1295–302، doi:10.1093/treephys/25.10.1295، PMID 16076778.
- "Chromosomes of American Marsupials"، Science، 148 (3677): 1602–3، يونيو 1965، Bibcode:1965Sci...148.1602B، doi:10.1126/science.148.3677.1602، PMID 14287602.
- Argyris؛ Ruiz-Herrera؛ Madriz-Masis؛ Sanseverino؛ Morata؛ Pujol؛ Ramos-Onsins؛ Garcia-Mas (2015)، "Use of targeted SNP selection for an improved anchoring of the melon (Cucumis melo L.) scaffold genome assembly"، BMC Genomics، 16: 4، doi:10.1186/s12864-014-1196-3، PMC 4316794، PMID 25612459.
- Ivanova؛ Vladimirov (2007)، "Chromosome numbers of some woody species from the Bulgarian flora" (PDF)، Phytologia Balcanica، 13 (2): 205–207، مؤرشف من الأصل (PDF) في 3 يناير 2020.
- "Endogenous pararetroviral sequences in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and related species."، BMC Plant Biol، 7: 24، 2007، doi:10.1186/1471-2229-7-24، PMC 1899175، PMID 17517142.
- Packham؛ Thomas؛ Atkinson؛ Degen (2012)، "Biological Flora of the British Isles:Fagus sylvatica"، Journal of Ecology، 100 (6): 1557–1608، doi:10.1111/j.1365-2745.2012.02017.x.
- Abrams, L. (1951)، Illustrated Flora of the Pacific States. Volume 3.، Stanford University Press، ص. 866.
- Stace, C. (1997)، New Flora of the British Isles. Second Edition.، Cambridge, UK، ص. 1130.
- Zaldoš V, Papeš D, Brown SC, Panaus O, Šiljak-Yakovlev S (1998) Genome size and base composition of seven Quercus species: inter- and intra-population variation. Genome, 41: 162–168. نسخة محفوظة 15 نوفمبر 2018 على موقع واي باك مشين.
- Zaleśna؛ Choleva؛ Ogielska؛ Rábová؛ Marec؛ Ráb (2011)، "Evidence for Integrity of Parental Genomes in the Diploid Hybridogenetic Water Frog Pelophylax esculentus by Genomic in situ Hybridization"، Cytogenetic and Genome Research، 134 (3): 206–212، doi:10.1159/000327716، ISSN 1424-859X، PMID 21555873.
- "Initial characterization of the large genome of the salamander Ambystoma mexicanum using shotgun and laser capture chromosome sequencing."، Sci Rep، 5: 16413، 2015، Bibcode:2015NatSR...516413K، doi:10.1038/srep16413، PMC 4639759، PMID 26553646.
- Sadílek؛ Angus؛ Šťáhlavský؛ Vilímová (2016)، "Comparison of different cytogenetic methods and tissue suitability for the study of chromosomes in Cimex lectularius (Heteroptera, Cimicidae)"، Comp Cytogenet، 10 (4): 731–752، doi:10.3897/CompCytogen.v10i4.10681، PMC 5240521، PMID 28123691.
- "Karyotype evolution of giraffes (Giraffa camelopardalis) revealed by cross-species chromosome painting with Chinese muntjac (Muntiacus reevesi) and human (Homo sapiens) paints."، Cytogenet Genome Res، 122 (2): 132–8، 2008، doi:10.1159/000163090، PMID 19096208، مؤرشف من الأصل في 14 مارس 2020.
- Sola-Campoy؛ Robles؛ Schwarzacher؛ Ruiz Rejón؛ de la Herrán؛ Navajas-Pérez (2015)، "The Molecular Cytogenetic Characterization of Pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) Suggests the Arrest of Recombination in the Largest Heteropycnotic Pair HC1"، PLOS ONE، 10 (12): e0143861، Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1043861S، doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143861، PMC 4669136، PMID 26633808.
- "Sex determination in honeybees: two separate mechanisms induce and maintain the female pathway."، PLoS Biol، 7 (10): e1000222، 2009، doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000222، PMC 2758576، PMID 19841734.
- Sillero-Zubiri, Claudio؛ Hoffmann, Michael J.؛ Dave Mech (2004)، Canids: Foxes, Wolves, Jackals and Dogs: Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan، World Conservation Union، ISBN 978-2-8317-0786-0.[بحاجة لرقم الصفحة]
- Feng؛ Liu؛ Cai؛ Jan (2013)، "Toward a molecular cytogenetic map for cultivated sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) by landed BAC/BIBAC clones"، G3 (Bethesda)، 3 (1): 31–40، doi:10.1534/g3.112.004846، PMC 3538341، PMID 23316437.
