Ampyrone
Ampyrone is a metabolite of aminopyrine with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties.[2] Its use as a drug is discouraged due to the risk of agranulocytosis.[3] It is used as a reagent for biochemical reactions producing peroxides or phenols.[2] Ampyrone stimulates liver microsomes and is also used to measure extracellular water.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
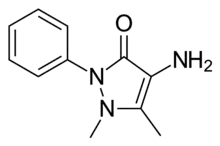
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Amino-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-3H-pyrazol-3-one[1] | |
| Other names
solvapyrin A, aminoazophene, aminoantipyrene, aminoantipyrine, metapyrazone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.321 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H13N3O1[2] | |
| Molar mass | 203.24 g/mol |
| Density | 1.207g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 106 to 110 °C (223 to 230 °F; 379 to 383 K) |
| Boiling point | 309 °C (588 °F; 582 K) @760mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 140.7 °C (285.3 °F; 413.8 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- PubChem (25 March 2005). "4-Aminoantipyrine". PubChem. Retrieved 2022-05-09.
- "4-Aminoantipyrine". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. 25 March 2005. Retrieved 2022-05-09.
- "On-line encyklopedia PWN (in Polish)". Archived from the original on 2011-06-07. Retrieved 2008-10-17.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.