- "Metapress – Discover More"، 24 يونيو 2016، مؤرشف من الأصل في 26 يوليو 2019.
- Giorgi؛ Pandozy؛ Farina؛ Grosso؛ Lucretti؛ Gennaro؛ Crinò؛ Saccardo (2016)، "First detailed karyo-morphological analysis and molecular cytological study of leafy cardoon and globe artichoke, two multi-use Asteraceae crops"، Comp Cytogenet، 10 (3): 447–463، doi:10.3897/CompCytogen.v10i3.9469، PMC 5088355، PMID 27830052.
- "Comparison of leaf proteomes of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) cultivar NZ199 diploid and autotetraploid genotypes"، PLOS ONE، 9 (4): e85991، 2014، Bibcode:2014PLoSO...985991A، doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085991، PMC 3984080، PMID 24727655.
- "Chromosome painting shows that skunks (Mephitidae, Carnivora) have highly rearranged karyotypes"، Chromosome Res.، 16 (8): 1215–31، 2008، doi:10.1007/s10577-008-1270-2، PMID 19051045.
- The Jackson Laboratory نسخة محفوظة 2013-01-25 على موقع واي باك مشين.: "Mice with chromosomal aberrations".
- "Taxonomic relationships among Arachis sect. Arachis species as revealed by AFLP markers."، Genome، 48 (1): 1–11، 2005، doi:10.1139/g04-089، PMID 15729391.
- Moore؛ Dunn؛ McMahan؛ Lane؛ Roth؛ Ingram؛ Mattison (2007)، "Effects of calorie restriction on chromosomal stability in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta)"، Age (Dordr)، 29 (1): 15–28، doi:10.1007/s11357-006-9016-6، PMC 2267682، PMID 19424827.
- "Rnor_6.0 - Assembly - NCBI"، www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov، مؤرشف من الأصل في 9 أبريل 2019.
- Diupotex-Chong؛ Ocaña-Luna؛ Sánchez-Ramírez (يوليو 2009)، "Chromosome analysis of Linné, 1758 (Scyphozoa: Ulmaridae), southern Gulf of Mexico"، Marine Biology Research، 5 (4): 399–403، doi:10.1080/17451000802534907.
- Geleta؛ Herrera؛ Monzón؛ Bryngelsson (2012)، "Genetic diversity of arabica coffee (Coffea arabica L.) in Nicaragua as estimated by simple sequence repeat markers"، ScientificWorldJournal، 2012: 939820، doi:10.1100/2012/939820، PMC 3373144، PMID 22701376.
- "Human Genome Project"، المركز الوطني لمعلومات التقانة الحيوية، مؤرشف من الأصل في 9 أبريل 2010، اطلع عليه بتاريخ 29 أبريل 2009.
- "The tobacco genome sequence and its comparison with those of tomato and potato"، Nat Commun، 5: 3833، 2014، Bibcode:2014NatCo...5.3833S، doi:10.1038/ncomms4833، PMC 4024737، PMID 24807620.
- Machida-Hirano R (2015)، "Diversity of potato genetic resources"، Breed Sci، 65 (1): 26–40، doi:10.1270/jsbbs.65.26، PMC 4374561، PMID 25931978.
- T.J. Robinson؛ F. Yang؛ W.R. Harrison (2002)، "Chromosome painting refines the history of genome evolution in hares and rabbits (order Lagomorpha)"، Cytogenetic and Genome Research، 96 (1–4): 223–227، doi:10.1159/000063034، PMID 12438803.
- "4.W4"، Rabbits, Hares and Pikas. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan، ص. 61–94، مؤرشف من الأصل في 05 مايو 2011.
- "Chromosome number of the chimpanzee, Pan troglodytes"، Science، 131 (3414): 1672–3، يونيو 1960، Bibcode:1960Sci...131.1672Y، doi:10.1126/science.131.3414.1672، PMID 13846659.
- Postlethwait؛ Woods؛ Ngo-Hazelett؛ Yan؛ Kelly؛ Chu؛ Huang؛ Hill-Force؛ Talbot (01 ديسمبر 2000)، "Zebrafish Comparative Genomics and the Origins of Vertebrate Chromosomes"، Genome Research، 10 (12): 1890–1902، doi:10.1101/gr.164800، PMID 11116085.
- Brien, Stephen (2006)، Atlas of mammalian chromosomes، Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Liss، ص. 2، ISBN 978-0-471-35015-6، مؤرشف من الأصل في 8 أبريل 2019.
- Warren؛ وآخرون (2008)، "Genome analysis of the platypus reveals unique signatures of evolution"، Nature، 453 (7192): 175–183، Bibcode:2008Natur.453..175W، doi:10.1038/nature06936، PMC 2803040، PMID 18464734.
- "A high-density SSR genetic map constructed from a F2 population of Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium darwinii"، Gene، 574 (2): 273–86، 2015، doi:10.1016/j.gene.2015.08.022، PMID 26275937، مؤرشف من الأصل في 14 مارس 2020.
- "Hyrax: The Little Brother of the Elephant", Wildlife on One, BBC TV.
- O'Brien, Stephen J., Meninger, Joan C., Nash, William G. (2006)، Atlas of Mammalian Chromosomes، John Wiley & sons، ص. 78، ISBN 978-0-471-35015-6.
{{استشهاد بكتاب}}: صيانة CS1: أسماء متعددة: قائمة المؤلفون (link) - Måkinen (1986)، "A chromosome-banding study in the Finnish and the Japanese raccoon dog"، Hereditas، 105 (1): 97–105، doi:10.1111/j.1601-5223.1986.tb00647.x، PMID 3793521.
- Elaine A. Ostrander (01 يناير 2012)، Genetics of the Dog، CABI، ص. 250–، ISBN 978-1-84593-941-0، مؤرشف من الأصل في 8 أبريل 2019.
- Barnabe؛ Guimarães؛ Oliveira؛ Barnabe (2002)، "Analysis of some normal parameters of the spermiogram of captive capuchin monkeys (Cebus apella Linnaeus, 1758)"، Brazilian Journal of Veterinary Research and Animal Science، 39 (6)، doi:10.1590/S1413-95962002000600010.
- "Samia cynthia versus Bombyx mori: comparative gene mapping between a species with a low-number karyotype and the model species of Lepidoptera" (PDF)، Insect Biochem Mol Biol، 41 (6): 370–7، 2011، doi:10.1016/j.ibmb.2011.02.005، hdl:2115/45607، PMID 21396446، مؤرشف من الأصل (PDF) في 8 أبريل 2019.
- "Molecular phylogeny of silk-producing insects based on 16S ribosomal RNA and cytochrome oxidase subunit I genes."، J Genet، 85 (1): 31–8، 2006، doi:10.1007/bf02728967، PMID 16809837.
- "The Bombyx mori karyotype and the assignment of linkage groups."، Genetics، 170 (2): 675–85، 2005، doi:10.1534/genetics.104.040352، PMC 1450397، PMID 15802516.
- Liu؛ Davis (2011)، "Conservation and loss of ribosomal RNA gene sites in diploid and polyploid Fragaria (Rosaceae)"، BMC Plant Biol، 11: 157، doi:10.1186/1471-2229-11-157، PMC 3261831، PMID 22074487.
- Seabury؛ Dowd؛ Seabury؛ Raudsepp؛ Brightsmith؛ Liboriussen؛ Halley؛ Fisher؛ Owens؛ Viswanathan, G؛ Tizard, IR (2013)، "A multi-platform draft de novo genome assembly and comparative analysis for the Scarlet Macaw (Ara macao)"، PLoS ONE، 8 (5): e62415، Bibcode:2013PLoSO...862415S، doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062415، PMC 3648530، PMID 23667475.
- Rens, W.؛ وآخرون (2007)، "The multiple sex chromosomes of platypus and echidna are not completely identical and several share homology with the avian Z"، Genome Biology، 8 (11): R243، doi:10.1186/gb-2007-8-11-r243، PMC 2258203، PMID 18021405.
- Svartman؛ Stone؛ Stanyon (2006)، "The ancestral eutherian karyotype is present in Xenarthra"، PLoS Genet، 2 (7): e109، doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0020109، PMC 1513266، PMID 16848642.
- de Oliveira؛ Tagliarini؛ dos Santos؛ O'Brien؛ Ferguson-Smith (2013)، "Chromosome painting in three species of buteoninae: a cytogenetic signature reinforces the monophyly of South American species"، PLOS ONE، 8 (7): e70071، Bibcode:2013PLoSO...870071D، doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070071، PMC 3724671، PMID 23922908.
- Smith, Hugh (1927)، "Chromosome counts in the varieties of Solanum tuberosum and allied wild species"، Genetics، 12 (1): 84–92، PMC 1200928، PMID 17246516.
- "Comparative chromosome painting of chicken autosomal paints 1–9 in nine different bird species"، Cytogenetic and Genome Research، 103 (1–2): 173–84، 2003، doi:10.1159/000076309، PMID 15004483.
- https://web.archive.org/web/20191115200443/https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/guide/dog/، مؤرشف من الأصل في 15 نوفمبر 2019.
{{استشهاد ويب}}: الوسيط|title=غير موجود أو فارغ (مساعدة) - Maeda؛ Yurkon؛ Fujisawa؛ Kaneko؛ Genet؛ Roybal؛ Rota؛ Saffer؛ Rose؛ Hanneman, WH؛ Thamm, DH؛ Kato, TA (2012)، "Genomic instability and telomere fusion of canine osteosarcoma cells"، PLOS ONE، 7 (8): e43355، Bibcode:2012PLoSO...743355M، doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0043355، PMC 3420908، PMID 22916246.
- "Genome sequence, comparative analysis and haplotype structure of the domestic dog"، Nature، 438 (7069): 803–19، ديسمبر 2005، Bibcode:2005Natur.438..803L، doi:10.1038/nature04338، PMID 16341006.
- Muhammad L Aslam؛ John WM Bastiaansen؛ Richard PMA Crooijmans؛ Addie Vereijken؛ Hendrik-Jan Megens؛ Martien AM Groenen (2010)، "A SNP based linkage map of the turkey genome reveals multiple intrachromosomal rearrangements between the Turkey and Chicken genomes" (PDF)، BMC Genomics، 11: 647، doi:10.1186/1471-2164-11-647، PMC 3091770، PMID 21092123، مؤرشف من الأصل (PDF) في 24 سبتمبر 2015.
- "Microcollinearity between autopolyploid sugarcane and diploid sorghum genomes."، BMC Genomics، 11: 261، 2010، doi:10.1186/1471-2164-11-261، PMC 2882929، PMID 20416060.
- "Saccharum officinarum L. | Plants of the World Online | Kew Science"، مؤرشف من الأصل في 6 سبتمبر 2018، اطلع عليه بتاريخ 02 يوليو 2017.
- Robert J. Henry؛ Chittaranjan Kole (15 أغسطس 2010)، Genetics, Genomics and Breeding of Sugarcane، CRC Press، ص. 70، ISBN 978-1-4398-4860-9، مؤرشف من الأصل في 8 أبريل 2019.
- Susumu Ohno؛ Christina Stenius؛ L. C. Christian؛ Willy Beçak؛ Maria Luiza Beçak (1964)، "Chromosomal uniformity in the avian subclass Carinatae"، Chromosoma، 14 (3): 280–288، doi:10.1007/BF00321513.
- Gregory, T.R. (2015). Animal Genome Size Database. http://www.genomesize.com/result_species.php?id=1701 نسخة محفوظة 2019-04-08 على موقع واي باك مشين.
- Schmid؛ Fernández-Badillo؛ Feichtinger؛ Steinlein؛ Roman (1988)، "On the highest chromosome number in mammals"، Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics، 49 (4): 305–8، doi:10.1159/000132683، PMID 3073914.
- "The Chromosome Number of the Persian Gulf Shrimp Penaeus semisulcatus"، Iranian Int. J. Sci، 5 (1): 13–23، 2004.
- Spoz؛ Boron؛ Porycka؛ Karolewska؛ Ito؛ Abe؛ Kirtiklis؛ Juchno (2014)، "Molecular cytogenetic analysis of the crucian carp, Carassius carassius (Linnaeus, 1758) (Teleostei, Cyprinidae), using chromosome staining and fluorescence in situ hybridisation with rDNA probes"، Comp Cytogenet، 8 (3): 233–48، doi:10.3897/CompCytogen.v8i3.7718، PMC 4205492، PMID 25349674.
- Gallardo, M.H.؛ González؛ Cebrián (2006)، Molecular cytogenetics and allotetraploidy in the red vizcacha rat, Tympanoctomys barrerae (Rodentia, Octodontidae)تاريخ النشر: أغسطس 2006، ج. 88، ص. 214–221، doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2006.02.010، PMID 16580173
{{استشهاد}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|دورية=تم تجاهله (مساعدة) - "The largest known chromosome number for a mammal, in a South American desert rodent"، Experientia، 46 (5): 506–508، 1990، doi:10.1007/BF01954248، PMID 2347403.
- Maneechot؛ Yano؛ Bertollo؛ Getlekha؛ Molina؛ Ditcharoen؛ Tengjaroenkul؛ Supiwong؛ Tanomtong؛ de Bello Cioffi, M (2016)، "Genomic organization of repetitive DNAs highlights chromosomal evolution in the genus Clarias (Clariidae, Siluriformes)"، Mol Cytogenet، 9: 4، doi:10.1186/s13039-016-0215-2، PMC 4719708، PMID 26793275.
- Symonová؛ Havelka؛ Amemiya؛ Howell؛ Kořínková؛ Flajšhans؛ Gela؛ Ráb (2017)، "Molecular cytogenetic differentiation of paralogs of Hox paralogs in duplicated and re-diploidized genome of the North American paddlefish (Polyodon spathula)"، BMC Genet، 18 (1): 19، doi:10.1186/s12863-017-0484-8، PMC 5335500، PMID 28253860.
- William N. Eschmeyer، "Family Petromyzontidae – Northern lampreys"، مؤرشف من الأصل في 5 أكتوبر 2018.
- Flora of North America Editorial Committee, eds (1993)، Flora of North America، Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis، مؤرشف من الأصل في 24 يناير 2019.
{{استشهاد بكتاب}}:|الأخير=has generic name (مساعدة) - Zeng, Q؛ Chen (2015)، "Definition of Eight Mulberry Species in the Genus Morus by Internal Transcribed Spacer-Based Phylogeny."، PLoS ONE، 10 (8): e0135411، Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1035411Z، doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0135411، PMC 4534381، PMID 26266951.
- Lukhtanov (2015)، "The blue butterfly Polyommatus (Plebicula) atlanticus (Lepidoptera, Lycaenidae) holds the record of the highest number of chromosomes in the non-polyploid eukaryotic organisms"، Comp Cytogenet، 9 (4): 683–90، doi:10.3897/CompCytogen.v9i4.5760، PMC 4698580، PMID 26753083.
- Lukhtanov, Vladimir (10 يوليو 2015)، "The blue butterfly Polyommatus (Plebicula) atlanticus (Lepidoptera, Lycaenidae) holds the record of the highest number of chromosomes in the non-polyploid eukaryotic organisms"، Comparative Cytogenetics (باللغة الإنجليزية)، 9 (4): 683–690، doi:10.3897/compcytogen.v9i4.5760، PMC 4698580، PMID 26753083.
- Sinha؛ Srivastava؛ Jha (1979)، "Occurrence of Various Cytotypes of Ophioglossum ReticulatumL. In a Population from N. E. India"، Caryologia، 32 (2): 135–146، doi:10.1080/00087114.1979.10796781.
- Mochizuki (2010)، "DNA rearrangements directed by non-coding RNAs in ciliates"، Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA، 1 (3): 376–87، doi:10.1002/wrna.34، PMC 3746294، PMID 21956937.
- Kumar, Sushil؛ Kumarik Renu (يونيو 2015)، "Origin, structure and function of millions of chromosomes present in the macronucleus of unicellular eukaryotic ciliate, Oxytricha trifallax: a model organism for transgenerationally programmed genome rearrangements"، Journal of Genetics، 94 (2): 173، doi:10.1007/s12041-015-0504-2، مؤرشف من الأصل في 8 أبريل 2019، اطلع عليه بتاريخ 14 مارس 2017.
- Estienne C. Swart؛ John R. Bracht؛ Vincent Magrini؛ Patrick Minx؛ Xiao Chen؛ Yi Zhou؛ Jaspreet S. Khurana؛ Aaron D. Goldman؛ Mariusz Nowacki؛ Klaas Schotanus؛ Seolkyoung Jung؛ Robert S. Fulton؛ Amy Ly؛ Sean McGrath؛ Kevin Haub؛ Jessica L. Wiggins؛ Donna Storton؛ John C. Matese؛ Lance Parsons؛ Wei-Jen Chang؛ Michael S. Bowen؛ Nicholas A. Stover؛ Thomas A. Jones؛ Sean R. Eddy؛ Glenn A. Herrick؛ Thomas G. Doak؛ Richard K. Wilson؛ Elaine R. Mardis؛ Laura F. Landweber (29 يناير 2013)، "The Oxytricha trifallax Macronuclear Genome: A Complex Eukaryotic Genome with 16,000 Tiny Chromosomes"، PLOS Biology، 11 (1): e1001473، doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001473، PMC 3558436، PMID 23382650.
- "You Have 46 Chromosomes. This Pond Creature Has 15,600", National Geographic, . نسخة محفوظة 11 يونيو 2018 على موقع واي باك مشين.
روابط خارجية
- قائمة الصفحات باللغة الإنجليزية من موقع البيونيت الروسي
- الكلب من خلال التطور
- المخلوقات المشتركة للكروموسوم البشري 17 loci في Canids
- أطلس لأعداد الكروموسوم في الحيوانات (1951) ؛ تنزيلات PDF لكل فصل
- بوابة علم الأحياء الخلوي والجزيئي
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.